Principles
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Functional Requirements
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll talk about functional requirements in building planning. Can anyone tell me why it’s important to arrange spaces effectively?

Isn't it to make sure the building serves its purpose well?

Exactly, Student_1! We ensure effective functionality by zoning areas into public, private, and service zones. Let's use the acronym 'ZPS' to remember: Zoning, Public, Service.

What does that mean? Can you give an example?

Sure! For instance, placing a living room near the dining area enhances social interaction. How about circulation? Why do you think clear movement paths are crucial?

So people can move freely without getting lost or bumping into things?

Correct! Logical circulation includes corridors for horizontal movement and stairs or lifts for vertical movement. Remember, efficient flow improves overall building usability.

How do room relationships fit into this?

Good question, Student_4! Having related rooms close together, like kitchens near dining areas, promotes convenience. In summary, functional requirements ensure our buildings not only look good but serve their intended purpose effectively.
Orientation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s dive into orientation. Who can tell me why orientation is important in building planning?

It helps with light and ventilation, right?

Exactly! Proper orientation can maximize sunlight in the winter and minimize it in the summer. Remember the sun path principle. Can anyone describe how we use wind direction in orientation?

We can place windows to align with the wind, making sure it's always breezy inside!

That's correct! This natural ventilation achieves comfort without relying heavily on AC. How about views? Why are they essential in orientation?

So we can enjoy nice looks instead of looking at a wall or something ugly?

Exactly, Student_3! Pleasing views improve our quality of life within the building.

To sum it up, we want to ensure buildings get sunlight, air, and good sights?

Yes, that's the essence of orientation! Takeaways: Optimize placement to ensure energy efficiency and comfort.
Sustainability and Green Building Principles
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about sustainability in building planning. Why do you think sustainability matters?

To protect the environment and help future generations?

Exactly! Sustainable practices include rainwater harvesting and using eco-friendly materials. Let’s remember the acronym 'SHED': Sustain, Harvest, Eco, Design. This helps us focus on what we can do.

What about solar orientation?

Great point! Solar orientation allows us to harness solar energy, reducing dependency on other energy sources. Can anyone suggest other green practices?

Maybe using less water and recycling it?

Yes! Greywater recycling is crucial for sustainability. Let's summarize: incorporating sustainable practices leads to greener buildings and a healthier environment for all.
Safety and Security
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s shift our focus to safety and security in building planning. Why is this a priority?

To keep people safe from accidents or intruders?

Exactly! Safety encompasses structural integrity against various loads and fire safety provisions. Can anyone name some safety features?

Fire exits and alarms could be important.

Right! Installing extinguishers and using fire-resistant materials are critical. What about security measures?

CCTV and nice locks?

Yes! Security is all about protecting its occupants. Remember: safety is not just about sound structures but also about practical features to ensure security.

So, to summarize, we need to consider both structural safety and active security measures?

Exactly! That ensures buildings are not just aesthetically pleasing but safe for their occupants.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The principles of building planning guide architects and engineers in creating structures that balance functional needs with safety, aesthetics, and legal regulations. Key principles include functional requirements, orientation, privacy, circulation, and sustainability, which foster efficiency and comfort in building designs.
Detailed
Principles of Building Planning
Building planning is an integral phase of architectural design and civil engineering, focusing on the optimal arrangement of structures to balance functional requirements, safety, aesthetics, economy, and adherence to legal regulations. Effective planning enhances both utility and comfort while contributing to a building's structural efficiency and sustainability.
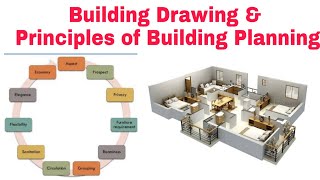
Key Principles of Building Planning
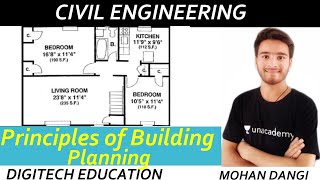
- Functional Requirements: Structures must effectively serve their intended purpose. Key aspects include zoning areas into public, private, and service zones and ensuring logical relationships between rooms.
- Orientation: This principle emphasizes positioning buildings to maximize natural light, ventilation, and energy efficiency, considering factors like sun paths and wind directions.
- Aspect and Prospect: Rooms should be strategically positioned for optimal sunlight and pleasant views while avoiding undesirable sights.
- Grouping: Similar functions should be clustered together to improve efficiency and comfort.
- Privacy: Adequate privacy is crucial, achieved through separate entrances and strategic placement of walls and landscaping.
- Circulation: Smooth and logical movement inside the building is essential, requiring effective horizontal and vertical circulation.
- Sanitation: This entails ensuring cleanliness and health standards, including proper placement of toilets and drainage systems.
- Lighting and Ventilation: Adequate natural light and ventilation enhance indoor comfort while reducing reliance on artificial systems.
- Flexibility and Future Expansion: Planning should account for future modifications in usage or size.
- Economy: Cost-efficient planning minimizes construction and maintenance costs without sacrificing quality.
- Aesthetics: Visual appeal is vital, achieved through symmetry, colors, and materials in harmony with the surroundings.
- Safety and Security: Building safety involves conforming to structural safety standards and implementing fire and security measures.
- Compliance with Building Bye-Laws: Adhering to local regulations, such as setback requirements and building heights, is essential.
- Climate Responsiveness: Adapting designs for local climate conditions optimizes thermal comfort and energy efficiency.
- Sustainability and Green Building Principles: Modern planning should incorporate environmental considerations and sustainable practices.
Youtube Videos






Key Concepts
-
Functional Requirements: Planning for effective utility and comfort.
-
Orientation: Positioning buildings for light, ventilation, and energy efficiency.
-
Grouping: Clustering similar functions for efficiency.
-
Privacy: Creating spaces that allow for personal boundaries.
-
Circulation: Facilitating smooth movement within the structure.
-
Sustainability: Incorporating environmental considerations in design.
Examples & Applications
Zoning a home into public (living room), private (bedrooms), and service (kitchen) areas.
Aligning windows with prevailing wind direction to enhance natural ventilation.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For buildings to thrive, group rooms alive, safety and comfort will surely arrive.
Stories
Imagine a house designed so well that the sunlight pours in during the day while keeping the heat out in summer. It's peaceful with clusters of rooms, just like a cozy family gathering.
Memory Tools
CIRCLE - Circulation, Interior, Room layout, Climate, Lighting, Economy: important planning elements.
Acronyms
SPECS - Safety, Privacy, Economy, Comfort, Sustainability
what every building should aim to integrate.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Functional Requirements
The essential needs a building must fulfill to serve its intended purpose effectively.
- Orientation
The positioning of a building in relation to the sun, wind, and surroundings to optimize energy efficiency and comfort.
- Aspect
The positioning of rooms concerning sunlight and wind to enhance the indoor environment.
- Privacy
The state of being free from intrusion and being able to maintain personal boundaries within a building.
- Circulation
The movement pathways within a building, encompassing horizontal and vertical movement provisions.
- Sanitation
The planning and implementation of hygiene and cleanliness standards in and around a building.
- Sustainability
Design practices aimed at minimizing the environmental impact of building construction and operation.
- Safety and Security
Measures taken to ensure the structural integrity of a building and the protection of its occupants.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
