Debates within Christianity
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Humanism and Christianity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we explore the influence of humanism on Christianity during the Renaissance. Can anyone tell me what humanism is?

Isn't humanism about focusing on human potential and achievements?

Exactly! Humanism emphasized human potential and encouraged the study of classical texts. But how do you think this might have influenced religion?

It probably made people question the Church's authority and practices, right?

Yes! Many scholars called for a return to the original teachings of Christianity, criticizing the Church for added rituals. This laid the groundwork for the debates we will discuss.

So, figures like Erasmus and Luther were part of this debate?

Correct! Erasmus highlighted Church corruption, and Luther argued that salvation comes from faith alone. Let’s remember 'Erasmus critiques corruption and Luther champions faith' as a mnemonic.

What did Luther specifically challenge in the Church?

Great question! Luther criticized indulgences, claiming people could not buy salvation. This was a fundamental shift towards personal faith.

To summarize: Humanism sparked critical debates about Christianity, inspiring figures like Erasmus and Luther to challenge Church practices.
The Protestant Reformation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's delve into the Protestant Reformation. What initiated this movement?

Luther’s Ninety-Five Theses in 1517, right?

Exactly! And what key message did Luther convey in these theses?

That faith, not works or indulgences, is what saves you?

Yes! This radical idea fueled a new understanding of Christian faith. How did this affect Church authority?

It weakened it, especially as people started to read the Bible in their own languages.

Correct! With translations like William Tyndale’s English Bible, personal interpretation became essential. Let’s remember 'Translate for Truth' to highlight this change.

Did this lead to any social movements?

Absolutely! The Anabaptist movement pushed for equality. They believed all are equal before God. Remember 'All are Equal' for this concept.

In summary, the Protestant Reformation fundamentally altered Christianity, emphasizing faith and personal interpretation, challenging established Church authority.
Consequences of Reformation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s now discuss the consequences of the Reformation. What societal changes did it trigger?

There were conflicts between Catholics and Protestants.

Correct! These conflicts often turned violent. Can anyone think of a specific event?

The Peasants' War in Germany was one example.

Great recall! That war exemplifies how reform ideas stirred unrest. How did this affect rulers?

Some rulers supported Protestantism to gain power.

Exactly! They wanted to diminish the Pope’s influence. It leads us to another mnemonic: 'Power and Protestantism Go Together.'

Was there any pushback from the Catholic Church?

Yes! The Church began reforms, emphasizing service and the Jesuits' establishment aimed to combat Protestantism. Remember 'Jesuits for Justice' to connect this.

