Glacial Valleys/Troughs
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Characteristics of Glacial Valleys
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will be discussing glacial valleys. Can anyone tell me what makes a glacial valley different from a river valley?

Is it because river valleys are V-shaped while glacial valleys are U-shaped?

Exactly! Glacial valleys have a distinct U-shaped profile due to the eroding power of glaciers. Can anyone explain how glaciers create these shapes?

Glaciers move down mountains and scrape the land, right?

That's correct! This erosion is key to forming the characteristic shape of these valleys. Let’s summarize: Glacial valleys are U-shaped due to glacier movement.
Formation Processes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Glacial valleys are formed primarily during the advance of glaciers. What do you think happens to the landscape during this movement?

The landscape gets scraped away, and debris is left behind!

Correct! As glaciers advance, they carry debris and reshape the environment. This leads to features like moraines. Can anyone remind us what moraines are?

They are the piles of debris pushed along by glaciers, right?

Yes, great job! So, glacial valleys not only change shape but also contribute to the landscape through these deposits. Let’s recap: Glacial valleys are formed mainly through the scraping of glaciers.
Hanging Valleys and Fjords
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about hanging valleys. Why do you think hanging valleys might exist?

I think they are formed by tributary glaciers that are smaller than the main glacier?

Exactly! These smaller valleys often lead to waterfalls. What about fjords? How are they different?

Are fjords deeper and filled with sea water?

Correct! Fjords are indeed deep, U-shaped valleys that have been submerged by seawater. They often symbolize significant geological history. To summarize: Fjords are created by the flooding of glacial troughs.
Significance of Glacial Valleys
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Understanding glacial valleys is crucial for studying past climates. Can anyone tell me how studying these valleys assists geologists?

They help reveal the extent of ancient glaciers and climate changes!

Absolutely! Glacial valleys provide insights into geological history and climate shifts. What else can you think might be affected by these valleys?

Maybe ecosystems or land use in those areas?

That's right! Glacial valleys shape not just the landscape but also the ecosystems and human activities. Let's remind ourselves: Glacial valleys are indicators of Earth's past conditions.
Review and Personal Reflections
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let’s reflect on what we've learned about glacial valleys. Why do you think they are important in geography?

They show how glaciers impact the landscape and give clues about climate change!

Excellent point! Can anyone summarize the differences between glacial and river valleys once more?

Glacial valleys are U-shaped and broader, while river valleys are V-shaped and narrower.

