Challenges in Optimization and Automation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Complexity of Tools
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll discuss the complexity involved in optimization and automation tools in VLSI design. Can anyone share what they think makes these tools complex?

I think it's because there are so many features that you need to understand.

Exactly! Tools like Cadence Genus and Synopsys Design Compiler have many features that require a deep understanding of design principles. This complexity can be a major barrier to efficient use.

Are there any specific skills we need to learn to handle these tools?

Absolutely, a strong foundation in circuit design and familiarity with HDL is critical. To remember the complexity elements, think of the acronym TCO—Tools, Complexity, and Understanding!

Can you provide an example of how this complexity affects the design process?

Certainly! If a designer misinterprets a tool’s functionality, it could lead to erroneous design choices, ultimately delaying the project. So, mastering these tools is vital.

To summarize, the complexity of optimization and automation tools can create obstacles in VLSI design, necessitating thorough training and understanding.
Tool Integration Challenges
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s focus on tool integration. Why is it challenging to integrate different optimization and automation tools?

I think it’s because they might use different data formats, right?

Exactly! Different tools often utilize unique data formats, which can lead to compatibility issues. This can complicate the design flow.

What happens if the tools fail to integrate properly?

Poor integration can result in inconsistent data, increased error rates, and ultimately wasted time in the design process. To help remember this, think of the phrase FIT—Format incompatibility Troubles!

Are there best practices to mitigate these integration issues?

Certainly! Standardizing data formats and using common interfaces can help streamline the integration process.

In summary, integrating various tools can pose significant challenges, and awareness of compatibility and data formats is crucial for a successful design flow.
Optimization Trade-offs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s delve into optimization trade-offs. Can anyone explain what trade-offs are in the context of VLSI design?

I believe trade-offs are where you gain an advantage in one area while sacrificing another.

Correct! For example, optimizing for power efficiency can lead to an increase in chip area. This is a critical aspect designers need to navigate.

Are there strategies we can use to manage these trade-offs?

Yes! Simulation tools can help identify the best compromises for power, area, and performance. To remember this, think of the acronym OPT—Optimization Prioritization and Trade-offs!

Can you give us an example of a design choice that demonstrates this?

Certainly! If a designer prioritizes performance, it may require higher power consumption, which might not be ideal for battery-operated devices. Remember that balancing these factors is vital.

To conclude, understanding the trade-offs involved in optimization is essential for making informed design decisions.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, the challenges of utilizing optimization and automation tools in VLSI design are discussed. These include the complexity of the tools themselves, issues with integrating different tools within the design flow, and the trade-offs involved in optimization processes.
Detailed
Challenges in Optimization and Automation
In VLSI design, while optimization and automation tools significantly enhance design efficiency and productivity, they also present several notable challenges:
- Complexity:
- The optimization and automation tools are often intricate and require users to have a profound understanding of both the design processes and the capabilities of the tools.
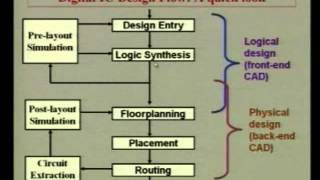
- Tool Integration:
- Integrating various optimization and automation tools into a coherent design flow can pose difficulties due to compatibility issues and discrepancies in data formats. This can lead to inefficiencies and potential errors.
- Optimization Trade-offs:
- The process of optimization frequently involves making trade-offs, meaning that improving one aspect of the design, such as power efficiency, may adversely affect another aspect, such as the area or speed of the integrated circuit. Hence, designers must carefully consider the implications of their choices.
Understanding these challenges is essential for engineers to navigate the complexities of VLSI design effectively.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Complexity of Tools
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Complexity: The tools used for optimization and automation can be complex and require a deep understanding of both the design and tool-specific features.
Detailed Explanation
The tools employed for optimization and automation in VLSI design are often intricate and multifaceted. Designers need to grasp not only the general principles of electronic design but also how to effectively use these specialized software tools. This means learning to navigate their features, understanding their algorithms, and knowing how to set optimal parameters for specific design objectives.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like using a sophisticated software program to edit videos. Just having the software isn’t enough; you need to know how to use its various features, such as cutting, merging, and adding effects. Similarly, in VLSI design, simply having the tools isn’t enough; you must also understand how they work and how to apply them effectively to achieve your design goals.
Tool Integration Challenges
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Tool Integration: The integration of different tools in the design flow can be difficult due to compatibility issues and differences in data formats.
Detailed Explanation
In VLSI design, various tools are often used in a sequence to aid different stages of the design flow. However, integrating these tools can pose challenges. Compatibility issues arise when different software programs cannot communicate effectively, which might lead to difficulties in sharing data. Moreover, if the tools use different data formats, it can become cumbersome to transfer information from one tool to another without losing critical details.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to put together a complex puzzle where every piece has a different shape or size. You may have all the pieces, but if they don’t fit together properly, you can’t complete the picture. In the same way, if VLSI design tools don’t work together seamlessly, it’s challenging to create a successful design.
Trade-offs in Optimization
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Optimization Trade-offs: Optimization often involves trade-offs. For instance, optimizing for low power may result in higher area, or optimizing for speed may increase power consumption.
Detailed Explanation
Optimization is about finding the best possible balance between conflicting objectives. In VLSI design, each optimization goal can sometimes hinder others. For example, making a circuit consume less power might require a larger area on the chip, while increasing the speed of a circuit could lead to higher power usage. Designers must understand these trade-offs and decide which factors are the highest priority based on the specific application.
Examples & Analogies
Consider preparing a meal. If you want to make a dish that’s extremely healthy, it might take longer to prepare, while a quick meal might not be as nutritious. Similarly, when designing VLSI circuits, you have to choose between efficiency, speed, and power consumption—each choice affects the other.
Key Concepts
-
Complexity: The intricate nature of optimization and automation tools requiring deep understanding.
-
Tool Integration: Challenges arising from the need to combine various tools and manage compatibility.
-
Optimization Trade-offs: The necessity of making compromises to improve certain aspects of a design at the expense of others.
Examples & Applications
When power consumption is optimized in a design, the area of the circuit may increase to accommodate additional components.
In optimizing speed, a designer might increase the clock frequency, which can lead to greater power consumption.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Complex systems can cause great strife, choosing the right tools is vital for design life.
Stories
Once upon a time, a designer had to balance power, speed, and area, learning that optimizing one could adversely affect the others.
Memory Tools
To remember challenges: C.I.T—Complexity, Integration, Trade-offs.
Acronyms
CIT for Challenges in Integration and Trade-offs.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Optimization
The process of making trade-offs to improve a circuit design in terms of factors like power, area, speed, and manufacturability.
- Automation
The use of tools and algorithms to perform tasks without human intervention, simplifying the design process.
- Tool Integration
The process of combining different design tools to work together in a cohesive manner.
- Tradeoffs
The concept of compromising one aspect of a design to improve another, such as power vs. speed.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
