Introduction to Communication System Performance
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Communication System Performance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore how we evaluate the performance of communication systems. What do you think is the main goal of a communication system?

I think it's to send information from one place to another!

Exactly! The performance is judged by how accurately and efficiently it transmits information. Now, can anyone name some factors that might affect this performance?

Maybe noise? I've heard that can mess up signals.

Great point! Noise is a major factor. We also have distortion and bandwidth constraints. Remember the acronym 'NDB' for Noise, Distortion, and Bandwidth. Let's keep this in mind as we discuss further!
Identifying Key Performance-Limiting Factors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk more about noise. What are some different types of noise you might encounter in communication systems?

I think thermal noise is one since it has to do with temperature, right?

Correct! Thermal noise comes from the random motion of electrons. Can someone think of another type?

How about intermodulation noise? I've heard it occurs when signals mix!

Perfect! Intermodulation noise happens due to non-linear mixing. Understanding these noises is key to minimizing their impact and improving performance.
Implications of Bandwidth on Communication Performance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s shift our focus to bandwidth. Why do you think bandwidth is crucial in communication systems?

Bandwidth determines how much data we can send, right?

Exactly! Every channel has limited bandwidth, which directly restricts the data rate. Can anyone explain Nyquist Bandwidth?

It's like the maximum rate of information transmission that can fit in that bandwidth!

Well said! And remember, fulfilling Nyquist criteria can help us optimize bandwidth usage.
Performance Metrics Summary
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Before we wrap up, let's review some performance metrics we discussed. Who remembers what SNR stands for?

It's Signal-to-Noise Ratio! It helps us understand how clear a signal is against noise.

Exactly! Keep in mind that a high SNR indicates better performance. Any other metrics we should remember?

Throughput! It’s about how much data is effectively transmitted.

Great job, everyone! Remembering these metrics can significantly enhance our understanding of communication systems.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore how communication system performance is assessed based on its ability to transmit information accurately and efficiently. Key factors such as noise, distortion, and bandwidth constraints are discussed, highlighting their significance in achieving high-quality transmission and optimal data rates.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Communication system performance is primarily evaluated by how well it transmits information from the source to the destination. The effectiveness of any communication system can be significantly limited by three key factors:
- Noise: Unwanted electrical signals that can interfere with the intended message signal. Understanding noise types, such as thermal noise and impulse noise, is essential for mitigating their impact.
- Distortion: The alteration of the signal during transmission that results in changes to its shape or form. Types of distortion include amplitude and phase distortion.
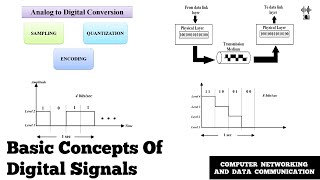
- Bandwidth Constraints: The limited frequency range that a communication channel can utilize, impacting the data rate that can be achieved. Concepts of Nyquist Bandwidth and Shannon's capacity theorem are critical in evaluating performance.
Effectively managing these factors is crucial to ensure reliable communication and maximize data rates. By utilizing performance metrics like Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), one can better quantify system performance and work towards the optimization of communication protocols.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Communication System Performance
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Communication system performance is judged by how accurately and efficiently it transmits information from source to destination.
Detailed Explanation
This statement defines the fundamental goal of any communication system: to transfer information accurately and efficiently from the sender (source) to the receiver (destination). This means that the system should not only convey the intended message correctly but also do so in a way that minimizes the time and resources used.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a letter being sent through the postal service. If the letter reaches the recipient quickly and without errors, we judge the postal service as effective. Similarly, in communication systems, success is measured by accuracy and efficiency.
Key Performance-Limiting Factors
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Key performance-limiting factors:
○ Noise
○ Distortion
○ Bandwidth constraints
Detailed Explanation
This chunk identifies three critical factors that can negatively impact the performance of communication systems:
1. Noise: Any unwanted signals that can distort or interfere with the original message.
2. Distortion: Changes in the shape or form of the signal during transmission that can lead to misunderstanding the message.
3. Bandwidth constraints: Limitations on the range of frequencies that the communication system can effectively use, which can restrict how quickly data is sent.
Understanding these factors is essential for building systems that perform effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to have a conversation in a crowded room. You might struggle to hear the person you're talking to because of the background noise (noise), and they might not communicate clearly because they're using a wrong accent (distortion). Additionally, if the room is too small or crammed with too many people (bandwidth constraints), it hinders how freely you can exchange information.
Importance of Understanding Performance Factors
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Understanding and minimizing these factors ensures high-quality transmission, reliability, and optimal data rates.
Detailed Explanation
This statement emphasizes the importance of recognizing and addressing the key performance-limiting factors. By tackling noise, distortion, and bandwidth issues, communication systems can achieve better quality, making them more reliable. For instance, high-quality transmission means that the information can be understood and utilized effectively, while optimal data rates ensure that a maximum amount of information can be communicated in a given timeframe.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a Wi-Fi network. If your router has strong signal quality (minimized noise and distortion) and ample bandwidth, you can stream videos smoothly and download files quickly. If any of these performance factors are poor, you may experience buffering or interruptions.
Key Concepts
-
Communication System Performance: Evaluated by the accuracy and efficiency of information transmission.
-
Noise: Unwanted interference that disrupts the clarity of signals.
-
Distortion: Alteration of signal forms during the communication process.
-
Bandwidth: The frequency range available for signal transmission, crucial for determining data rates.
-
Signal-to-Noise Ratio: A key metric that measures signal quality against noise.
Examples & Applications
In a telephone conversation, background noise can affect the clarity of the voice signal, demonstrating the impact of noise.
When streaming a video, a bandwidth constraint might result in buffering if the data rate exceeds the channel capacity.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Noise can interfere, distortion may steer, bandwidth keeps signals clear.
Stories
Imagine a phone call in a noisy crowd—voices blend in distortion. Finding a quiet place enhances clarity, much like managing noise and bandwidth in communication.
Memory Tools
Remember 'NDB' for performance factors: Noise, Distortion, Bandwidth.
Acronyms
NDB
Noise
Distortion
Bandwidth.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Communication System Performance
The ability of a communication system to accurately and efficiently transmit information.
- Noise
Unwanted electrical signals that interfere with the intended message.
- Distortion
Changes in the signal shape during transmission, affecting clarity.
- Bandwidth
The range of frequencies a communication channel can transmit.
- SignaltoNoise Ratio (SNR)
A measure of signal clarity compared to background noise.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