Exactly! Glacial valleys help us understand our planet's history and future. Well done everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Glacial valleys are formed through the movement of glaciers, resulting in U-shaped troughs with broad floors and steep sides. These valleys may contain debris and lakes, and can feature hanging valleys and fjords. Understanding their formation helps in comprehending the geological history of an area.
Detailed
Glacial Valleys/Troughs
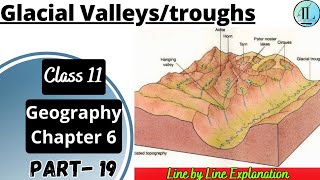
Glacial valleys, also known as troughs, result from the erosional power of glaciers as they move over the land. Unlike river valleys, which typically form through the action of water, glacial valleys are characterized by their U-shape, broad floors, and steep sides. The glaciers erode and carve out these valleys, picking up debris and shaping the landscape.
Characteristics of Glacial Valleys
- Formation: Glacial valleys form during the advance of glaciers, which scrape and scour the land. As glaciers move, they create distinct valleys by eroding the earth beneath them.
- Shape: Glacial valleys are U-shaped, contrasting with V-shaped river valleys due to the different processes of erosion involved.
- Debris: As glaciers melt, they leave behind a variety of debris, often forming moraines or being mixed within the valley.
- Associated Features: Hanging valleys may be found at higher elevations, often resulting in waterfalls when they feed into the main valley. Fjords are deep glacial troughs filled with seawater, typically found in coastal areas with a history of glacial activity.
Significance
Understanding glacial valleys is essential for studying glacial processes, interpreting past climate conditions, and assessing geological history. These features not only reveal information about past glacial movement but also influence present-day ecosystems and human activities.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Characteristics of Glacial Valleys
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Glaciated valleys are trough-like and U-shaped with broad floors and relatively smooth, and steep sides. The valleys may contain littered debris or debris shaped as moraines with swampy appearance. There may be lakes gouged out of rocky floor or formed by debris within the valleys. There can be hanging valleys at an elevation on one or both sides of the main glacial valley. The faces of divides or spurs of such hanging valleys opening into main glacial valleys are quite often truncated to give them an appearance like triangular facets. Very deep glacial troughs filled with sea water and making up shorelines (in high latitudes) are called fjords.
Detailed Explanation
Glacial valleys are formed by the movement of glaciers, resulting in a distinct U-shape. Unlike river valleys, which tend to be V-shaped, glacial valleys are broader and have steeper sides. This unique shape arises from the glacier's grinding action as it flows downhill, carving out the valley floor and creating dramatic landscapes. The debris left behind, called moraines, contributes to a swampy appearance in some areas. Additionally, lakes can form in these valleys, either from glacier melt or from sediments obstructing water flow. Hanging valleys, which are elevated relative to the main valley, often open into these glacial valleys, characterized by their sharp-edged divides. Fjords, another type of glacial valley, are submerged valleys created when sea water fills in the deep troughs, common in areas with extreme glacial activity.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a giant ice cube moving down a slope, melting a path as it goes. Just like the ice cube carves out a groove in a sandy beach, glaciers carve out deep valleys in mountains. The U-shaped valleys left behind are like the prints left by that ice cube, indicating how the glacier once moved and shaped the landscape. Fjords, on the other hand, are like giant, deep bathtubs formed where the glacier retreated and allowed the sea to flow in.
Differences between Glacial and River Valleys
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
What are the basic differences between glacial valleys and river valleys?
Detailed Explanation
Glacial valleys differ from river valleys in several key aspects: shape, formation process, and surrounding geography. Glacial valleys are typically U-shaped, formed by the massive weight and movement of glaciers. The ice grinds away rock and soil, creating a broad and flat base with steep sides. In contrast, river valleys are usually V-shaped, created by the erosional power of flowing water, which carves narrow channels through rock and sediment over time. Additionally, glacial valleys often feature larger amounts of debris and moraines deposited by the melting ice, while river valleys may contain sedimentary layers from river erosion and deposition. The conditions surrounding these valleys also vary; glacial valleys tend to be found in colder climates where glacial activity can occur, while river valleys can be found in any type of climate where rivers flow.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a baker using a rolling pin (the glacier) to flatten out dough (the landscape). The rolling pin creates a broad, flat surface with steep sides—akin to a glacial valley (U-shape). Now picture a chef cutting a V-shape into the dough with a knife (the river), creating a deep, narrow groove. This represents a river valley, shaped differently from the glacial valley because of the tool used. Just as the rolling pin leaves behind crumbs and dough residue (moraines) while flattening, glaciers leave behind rock debris that can form unique landscapes as well.
Key Concepts
-
Glacial valleys are U-shaped.
-
Glacial valleys differ significantly from river valleys.
-
Moraines are important landscape features associated with glaciers.
-
Hanging valleys often create waterfalls.
-
Fjords are flooded glacial valleys that offer insight into past climate.
Examples & Applications
The Yosemite Valley in California is a well-known example of a glacial valley.
The Norwegian fjords are famous examples of submerged glacial valleys.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Glacial valleys, U-shaped so wide, scraped by ice as it slides.
Stories
Once upon a time, a giant glacier roamed the mountains, carving deep U-shaped valleys and leaving behind its rocky treasures, called moraines, for future explorers to find.
Memory Tools
For fjords and hanging valleys, remember 'Deep Hangs Carefully' to recall their unique characteristics.
Acronyms
Use ‘M.U.F.’ to remember key glacial valley features
Moraines
U-shaped valleys
Fjords.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Glacial Valley
A trough-like, U-shaped valley formed by the erosion of a glacier.
- Moraines
Accumulations of debris transported and deposited by glaciers.
- Hanging Valley
A valley cut across by a deeper valley or glacial trough, typically leading to waterfalls.
- Fjord
A deep, narrow, U-shaped valley that has been flooded by seawater.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
