Key Features of AMBA 3 AHB-Lite
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to AHB-Lite
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re going to discuss AHB-Lite, a crucial part of the AMBA architecture. Can anyone share what they think AHB-Lite stands for?

Is it Advanced High-performance Bus Lite?

Exactly! AHB-Lite is a simplified version of the AHB designed for systems with simpler connectivity needs. What do you think makes it advantageous for embedded systems, Student_2?

Maybe it’s because it’s simpler to use?

Right! It offers high performance while being easy to integrate, making it suitable for various applications. Remember: SIMPLER = BETTER!.
Support for Single Master
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

One of the key features of AHB-Lite is single master support. Student_3, can you explain what that means?

It means that usually only one device, like a processor, controls the data transfers?

Exactly! This design simplifies the architecture and reduces complexity. Why do you think having a single master is beneficial, Student_4?

It probably helps avoid conflicts that can happen with multiple masters.

Great point! Having just one master reduces the need for complex arbitration mechanisms. Just remember: ONE MASTER, LESS COMPLEXITY!
Low Latency and High Throughput
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Another vital feature of AHB-Lite is its low latency and high throughput. Can anyone tell me how this is achieved? Student_1, what do you think?

I believe it’s because of the pipelined access to memory?

Correct! The pipelining allows multiple data transactions to occur simultaneously, which reduces the waiting time for data transfers. Can anyone relate this to a real-life scenario?

Like how a factory might work, where different tasks are done at the same time without waiting?

Exactly! Pipelining in AHB-Lite is like parallel processing in a factory, allowing for efficiency. Remember: PIPELINE = FAST!
Burst Transfers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

The ability to support burst transfers is another interesting aspect of AHB-Lite. Student_3, can you explain what burst transfers are?

It means transferring multiple data items at once without sending a new address again?

Exactly right! This capability improves data transfer efficiency significantly. Student_4, why do you think this feature is helpful in certain applications?

I guess for situations where large blocks of data need to be transferred quickly, like in video or audio processing.

