Object Serialization Example
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Serialization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into serialization, specifically how we can write a Java object to a file. Who can remind me what serialization is?

Isn't serialization the process of converting an object into a byte stream?

Correct! Serialization converts an object into a format that can be easily saved or transmitted. Why do you think that might be important?

It helps in storing data permanently or sending it over a network!

Exactly! Now, let's look at an example of how we can achieve this using Java's built-in classes.
Creating the Student Class
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To start, we need a class that implements `Serializable`. Can someone explain what this interface does?

It's a marker interface that tells Java this class can be serialized?

That's right! Let's say we have a class `Student` with some attributes. What do we need to ensure before serializing these attributes?

All non-static and non-transient fields are serialized.

Exactly! Now, let's write our `Student` class. Remember to keep the attributes simple.
Writing the Object to a File
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we have our `Student` class, let's look at how to write an object of this class into a file. Who can explain the main classes we will use here?

We will use `FileOutputStream` to create a file and `ObjectOutputStream` to serialize the object into that file.

Excellent! Now, let's look at the code snippet that writes the `Student` object, `s`, to `student.ser`.

And once we run this code, we should see a message saying 'Object has been serialized,' right?

Yes! That's our confirmation. Now let’s proceed to how we might read this object back from the file.
Key Takeaways
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To summarize what we’ve learned today, what is the main purpose of serialization in Java?

To convert an object into a byte stream for storage or transmission!

Great! And what interface must our classes implement for serialization?

The Serializable interface!

Exactly! Any final thoughts or questions before we wrap up?

Can we serialize any object, or are there restrictions?

Interesting question! In fact, all non-transient and non-static fields will be serialized, but superclass fields also need to be serializable. Good job today, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section illustrates the process of serializing a 'Student' object to a file using Java's I/O classes, providing a concrete example that helps understand serialization mechanics in practice.
Detailed
Object Serialization Example
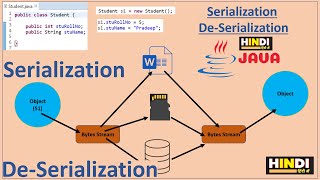
In this section, we explore an example of object serialization in Java. Serialization is a vital process that allows an object to be converted into a byte stream for storage or transmission. Java simplifies this process through its I/O classes.
The example provided shows how to create a Java class Student, implement the Serializable interface, and serialize it using ObjectOutputStream. The following steps are demonstrated:
1. Creating the Student Class: The Student class includes necessary attributes and implements the Serializable interface.
2. Writing to a File: The SerializeDemo class creates an instance of Student and writes it to a file called student.ser. The use of FileOutputStream and ObjectOutputStream shows how the object is serialized into a file.
3. Output Confirmation: A confirmation message is printed to indicate successful serialization.
This section lays the foundation for understanding how serialized objects can be stored and retrieved, which is critical for applications involving data persistence and communication in distributed environments.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Writing an Object to File
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
import java.io.*;
public class SerializeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Student s = new Student(101, "Abraham");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("student.ser");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeObject(s);
oos.close();
fos.close();
System.out.println("Object has been serialized");
}
}
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, we're given a simple program that demonstrates how to serialize an object in Java. The program starts by creating an instance of the Student class with an ID and name. Then, it opens a file output stream that points to a file named student.ser. An object output stream is created using this file output stream. The writeObject method of the object output stream is then called to serialize the Student object and write it into the file. After writing the object, both streams are closed to free resources. Finally, a message is printed to indicate successful serialization.
Examples & Analogies
Think of serialization as packing a suitcase for a trip. When we pack a suitcase, we carefully arrange our clothes and belongings into it so that we can carry them easily. Similarly, serialization takes an object and 'packs' it into a byte stream which can be then saved to a file or sent to another machine. Once we reach our destination, we can 'unpack' the suitcase, which is like deserialization where we read the byte stream back into an object.
Key Concepts
-
Serialization: The process of converting an object to a byte stream.
-
Serializable interface: A marker interface indicating that a class can be serialized.
-
ObjectOutputStream: Used to serialize objects into an output stream.
-
FileOutputStream: Writes byte streams to a file.
Examples & Applications
Creating a Student object, setting its properties, and serializing it to a file using ObjectOutputStream.
Using FileInputStream and ObjectInputStream to read back a serialized object.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To serialize your class with ease, implement Serializable if you please!
Stories
Imagine a student named Sam who wanted to share his report card with his friend. He found a magical box (the file) that could hold his report (the object) forever!
Memory Tools
Think 'S.O.F.' to remember serialization: S for Stream, O for Object, F for File.
Acronyms
Remember 'S.O.S.' - Serialize, Output, Store.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Serialization
The process of converting an object into a byte stream for storage or transmission.
- Deserialization
The reverse process of converting a byte stream back into a copy of the original object.
- Serializable
A marker interface in Java indicating that a class can be serialized.
- ObjectOutputStream
A class in Java used to serialize an object to an output stream.
- FileOutputStream
A class in Java used to write data to a file as a byte stream.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
