Functional Programming in Java
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Functional Programming in Java
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into functional programming in Java. Can anyone tell me how functional programming differs from traditional OOP?

Isn't it that OOP focuses on objects and classes, while functional programming emphasizes functions?

Exactly! Functional programming indeed focuses on functions as first-class citizens. It allows us to pass behaviors as parameters and write more concise code. This approach helps in reducing boilerplate code significantly.

How does passing behaviors as parameters work?

Great question! By using lambda expressions, we can define behaviors right where we need them, allowing for more flexible and reusable APIs. Remember the mnemonic 'LAM' for Lambda: 'Light And Modular'.

So, functional programming is like another tool in our toolbox for writing better Java code?

Exactly! It helps us write cleaner, less error-prone code when used properly. Let’s explore more about lambda expressions and functional interfaces.
The Importance of Lambda Expressions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the foundation, let's discuss lambda expressions. What are they?

Are they like anonymous functions we can use without declaring them?

Yes! Lambda expressions allow us to create anonymous functions on the fly. The syntax is simple: `(parameters) -> expression`. For example, the lambda expression `(a, b) -> a + b` adds two numbers.

Why do we need lambda expressions if we have regular methods?

Excellent point! Lambda expressions help reduce boilerplate code and enhance readability, especially useful in APIs like Streams and Collections. Remember LAMBDA: 'Less Anonymous, More Behavioral Define Actions'.

How do they relate to functional interfaces?

Lambda expressions are specifically designed to provide implementations for functional interfaces, which contain a single abstract method. This connection is vital in Java's functional programming landscape.
Functional Interfaces and Their Role
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's move on to functional interfaces. What do you think makes an interface a functional interface?

Is it the number of methods it has?

Exactly! A functional interface must have exactly one abstract method. This simple rule makes them ideal for use with lambda expressions. A neat mnemonic for remembering is SAM: 'Single Abstract Method'.

Can you give us an example of a functional interface?

"Sure! For instance, we can define a functional interface like this:
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The integration of functional programming in Java since version 8 enhances code readability and reduces boilerplate. By utilizing lambda expressions and functional interfaces, developers can pass behavior as parameters and create reusable APIs, promoting immutability and statelessness.
Detailed
Functional Programming in Java
Java, traditionally known as an object-oriented programming (OOP) language, began incorporating functional programming paradigms starting with Java 8. This shift allows developers to utilize a more flexible and concise coding style, primarily through the use of lambda expressions and functional interfaces.
Key Features of Functional Programming in Java:
- Passing Behavior as Parameters: Functions or behaviors can be passed easily as parameters to other methods.
- Reduced Boilerplate Code: By eliminating the need for verbose implementations, lambda expressions help keep code clean and maintainable.
- Reusable APIs: Functional programming supports the development of more versatile and reusable APIs.
Functional programming focuses on the use of pure functions, which do not contain side effects, and emphasizes immutability and statelessness. Lambda expressions serve as the foundation for these capabilities in Java, allowing developers to write more compact and expressive code and improve the overall efficiency of applications.
Youtube Videos



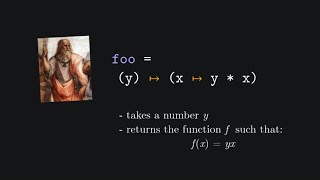






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Object-Oriented to Functional Programming Shift
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Java has traditionally been an object-oriented language. However, from Java 8 onwards, functional programming paradigms have been integrated into Java to allow:
Detailed Explanation
Java, historically known for its object-oriented paradigm, has incorporated functional programming features starting with Java 8. This means that developers can now use functions as first-class citizens, which opens up new ways of structuring applications that can lead to simpler and more maintainable code.
Examples & Analogies
Think of traditional Java as a vehicle built for speed (object orientation), where every part has a specific purpose like the engine, wheels, and body structure. When functional programming aspects are added, it’s akin to adding electric motors to different parts of the vehicle that enhance its performance, allowing functions to work together in innovative ways.
Key Benefits of Functional Programming in Java
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Passing behavior as a parameter
• Reducing boilerplate code
• Creating more flexible and reusable APIs
Detailed Explanation
Functional programming in Java brings several benefits. First, it allows developers to pass methods as parameters (think of 'behavior' being sent where needed). This helps in reducing repetitive code (boilerplate), making it cleaner. Additionally, functional programming promotes the creation of APIs that are more adaptable and can be reused across different parts of an application, thus increasing efficiency.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a chef who can either create his own dishes or use a set of predetermined recipes. The ability to pass different ingredients (behaviors) allows the chef to tailor meals to customers’ tastes without reinventing the wheel every time, thus saving time and making the kitchen more efficient.
Core Principles of Functional Programming
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Functional programming emphasizes pure functions, immutability, and statelessness. Lambda expressions are the foundation of this functional capability.
Detailed Explanation
The core principles of functional programming include: 1) Pure Functions - These always produce the same output for the same input without side effects. 2) Immutability - Data or objects don’t change state once created. 3) Statelessness - Functions do not rely on external state. Lambda expressions serve as a practical tool that embodies these principles, making it easier to implement functional programming in Java.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a vending machine as a representation of pure functions and immutability. Each time you press the button for 'Coke,' you get the same 'Coke' (output) without it being affected by previous orders (state) or changing the machine’s internal workings. You simply put in your money and request a drink; that's all there is to it.
Key Concepts
-
Functional Programming: A programming paradigm that treats computation as the evaluation of mathematical functions and avoids changing state and mutable data.
-
Lambda Expressions: Functions defined without a name; allows passing behavior directly.
-
Functional Interfaces: Interfaces that have a single abstract method, allowing them to be implemented using lambda expressions.
Examples & Applications
An example of a lambda expression for adding two numbers: (int a, int b) -> a + b.
An example of a functional interface: @FunctionalInterface interface MyFunction { int operation(int a, int b); }.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In Java, we don’t just play, / Lambdas help to save the day. / With one method, they define, / Making code more clean and fine!
Stories
Imagine a baker who decides to bake a special cake every day. Each day, they use a different recipe (lambda expression) from their recipe book (functional interface), resulting in delightful variations without cluttering their kitchen with too many pans (boilerplate code).
Memory Tools
Use 'FLEX' to remember functional programming benefits: Flexibility, Less boilerplate, Enhances readability, eXpressions as functions.
Acronyms
Remember SAM for functional interfaces
Single Abstract Method.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Lambda Expression
An anonymous function that can be passed around and executed, used for implementing methods of functional interfaces.
- Functional Interface
An interface that has exactly one abstract method, which can be implemented with a lambda expression.
- Pure Function
A function where the output is determined only by its input values, with no side effects.
- Immutability
The state of an object cannot be modified after it's created.
- Statefulness
A characteristic of a system where the state can change over time.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
