Distortion in Communication Systems
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Distortion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore distortion in communication systems. Can anyone tell me what they think distortion means?

Does it mean changing the shape of the signal?

Exactly! Distortion occurs when the signal changes form during transmission. Let's discuss the different types of distortion. First up is amplitude distortion. Who can guess what that means?

Is it when the signal's strength varies?

Correct! Amplitude distortion alters the signal levels, which can lead to confusion at the receiving end.
Types of Distortion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's look at phase distortion. What do you think that involves?

Maybe it has to do with timing or when the signal peaks?

Good deduction! Phase distortion shifts the timing of the signal based on frequency. How about frequency distortion? Any thoughts?

I think it's when some frequencies are weaker than others.

That's spot on! It results in uneven signal power, which impacts the quality of transmission.
Linear vs. Non-linear Distortion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's clarify the difference between linear and non-linear distortion. Who can define linear distortion?

Isn't that when the shape stays the same but the amplitude changes?

Exactly! Linear distortion affects amplitude or phase but keeps the signal shape intact. Now, what about non-linear distortion?

It causes the waveform to change, right?

Correct! Non-linear distortion introduces new frequency components, making it more complex.
Implications of Distortion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

So, why is it important to understand these distortions in communication systems?

To improve signal clarity and quality?

Absolutely! Minimizing distortion is crucial for effective communication. Let's summarize what we've learned about distortion today.

We talked about amplitude, phase, and frequency distortion, right?

Yes! Remember, understanding these concepts helps engineers design better communication systems.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
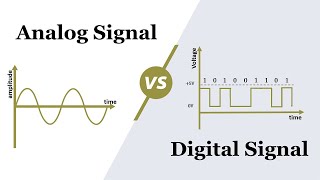
Distortion in communication systems alters the original signal's form, impacting communication clarity and fidelity. It is categorized into amplitude, phase, and frequency distortion, with distinctions between linear and non-linear kinds of distortion, which can introduce new frequency components.
Detailed
Distortion in Communication Systems
Distortion refers to the alteration of a signal's original form or shape during its transmission through a communication system. It can significantly affect the clarity and quality of communication, making it essential to understand the different types and their implications. There are three primary types of distortion:
- Amplitude Distortion: This occurs when the levels of the signal are changed, leading to inconsistencies in signal strength.
- Phase Distortion: This type involves a variation in phase shifts based on frequency, which can lead to misalignment in signal synchronization.
- Frequency Distortion: Certain frequencies may be attenuated more than others, causing uneven signal power across the frequency spectrum.
Additionally, distortions can be classified into linear and non-linear types:
- Linear Distortion alters the signal amplitude or phase but does not change its shape. It typically introduces a predictable timing discrepancy.
- Non-linear Distortion, on the other hand, affects the waveform's shape by introducing new frequency components, such as harmonics and intermodulation, complicating the transmission further.
Understanding these distortions is crucial in designing effective communication systems, enabling engineers to employ methods to mitigate their effects and ensure high-quality data transmission.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is Distortion?
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Distortion occurs when the signal changes its form or shape during transmission.
Detailed Explanation
Distortion in communication systems refers to any alteration in the original signal during transmission. This means the signal is no longer identical to what was sent; it has changed in some way. Understanding distortion is crucial because it can affect how well the information is received and interpreted at the other end.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are singing a song and someone records it. If the microphone is of poor quality or if there is interference, your voice may sound different when played back – higher in pitch or off-tempo. This alteration is similar to how distortion changes a transmitted signal.
Types of Distortion
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Types: 1. Amplitude Distortion:
○ Signal levels are altered. 2. Phase Distortion:
○ Phase shift varies with frequency. 3. Frequency Distortion:
○ Certain frequencies are attenuated more than others.
Detailed Explanation
There are three primary types of distortion:
1. Amplitude Distortion: This occurs when the amplitude (or strength) of the signal varies, causing some parts of the signal to be louder or softer than intended.
2. Phase Distortion: This distortion happens when the timing of specific parts of the signal is shifted based on frequency. Different frequencies may arrive at the receiver at different times.
3. Frequency Distortion: In this type, some frequencies lose strength more than others during transmission, which changes the balance of the signal.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a music equalizer. If you boost the bass too much, the higher frequencies (like vocals or cymbals) may become less audible. This imbalance is akin to frequency distortion where some parts of the signal (or music) are altered more than others.
Linear vs. Non-linear Distortion
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Linear Distortion: Alters signal amplitude or phase but not shape.
● Non-linear Distortion: Causes waveform shape changes, introducing new frequency components (harmonics, intermodulation).
Detailed Explanation
Distortion can be further classified into linear and non-linear distortion:
- Linear Distortion: This type tends to affect the amplitude or phase of the signal without changing its waveform shape. For example, if a sound signal is boosted overall, it remains recognizably the same in wave shape.
- Non-linear Distortion: This type alters the waveform itself, creating new frequency components that weren't present in the original signal, which can complicate the message. This often happens when a signal is amplified beyond capacity, leading to distortion you can hear, such as crackling or distortion in audio systems.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a graph. If you stretch it uniformly (like linear distortion), it still looks like a graph, just bigger. However, if you twist or warp it (like non-linear distortion), it changes completely, possibly creating shapes that are not reflective of the intended data, just as sound may become unrecognizable due to strong distortion.
Key Concepts
-
Distortion: Alteration of the original signal's form during transmission.
-
Types of Distortion: Includes amplitude, phase, and frequency distortion.
-
Linear Distortion: Makes changes to amplitude or phase without altering shape.
-
Non-linear Distortion: Alters waveform shape, introducing new frequency components.
Examples & Applications
An example of amplitude distortion is when a voice signal becomes louder or softer during transmission, affecting clarity.
Phase distortion can occur in audio transmission systems when different frequencies are delayed at different rates, causing echoes.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Distortion's a change, don't let it feel strange, amplitude shifts, phase can give rifts.
Stories
Imagine a painter mixing colors. If he mixes them correctly, the portrait looks great. But if he uses too much of one color, the picture distorts. Similarly, in communication, if signals mix incorrectly, they are distorted.
Memory Tools
Remember 'A.P.F.' for types of distortion: Amplitude, Phase, Frequency.
Acronyms
D.A.N. (Distortion Affects Networks) helps you remember that distortion affects how signals are transmitted.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Amplitude Distortion
A type of distortion where the signal levels are altered, affecting the signal's strength.
- Phase Distortion
Distortion characterized by a variation in phase shifts based on frequency.
- Frequency Distortion
A form of distortion where certain frequencies are attenuated more than others.
- Linear Distortion
Distortion that alters amplitude or phase without changing the overall signal shape.
- Nonlinear Distortion
Distortion that changes the signal waveform's shape and introduces new frequency components.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
