Provisions
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Functional Requirements
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will start with Functional Requirements in building planning. Can anyone tell me what they think functional requirements mean?

Does it mean how well the building serves its purpose?

Exactly! Functional planning makes sure the building meets its intended usage effectively, like having kitchens near dining areas. What are some other examples of functional zoning?

Obviously, separating public and private zones, right, like putting living rooms and bedrooms in different areas?

Correct! We can remember this as the 'F-P-Z Model' – Functional, Public-Private zoning. It's a great way to keep spaces thoughtfully arranged. Anyone want to summarize why functional planning is important?

It enhances usability and comfort in a building.

Well done! So remember, effective functional planning enhances comfort and utility.
Orientation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s move to Orientation! Who can explain why orientation matters in building planning?

Isn’t it about positioning the building for light and wind?

Exactly! Orientation focuses on sunlight and ventilation. In regions like India, buildings face south to capture winter sunlight. Can anyone think of how this might impact energy efficiency?

Less need for artificial heating or cooling, right?

Correct! Remember the 'S-W-P Principle': South-facing for warmth, Wind alignment for cooling, and Pleasant views for aesthetics. How do you think we can apply this?

We can plan window placements and openings based on local climate!

Exactly! That’s a crucial takeaway.
Safety and Security
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about Safety and Security! Why is this essential in building planning?

To protect the occupants from accidents or hazards?

Exactly! Safety measures include structural integrity and fire exits. Can anyone name some safety considerations for buildings?

Fire safety features, like extinguishers and exits!

Yes! Also, security features like CCTV and fencing for protection. Let’s remember 'S-S-F': Safety, Security, and Fire precautions. Why is understanding these vital?

It ensures the wellbeing of everyone using the building!

Right! Safety and security are non-negotiable in building planning.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Effective building planning integrates various principles such as functionality, orientation, privacy, circulation, and safety. These principles ensure that structures are not only compliant with legal standards but also comfortable, efficient, and responsive to environmental context.
Detailed
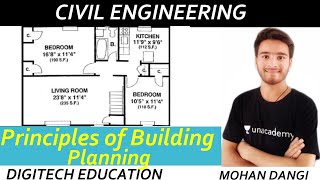
Provisions in Building Planning
Building planning is a foundational aspect of architectural design and civil engineering, requiring a precise balancing act between multiple factors:
- Functional Requirements: This principle focuses on the effective arrangement of spaces to meet specific functions (e.g., zoning, circulation, room relationships).
- Orientation: Proper orientation ensures optimal light, ventilation, and energy efficiency based on ecological considerations like the sun's path.
- Aspect and Prospect: Aspect refers to how the positioning of rooms maximizes sunlight and airflow, while prospect relates to the view from each room, emphasizing pleasing vistas.
- Grouping: Related functions are placed together (e.g., all bedrooms in one area), enhancing efficiency and comfort.
- Privacy: Adequate privacy is ensured through strategic layouts and partitions between public and private spaces.
- Circulation: Logical pathways for movement (horizontal and vertical) enhance usability.
- Sanitation: Adequate sanitation provisions promote health and hygiene, including strategic toilet placements and drainage systems.
- Lighting and Ventilation: Natural provisions are established to reduce dependence on artificial systems, thus improving comfort and sustainability.
- Flexibility and Future Expansion: Planning for adaptability allows for future changes in usage or expansion.
- Economy: Cost-effective methods and locally sourced materials aim to minimize construction and maintenance costs without compromising quality.
- Aesthetics: Aesthetically pleasing designs also hold cultural relevance, promoting visual harmony in the surrounding environment.
- Safety and Security: Robust construction and safety features address structural integrity that safeguards against environmental forces and ensures user safety.
- Compliance with Building Bye-Laws: Legal regulations set by local authorities guide and restrict building provisions, ensuring safety and neighborhood compatibility.
- Climate Responsiveness: Designs tailored to local climates improve thermal comfort and energy usage.
- Sustainability and Green Building Principles: Modern building planning embraces sustainable practices, reflecting the need for environmentally friendly designs.
Overall, these provisions help create buildings that are utility-oriented, compliant with legal frameworks, and environmentally conscious while enhancing user comfort and aesthetics.
Youtube Videos








Key Concepts
-
Functional Requirements: Arrangement of spaces for intended use.
-
Orientation: Positioning for optimal energy usage.
-
Privacy: Ensuring separate spaces for comfort.
-
Circulation: Smooth movement paths throughout the building.
-
Sanitation: Health and hygiene requirements.
Examples & Applications
An office layout that zones meeting rooms away from workspaces.
Using south-facing windows to maximize sunlight in winter.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In building designs, think of how light shines, with rooms aligned, comfort you'll find.
Stories
In a village, a wise architect named Asha always placed kitchens near dining rooms so families could eat together. She also ensured her houses had bright windows to greet the morning sun while cleverly designing spaces for privacy.
Memory Tools
P-Practical Layouts, U-Utilitarian Spaces, R-Realistic Safety, P-Pronounced Aesthetics - keep PURP in mind!
Acronyms
FOP- Functional, Orientation, Privacy – remember these key aspects for effective building planning.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Zoning
Dividing spaces into distinct areas, such as public, private, and service zones within a building.
- Aspect
The positioning of rooms concerning sunlight and wind for comfort.
- Circulation
The layout enabling movement through horizontal and vertical paths within a building.
- Sanitation
The planning of facilities to ensure health and hygiene standards are met.
- Compliance
Adhering to legal building regulations set forth by local authorities.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
