Texture
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Texture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to explore the concept of texture in image interpretation. Texture refers to how we perceive the arrangement and variation of tonal differences in an image. Can anyone think of how this might affect what we see?

Maybe it helps us tell if something is smooth or rough!

And it can help differentiate similar colors, right?

Exactly! The smoothness or coarseness defined by texture changes how we interpret the visual characteristics of various elements in an image.

So if we look at grass and a tree canopy, we can see how their textures differ?

Right again! Grass has a smooth texture while tree canopies may appear rough. Remember, texture is a combination of shape, size, pattern, shadow, and tone!

In summary, texture not only influences perception but is essential for classifying elements in images.
Impact of Scale on Texture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive deeper into how scale affects our perception of texture. What happens if we reduce the scale of an image?

The details in the texture might disappear, right?

Yeah! It seems like we lose the sense of texture when we zoom out.

That's correct! As the scale reduces, we see finer textures that ultimately fade. It's crucial because understanding this helps us better analyze and identify objects, especially in remote sensing.

So, does this mean texture is more pronounced at larger scales?

Absolutely! A larger scale can display more intricate textures clearly, enhancing our interpretive capabilities.

To summarize, recognizing the relationship between scale and texture helps improve our analysis and classification of images.
Texture in Radar Imaging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about the role of texture in radar imaging. How do you think texture can affect our interpretation of radar images?

Maybe it helps us distinguish between different types of land features?

Exactly! Texture is crucial in radar images because it provides vital distinctions between objects that otherwise might reflect similar wavelengths.

So, could it help identify features like vegetation vs water?

Precisely! Differences in texture allow us to classify various elements and can assist in resource management and environmental monitoring.

In summary, texture significantly enhances our understanding of radar images by making the identification of objects clearer.
Comparative Textures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s explore comparative textures. Why is it important to compare textures in images?

It helps us see differences between similar looking areas, like forests and grass!

Yeah, we can also differentiate features based on their smoothness or roughness.

Exactly! By recognizing textures, we can effectively distinguish between features such as grassland vs. forest canopies without relying solely on color.

And this would be essential for identifying land use patterns too!

Exactly! Understanding comparative textures can greatly enhance image analysis accuracy.

