DISORDERS OF MUSCULAR AND SKELETAL SYSTEM
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Myasthenia Gravis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll explore Myasthenia Gravis, which is an autoimmune disorder. Can anyone tell me what they think an autoimmune disorder means?

I think it means the body attacks its own cells?

Exactly! In the case of Myasthenia Gravis, the immune system mistakenly attacks the neuromuscular junctions, leading to muscle weakness and fatigue. Remember the acronym 'MG' – Myasthenia Gravis affects Muscle Groups. What are some symptoms, do you think?

I imagine fatigue and maybe weakness?

Right! Patients often experience increased muscle fatigue during activity, which is significant for understanding the impact of this disorder.
Muscular Dystrophy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's move on to muscular dystrophy. This is a genetic disorder that leads to the progressive degeneration of skeletal muscles. Student_3, what do you think happens over time with this condition?

I think the muscles get weaker and can’t function properly, right?

Correct! And this weakening generally starts in childhood. What do you think are the challenges for someone with muscular dystrophy?

They might have difficulties walking or doing everyday tasks?

Absolutely, such difficulties can severely impact their quality of life. Remember the phrase 'Mutating Muscles', as a way to recall muscular dystrophy.
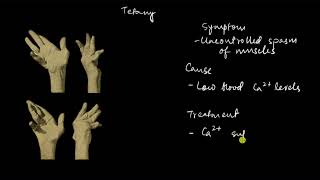
Tetany
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's discuss tetany. It's characterized by rapid muscle spasms caused by low calcium levels. What do you imagine can trigger these low calcium levels, Student_1?

Maybe a diet lacking calcium?

Yes! A deficiency can lead to this condition. It's essential to maintain a balanced diet containing adequate calcium. Also, the mnemonic 'TETANY - Tension due to Calcium Deficit' can help you remember this connection.

What are the symptoms of tetany?

Great question! Symptoms include muscle cramps and twitching. It’s essential to recognize them for prevention.
Arthritis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Arthritis is our next topic. It's the inflammation of joints. What kind of impact do you think this has on mobility?

It must make it hard to move, especially if the joints are swollen or painful.

Exactly! It can cause significant pain and stiffness. The term 'ART - Affected Range of motion in Joints' can help you remember the effects of arthritis.

Are there different types of arthritis?

Yes, there are several, with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis being the most common. Each has specific causes and treatments.
Osteoporosis and Gout
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's talk about osteoporosis and gout. Osteoporosis leads to decreased bone density, increasing fracture risk, while gout is caused by uric acid crystal accumulation. Can anyone connect these two conditions to lifestyle?

I think diet plays a big role, especially with gout due to rich foods increasing uric acid?

Great observation! A poor diet contributes to both conditions. You can remember 'Osteoporosis is Bone Weakness, and Gout is 'Go Out' pain because of flare-ups. This can help you recall their impacts.

What age group is mostly affected by osteoporosis?

