What is Serialization?
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Serialization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning class! Today, we’re diving into a fascinating topic called serialization. Can anyone tell me why converting an object into a byte stream might be useful?

Is it so we can save the object's state, like when we want to store data?

Exactly, Student_1! Serialization allows us to save an object's state to a file, which can then be retrieved later. It’s essential for data storage and communication between systems.

Can serialization be used to send objects over a network too?

Great question, Student_2! Yes, serialization is used to send objects through networks, especially in distributed applications. Imagine having a program running on different machines—serialization bridges the communication gap!

What happens to the object during this process?

When we serialize an object, its state converts to a byte stream. We can think of this byte stream like a unique fingerprint of the object, which can later be reconstituted. Let's remember this with the acronym 'S.O.B' - Save Objects as Bytes!

To recap, serialization lets us save, send, and restore the state of Java objects, ensuring efficient data management.
Use Cases of Serialization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand what serialization is, let's explore its primary use cases. Can anyone name some examples where serialization is applied?

Maybe in database storage, to save different objects?

Correct, Student_4! Databases often require serialized objects to store, retrieve, and manipulate data efficiently.

I’ve heard of deep copying—how does serialization help with that?

Good point, Student_1! Serialization facilitates deep copying by allowing us to create an independent duplicate of an object. When we serialize and then deserialize, it's like creating a new version of that object.

And in distributed systems, right?

Yes! In distributed systems, serialization ensures that objects can be sent over different machines seamlessly. Let’s remember: 'Save, Send, Duplicate!'—our mantra for serialization!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
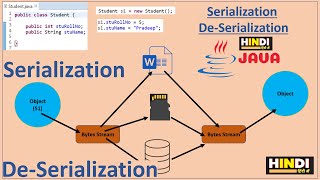
In Java, serialization transforms an object into a byte stream for easy saving to files, network transfer, or database storage, with various use cases like object persistence and deep copying. Deserialization, the reverse process, reconstructs the object from the byte stream.
Detailed
What is Serialization?
Serialization is a crucial mechanism in Java that involves converting the state of an object into a byte stream. This byte stream can be persisted to a file, transmitted across networks to other Java Virtual Machines (JVMs), or stored in databases. The process is not only important for saving object states but also plays a significant role in distributed systems, such as when working with Remote Method Invocation (RMI).
Java facilitates serialization through the use of the Serializable interface located in the java.io package. The benefits of serialization include:
- Saving object states to files for future use
- Sending objects over a network, such as through sockets or RMI
- Deep copying objects to create independent duplicates
- Caching data in distributed applications to improve performance
Understanding the principles of serialization helps developers manage object states effectively, ensuring data integrity and continuity across different computing environments.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Defining Serialization
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Serialization is the mechanism of converting the state of an object into a byte stream. This byte stream can then be persisted to a disk, transmitted to another JVM, or stored in a database.
Detailed Explanation
Serialization is a process in computer programming, particularly in Java, that involves taking an object (which is essentially a combination of data and behavior) and converting it into a linear format, specifically a byte stream. This byte stream is like a sequence of zeros and ones that can be easily stored or transmitted. Once you have serialized the object, you can save it on a disk, which means it lasts beyond the program's execution, send it over a network to another program running on a different machine, or store it in a database, allowing for retrieval later.
Examples & Analogies
Think of serialization like packing a suitcase for a trip. Just as you would carefully arrange your clothes and items into your suitcase to take them with you somewhere, serialization packs your object into a byte stream to transport it where needed—whether to storage or over the internet.
Uses of Serialization
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Saving object states to files
• Sending objects over a network (e.g., in sockets or RMI)
• Deep copying objects
• Caching in distributed applications
Detailed Explanation
There are several practical uses for serialization in programming. Firstly, it allows developers to save the current state of an object to a file, which they can later load back into memory. Secondly, it facilitates the transfer of objects over a network, which is essential for client-server communications, like in Remote Method Invocation (RMI). Moreover, serialization can be used for deep copying objects, where an exact duplicate of an object is needed—for instance, to avoid modifications to the original while working on a copy. Lastly, serialization supports caching in distributed applications, allowing data to be stored and retrieved quickly across different systems.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're at a library. Serialization is like taking a photo of your favorite book (the object) to capture its state. You can save that photo (the byte stream) in your phone (file), share it with friends (sending over a network), or create multiple copies for various book clubs (deep copying). Additionally, some libraries use a catalog (caching) to speed up the search for popular books.
Key Concepts
-
Serialization: Converting objects into byte streams.
-
Deserialization: Reconstructing objects from byte streams.
-
Serializable Interface: Marker interface to indicate a class can be serialized.
-
Byte Stream: The digital representation of serialized objects.
-
Use Cases: Saving, sending, and duplicating object states.
Examples & Applications
An object storing user information is serialized and written to a file for later retrieval.
An application transfers an object representing a user session over a network to a remote server.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Serialize to save, send, and clone; byte streams create a data throne.
Stories
Imagine a gardener who collects seeds (objects) and stores them in jars (byte streams) to grow new flowers (restore the objects) later.
Memory Tools
Think 'S.O.B' - Save Objects as Bytes to remember serialization.
Acronyms
S.O.D
Serialization = Objects to Data stream.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Serialization
The process of converting an object's state into a byte stream for storage, transmission, or persistence.
- Deserialization
The reverse process of serialization, which reconstructs an object from a byte stream.
- Serializable
A marker interface in Java that allows a class to be serialized.
- Byte Stream
A sequence of bytes used for storage or manipulation of digital data.
- RMI (Remote Method Invocation)
A Java API that allows the invocation of methods that reside on different Java Virtual Machines.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