Perfect answer! Burst transfers can indeed handle large amounts of data seamlessly. Keep in mind: BURST = SPEED!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section outlines the key features of AMBA 3 AHB-Lite, including its simplicity, support for single master configurations, low latency, high throughput, and capabilities for burst transfers, making it ideal for various embedded systems.
Detailed
Key Features of AMBA 3 AHB-Lite
AMBA 3 AHB-Lite is a streamlined version of the Advanced High-performance Bus (AHB) architecture, optimized for systems with simpler connectivity requirements. Key features include:
- Simple, High-Performance Bus: AHB-Lite supports fast communication yet maintains a user-friendly interface, promoting ease of integration and operation.
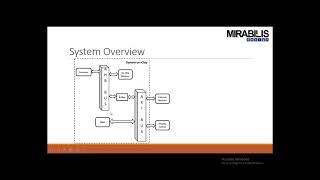
- Single Master Support: It is tailored for systems with one master (like a processor or DMA controller) managing multiple slave devices (peripherals or memory), simplifying design and operation.
- Low Latency and High Throughput: AHB-Lite offers efficient pipelined access to memory and peripherals, minimizing delays and allowing rapid data transfers for applications requiring high performance.
- High Bandwidth: It supports fast data transfer rates, particularly beneficial for memory-mapped I/O and high-performance memory operations.
- Support for Burst Transfers: The protocol allows burst transactions, enabling the transfer of multiple data items in succession while maintaining a single address, which is crucial for efficient data handling in various applications.
These features make AHB-Lite an attractive choice for embedded systems, microcontrollers, and cost-sensitive applications that still require high throughput.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Simple, High-Performance Bus
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AHB-Lite supports high-speed communication between components while maintaining a simple interface for ease of use.
Detailed Explanation
AHB-Lite is designed to facilitate fast communication between different parts of a system. It has a straightforward interface, making it easier for developers to use. This simplicity means that they can implement the bus without complex configurations, allowing for a smoother integration process while ensuring that data transfer remains quick and efficient.
Examples & Analogies
Think of AHB-Lite like a high-speed road with easy-to-read traffic signs. Just as the clear signs help drivers navigate quickly and efficiently, the simple interface of AHB-Lite enables developers to connect various components without confusion, ensuring rapid data transfer.
Single Master Support
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AHB-Lite is optimized for systems where there is typically one master (processor or DMA controller) initiating data transfers to one or more slaves (peripherals or memory).
Detailed Explanation
In AHB-Lite systems, there is usually one primary device known as the 'master' that controls the data flow. This master can be a processor or a Direct Memory Access (DMA) controller. The master sends commands to multiple devices called 'slaves' which could be peripherals or memory. This setup simplifies the design and operation of the system since only one master device is sending instructions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a classroom where a single teacher (the master) gives instructions to multiple students (the slaves). The teacher decides what each student needs to do, ensuring everyone works efficiently without multiple teachers giving conflicting instructions, simplifying the learning process.
Low Latency and High Throughput
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AHB-Lite provides efficient pipelined access to memory and peripherals, reducing latency and supporting high-throughput data transfers.
Detailed Explanation
Latency refers to the delay before a transfer of data begins following an instruction, while throughput measures how much data can be transferred in a given time frame. AHB-Lite minimizes latency through pipelining, which allows it to process multiple instructions simultaneously. This means that data moves more quickly between the master and the slaves without waiting for previous instructions to finish.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a fast-food restaurant where multiple orders are prepared simultaneously. Just like the cooks prepare different items at the same time to reduce wait times for customers, AHB-Lite uses pipelining to ensure data moves quickly, resulting in efficient operation and better resource use.
High Bandwidth
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Supports high-speed data transfers, typically used for memory-mapped I/O or high-performance memory operations.
Detailed Explanation
Bandwidth refers to the maximum rate of data transfer across a network or bus. AHB-Lite is equipped to handle high bandwidth requirements, allowing it to manage intense data movements, such as transferring large datasets from memory to processors efficiently. This capability is crucial in applications that demand rapid data processing.
Examples & Analogies
Think of bandwidth like a water main delivering water to a neighborhood. A larger pipe can deliver more water at once, just as a high-bandwidth bus can transfer larger amounts of data quickly, fulfilling the heavy demands of applications that need fast data access, like video games or simulations.
Support for Burst Transfers
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AHB-Lite allows for burst transfers, enabling efficient large data block transfer between a master and a slave.
Detailed Explanation
Burst transfers enable AHB-Lite to send a block of multiple data items with fewer control signals needed than if each item were sent individually. This enhances effectiveness, particularly when large data sets are handled, as it reduces overhead and improves the speed of data transmission.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine if you are filling a bucket with water. Instead of turning on the tap and filling it drop by drop (which takes a long time), you turn it on fully and fill the bucket quickly in one go. Burst transfers work similarly by sending large volumes of data more efficiently than sending each piece separately.
Key Concepts
-
Simple, High-Performance Bus: A bus system that balances performance with ease of use.
-
Single Master Support: Focus on single control for simplicity and reduced complexity.
-
Low Latency and High Throughput: Allows efficient and rapid data transfers.
-
High Bandwidth: Support for high-speed operations.
-
Support for Burst Transfers: Efficiently handles multiple data transfers in sequence.
Examples & Applications
AHB-Lite is used in microcontrollers where only one processor communicates with various components.
For real-time applications like video streaming that need to transfer large amounts of data rapidly, burst transfers enhance performance.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
AHB-Lite is light, easy and bright, for single masters, it's just right!
Stories
Imagine a library where only one librarian helps patrons check out books quickly and efficiently, similar to how AHB-Lite operates with just one master!
Memory Tools
Remember: S-High = Simple & High Performance of AHB-Lite!
Acronyms
B.E.S.T - Burst Efficiency Simplifies Transfers.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- AMBA
Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture; an open standard defining on-chip interconnect protocols.
- AHBLite
A simplified version of AHB, optimized for systems with single master and lower complexity.
- Single Master Support
A configuration that allows only one master device to initiate data transfers in the bus architecture.
- Low Latency
Minimal delay experienced in processing operations, enabling faster data transfer.
- High Throughput
The capability to transfer large amounts of data effectively within a certain timeframe.
- Burst Transfers
A transaction type allowing multiple data items to be transferred in sequence without needing a new address for each transfer.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