To summarize, comparative textures are fundamental for analyzing similar features, influencing land use classification significantly.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
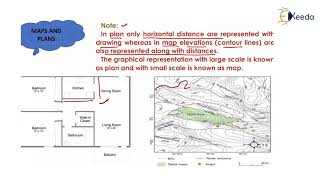
Texture is a significant aspect of image interpretation, characterized by the variation in tonal values which can highlight the smoothness or roughness of various elements. It plays a crucial role in distinguishing between objects based on their texture such as grass versus tree crowns, and is essential for analyzing features in images, including radar images.
Detailed
Detailed Overview of Texture in Image Interpretation
Texture in images refers to the arrangement and frequency of tonal variation within an image. It is established through a compilation of smaller, often indistinct elements (like tree leaves) that contribute to the visible characteristics of an image. The texture can dictate whether an aspect of the image appears smooth or coarse, directly impacting the interpretative process.
Key Aspects of Texture
- Scale Reduction: As the size of an image decreases, the texture details become finer and may eventually vanish, emphasizing the importance of scale in texture representation.
- Comparative Texture: Variations in texture can distinguish features with similar reflectance values—the smoothness of grass versus the rough bark of trees, for example. Such distinctions are critical for accurate object recognition.
- Radar Imaging: In radar images, texture serves as a key feature for differentiating objects, enhancing accuracy in remote sensing.
- Composition: Texture emerges from a blend of shape, size, pattern, shadow, and tone, which collectively inform how elements are perceived in an image.
Understanding and interpreting texture ultimately enhances the ability to classify and analyze images effectively.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Texture
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Texture is the arrangement and frequency of tonal variation in an image. It is created by an aggregation of unit features that may be too small to be discerned individually on the image, such as tree leaves. Texture determines the overall smoothness or coarseness of image features as visualized on the image.
Detailed Explanation
Texture refers to how smooth or rough an image appears, based on the arrangement and frequency of different tones. For instance, in an image of a forest, individual leaves might be too small to see, but their collective arrangement creates an overall texture. This texture can make the image appear smooth (like a flat surface) or coarse (like jagged rocks) depending on how the tonal variations are distributed.
Examples & Analogies
Think of texture like the surface of a cake. A smooth frosting represents a smooth texture. If the frosting has sprinkles or designs, it resembles a coarse texture. Similarly, an image can have areas that look very smooth or very rough depending on how the elements within the image are arranged.
Impact of Image Scale on Texture
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
If the scale of the image is reduced, texture of any given object or area becomes progressively finer and ultimately disappears. Texture is a combination of shape, size, pattern, shadow, and tone.
Detailed Explanation
As you zoom out of an image or decrease its scale, the details that create texture become less distinguishable. For example, the rough texture of tree bark might appear smooth when viewed from a large distance. This is because the finer details that contribute to the texture blend together, making it hard to perceive them as distinct features.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine looking at a city through a telescope vs. from an airplane. Up close, you can see the textural details of buildings, like the bricks or windows. But from high up, those details blend and you only see shapes and colors, losing the texture.
Distinguishing Features Based on Texture
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Various features with similar reflectances can be distinguished based on their texture differences, such as the smooth texture of green grass contrasted with the rough texture of crowns of green trees. Smooth textures would have very little tonal variation, e.g., fields, asphalt, or grasslands, whereas the grey levels change abruptly in a small area, e.g., forest canopy, where rough texture is present.
Detailed Explanation
Texture helps in identifying and distinguishing different features in an image based on their visual characteristics. For example, green grass appears smooth with little variation in tone, while tree crowns show more complex variations due to their roughness. This difference in texture allows us to differentiate between these two types of surfaces even if their colors might be similar.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine touching different surfaces: a soft cushion vs. rough concrete. Even if both are green in color, they feel very different. Similarly, in images, these different textures help us identify surfaces and their properties without needing to see every detail.
Texture in Radar Images
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Texture is also one of the most important elements for distinguishing features from Radar images.
Detailed Explanation
In the context of radar imagery, texture plays a crucial role in identifying and categorizing features since radar systems detect features based on how they reflect signals. The texture, resulting from the surface characteristics, allows for the distinction of different materials and objects on the ground.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how a camera captures images based on light, whereas a radar image looks at how surfaces reflect radio waves. Just like different materials (like a smooth lake vs. a rugged mountain) reflect light differently, they also reflect radar waves in unique ways that can be read as 'texture' on a radar image. This helps us understand and classify what is present in the images.
Key Concepts
-
Texture: Key for understanding tonal variation in images.
-
Scale: Affects the perception and clarity of textures in images.
-
Radar Imaging: Utilizes texture to enhance object identification.
-
Comparative Textures: Important for distinguishing similar features.
Examples & Applications
The contrast between a smooth surface, such as asphalt, and a rough surface, like a forest canopy, illustrates how texture helps in identifying different land features.
In radar images, the texture allows for the differentiation between water bodies and vegetation based on their distinct reflectance patterns.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When it's smooth like a beach, it's texture we teach, rough like a tree, is easy to see!
Stories
Imagine a king surveying his vast kingdom. The smooth paths of the towns contrast with the rough forest, helping him identify both easily. That's how texture helps us!
Memory Tools
S.P.E.C.T. - Shape, Pattern, Edge, Contrast, Tone; the elements of texture in image interpretation.
Acronyms
T.R.A.C.E. - Texture, Reflection, Arrangement, Contrast, and Elements; remember texture characteristics!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Texture
The arrangement and frequency of tonal variation in an image, influencing its smoothness or coarseness.
- Scale
The relative size of an image, which affects the visibility of texture details.
- Radar Imaging
A technique using radar to capture images that reflect different textures, aiding in distinguishing land features.
- Tonal Variation
The differences in brightness and color that define how objects appear in an image.
- Reflectance
The measure of light reflected from surfaces, relevant to identifying and classifying objects.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