Typically older adults, especially post-menopausal women due to decreased estrogen levels. Understanding these trends is crucial for prevention.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section discusses several significant disorders of the muscular and skeletal systems, such as myasthenia gravis, muscular dystrophy, tetany, arthritis, osteoporosis, and gout. Each condition is briefly defined, along with its implications for muscle and joint health.
Detailed
Disorders of Muscular and Skeletal System
The muscular and skeletal systems can be affected by various disorders, influencing how the body moves and functions. Understanding these disorders is crucial for diagnosis and treatment. This section covers:
- Myasthenia Gravis: An autoimmune disorder that targets the neuromuscular junction, leading to muscle fatigue and weakness, especially in skeletal muscles. This condition can cause paralysis if untreated.
- Muscular Dystrophy: A group of genetic disorders characterized by progressive degeneration of skeletal muscles, resulting in muscle weakness and loss of function. This disorder typically emerges in childhood or adolescence and severely impacts mobility.
- Tetany: A condition marked by rapid muscle spasms caused by low levels of calcium in the body. Symptoms may include muscle cramps, twitching, and involuntary contractions.
- Arthritis: Inflammation of one or more joints, which can lead to pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced range of motion. It can take many forms, with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis being the most common.
- Osteoporosis: A common age-related disorder characterized by decreased bone density, which increases the risk of fractures. It often results from hormonal changes, especially a drop in estrogen levels in women after menopause.
- Gout: A form of arthritis involving sudden, severe attacks of pain, redness, and tenderness in joints due to the accumulation of uric acid crystals. It can cause swelling and is commonly observed in the big toe.
These disorders exemplify the intricate relationship between muscle and joint health and emphasize the need for awareness and management of these conditions.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Myasthenia Gravis
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Myasthenia gravis: Auto immune disorder affecting neuromuscular junction leading to fatigue, weakening and paralysis of skeletal muscle.
Detailed Explanation
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder, which means that the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. In this case, it targets the neuromuscular junction—the point where nerve cells communicate with muscles. This results in symptoms like fatigue, muscular weakness, and paralysis of the skeletal muscles, which are essential for movement. The muscles affected often become weaker with activity and improve with rest.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to lift a heavy box. At first, you might be able to lift it easily, but as you keep lifting, your muscles get tired, and you find it harder and harder to lift the box. In a person with myasthenia gravis, this fatigue happens quickly, and even simple actions may become exhausting.
Muscular Dystrophy
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Muscular dystrophy: Progressive degeneration of skeletal muscle mostly due to genetic disorder.
Detailed Explanation
Muscular dystrophy refers to a group of genetic disorders that lead to progressive degeneration and weakness of the skeletal muscles. These muscles are used for movement, and over time, they weaken and deteriorate, making it difficult for individuals to perform everyday activities. The severity and specific symptoms can vary greatly depending on the type of muscular dystrophy.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a bridge that is gradually eroded by water. At first, it can still support weight, but as time passes and the erosion continues, it weakens until it can’t hold up anything anymore. Similarly, in muscular dystrophy, muscles lose strength and function over time due to genetic factors.
Tetany
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Tetany: Rapid spasms (wild contractions) in muscle due to low Ca++ in body fluid.
Detailed Explanation
Tetany is characterized by rapid muscle spasms or wild contractions, which can be a sudden and severe response of the muscles. This condition is commonly caused by low levels of calcium ions (Ca++) in the bloodstream. Calcium plays a critical role in muscle contraction and nerve signaling. When its levels drop, muscles can become overly excitable, leading to spasms.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a rubber band that is pulled too tightly. If you keep stretching it, it can snap back suddenly. In tetany, the muscles are reacting excessively, like that stretched rubber band, but rather than snapping, they contract rapidly, causing discomfort and sometimes pain.
Arthritis
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Arthritis: Inflammation of joints.
Detailed Explanation
Arthritis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the joints, which can lead to pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion. There are many types of arthritis, with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis being the most common. Inflammation can damage cartilage, the tissue that cushions joints, leading to further mobility issues.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a door hinge that hasn’t been lubricated in a long time. It becomes stiff, makes squeaking noises, and doesn’t open smoothly. Similarly, in arthritis, the inflammation in the joints causes pain and hinders fluid movement.
Osteoporosis
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Osteoporosis: Age-related disorder characterised by decreased bone mass and increased chances of fractures. Decreased levels of estrogen is a common cause.
Detailed Explanation
Osteoporosis is a condition that leads to fragile and less dense bones, making them more susceptible to fractures. As people age, particularly post-menopausal women, the production of estrogen decreases, which is crucial in maintaining bone density. This loss of estrogen can accelerate bone loss, leading to osteoporosis.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a sponge that has started to dry out and become brittle. The more it dries, the more holes appear, making it less effective at holding water. In a similar way, bones in osteoporosis become porous and brittle, increasing the risk of breaks and fractures.
Gout
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Gout: Inflammation of joints due to accumulation of uric acid crystals.
Detailed Explanation
Gout is a form of arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, which leads to painful inflammation. Uric acid is produced from the breakdown of purines, substances found in certain foods and drinks. When levels are too high, crystals can form, particularly in the joint of the big toe, causing intense pain and swelling.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a person trying to walk on a bed of sharp, tiny pebbles. Each step would cause intense discomfort and pain, similar to the experience of someone having a gout flare-up, where even the slightest touch can lead to severe pain in the affected joint.
Key Concepts
-
Myasthenia Gravis: An autoimmune disorder causing muscle weakness.
-
Muscular Dystrophy: Genetic disorders leading to muscle degeneration.
-
Tetany: Muscle spasms from low calcium levels.
-
Arthritis: Joint inflammation causing pain.
-
Osteoporosis: Age-related bone density loss.
-
Gout: Joint inflammation from uric acid accumulation.
Examples & Applications
Myasthenia gravis often leads to difficulty in activities such as climbing stairs or lifting objects due to muscle weakness.
Muscular dystrophy may manifest in children as delayed milestones in walking or running.
Tetany can be triggered by dietary deficiencies, leading to symptoms like a tingling sensation in extremities.
Arthritis patients may experience joint stiffness, especially in the morning, affecting their daily activities.
Osteoporosis manifests as increased fracture risks, even from minor falls.
Gout commonly affects the big toe, leading to sudden, intense pain.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When muscles weaken, don’t be grave, check for myasthenia, be strong and brave.
Stories
Imagine a boy named Dystro who loves to run but finds it hard because his muscles slowly won’t respond. His struggle shows muscular dystrophy's tale.
Memory Tools
Remember 'TEN: Tension Equals Need for calcium!' to recall causes of Tetany.
Acronyms
Use 'GOUT' for 'Glistening Uric acid Overload Triggers' to remember gout's cause.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Myasthenia Gravis
An autoimmune disorder that causes muscle weakness and fatigue due to attack on neuromuscular junctions.
- Muscular Dystrophy
A group of genetic disorders leading to progressive muscle degeneration.
- Tetany
A condition characterized by muscle spasms caused by low calcium levels.
- Arthritis
Inflammation of joints causing pain and stiffness.
- Osteoporosis
A condition characterized by decreased bone density and increased fracture risk.
- Gout
Inflammation of joints due to the accumulation of uric acid crystals.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