To summarize, the Reformation sparked societal conflicts and political changes, testing the very fabric of Christian society across Europe.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
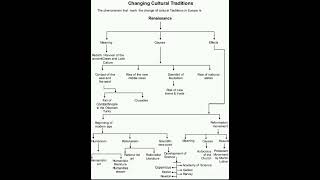
This section outlines how the Renaissance humanist movement influenced religious thought in Europe, leading to significant critiques of the Catholic Church by scholars such as Martin Luther and Erasmus. The emergence of the Protestant Reformation challenged established church practices and beliefs, ultimately leading to religious fragmentation.
Detailed
Debates within Christianity
The section examines the significant cultural and religious transformations during the Renaissance, particularly the influence of humanism on Christianity. Scholars in northern Europe, inspired by humanism, encouraged a return to the foundational texts of Christianity and rejected the additional rituals imposed by the Catholic Church. Figures like Thomas More and Erasmus criticized corruption and greed within the Church, while theologians promoted the idea of individuals having a direct relationship with God without intermediaries.
Martin Luther’s 1517 campaign against the Catholic Church marked the start of the Protestant Reformation, advocating for salvation through faith alone and challenging the authority of the Pope. This movement led to the establishment of various Protestant denominations, most notably in Germany and Switzerland, where figures like Ulrich Zwingli and Jean Calvin also made significant impacts. The rise of radical reformers like the Anabaptists further exemplified the demand for social equality within Protestant ideology.
The section concludes with the acknowledgment that these reforms not only reshaped Christianity but also influenced other aspects of society, creating enduring debates over the role of the Church in governance and daily life.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Cultural Exchange and Humanism
Chapter 1 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Trade and travel, military conquest and diplomatic contacts linked Italian towns and courts with the world beyond.
Detailed Explanation
During the time when new ideas were emerging in Europe, trade and travel were crucial factors. Italian towns were at the center of this cultural exchange, allowing not just goods but also ideas and philosophies to flow. This period saw a melding of cultures, where the wealthy and educated admired and often imitated the emerging humanist ideals originating from Italy. However, these new thoughts did not reach the common people who were largely illiterate.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a modern-day city like New York City, which attracts people from all over the world who bring their customs, foods, and languages. Just as the citizens of New York might adopt and adapt these influences into their lives, the educated citizens of Italian towns were adopting new ideas of humanism, even if elements of this did not affect the majority of the population.
Rise of Christian Humanism
Chapter 2 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In the fifteenth and early sixteenth centuries, many scholars in universities in north Europe were attracted to humanist ideas.
Detailed Explanation
In Northern Europe, universities began embracing humanism, emphasizing the importance of classical texts from ancient Greece and Rome, alongside Christian texts. Unlike in Italy, where humanism was led by professional scholars, in the North it attracted many clergy, who sought to reform the Church. They encouraged a return to the original teachings of Christianity and aimed to discard rituals seen as unnecessary embellishments.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how, today, some modern churches might look back to the Bible or early traditions to interpret faith and practice in a more original sense. This is similar to how Northern European humanists looked back to foundational texts and teachings to rediscover and instill a purer form of Christianity.
Criticism of the Church
Chapter 3 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Christian humanists like Thomas More and Erasmus felt that the Church had become an institution marked by greed.
Detailed Explanation
Prominent figures such as Thomas More in England and Erasmus in Holland expressed their concerns regarding the Church’s greedy practices, notably the selling of indulgences. They believed that those financial practices manipulated the faith of ordinary Christians and obscured the true teachings of Christianity. Their criticisms signaled a growing discontentment with institutional practices, ultimately leading to larger reform movements, such as the Protestant Reformation.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a modern nonprofit charity that claims to help the needy but instead is found to use donations for extravagant salaries for executives. Just as donors might feel betrayed, faithful individuals in the 16th century felt similarly when they realized that their contributions were being exploited rather than serving the spiritual needs of the community.
Martin Luther and the Protestant Reformation
Chapter 4 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In 1517, a young German monk called Martin Luther launched a campaign against the Catholic Church.
Detailed Explanation
Martin Luther’s criticism culminated in his posting of the Ninety-Five Theses, which challenged the Church's practices, particularly around indulgences. He argued that salvation came through faith alone, not through Church rituals or intermediaries. This pivotal moment led to what would be known as the Protestant Reformation, where various denominations broke away from the Catholic Church, seeking a more personal and direct relationship with God.
Examples & Analogies
This is akin to a whistleblower exposing wrongdoing within a corporation. Just as whistleblowers bring attention to unethical practices, Luther's bold actions illuminated the flaws within the Church and sparked a widespread movement for change.
Popular Revolts and the Role of Peasants
Chapter 5 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In almost every part of Europe, peasants began to rebel against the taxes imposed by the Church.
Detailed Explanation
As dissatisfaction grew among the common people due to heavy taxation from the Church, they began to revolt. These uprisings were fueled by both economic grievances and the radical ideas bred from humanist thought that equality before God implied equality on Earth. The idea that all people are created equal resonated with peasants, leading to further unrest against both the Church and the feudal system.
Examples & Analogies
You might think of the protests against high student tuition fees in some countries today. Just as students demand fair treatment and an overhaul of a flawed system that excludes many from education due to costs, peasants sought a fairer system that respected their contributions and treated them as equals.
Luther's Influence and the Spread of New Ideas
Chapter 6 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Luther did not support radicalism. He called upon German rulers to suppress the peasants’ rebellion.
Detailed Explanation
While Luther provided critical contributions to the Reformation, he was not in favor of radical changes regarding social structures. Instead, he urged rulers to quash the rebellions of the peasants, fearing that such upheaval might undermine his religious reforms and lead to chaos. This dichotomy underscored the complexity of the Reformation, which involved social change but was often tempered by established authority.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a community organizer who advocates for systemic change but also warns participants against violent protests, believing that peaceful means are more effective. Like this organizer, Luther sought reform but wanted to ensure stability over radical social upheaval.
Catholic Church Reforms and the Response to Protestantism
Chapter 7 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Catholic Church itself did not escape the impact of these ideas, and began to reform itself from within.
Detailed Explanation
In response to the criticisms and loss of followers to Protestantism, the Catholic Church initiated its own reformative actions, emphasizing simplicity and service. Figures like Ignatius Loyola founded the Society of Jesus, focusing on education, missionary work, and social outreach, effectively countering some Protestant claims and trying to regain followers.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a company that, facing public backlash over poor working conditions, implements new policies to improve employee welfare and transparency. Similarly, the Catholic Church sought to address its shortcomings by reforming its practices in the wake of the Reformation.
Key Concepts
-
Humanism: An intellectual movement emphasizing human potential.
-
Protestant Reformation: A movement challenging Catholic Church practices leading to new Christian denominations.
-
Indulgences: Church practices of selling forgiveness for sins are critiqued by reformers.
-
Anabaptism: Movement promoting social equality and adult baptism.
-
Catholic Reformation: Internal Church reforms in response to Protestantism.
Examples & Applications
Martin Luther's Ninety-Five Theses challenged the sale of indulgences, leading to the Protestant Reformation.
Thomas More's work, 'Utopia,' criticized societal issues influenced by humanist thought.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In days of yore, they sought the core, of faith and truth, not just folklore.
Stories
Once, a monk named Luther saw the Church was misled by greed, he nailed his Theses to a door, sparking a faith rebirth.
Memory Tools
Remember 'Luther's Faith' for thinking God leads to salvation, not just wealth.
Acronyms
PRAISE - for Protestant Reformation, Advocated by Individuals Sincerely Engaging.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Humanism
A cultural and intellectual movement emphasizing human potential and classical texts.
- Indulgences
Payments made to the Church for the forgiveness of sins.
- Protestant Reformation
A religious movement in the 16th century that led to the establishment of Protestant churches.
- Anabaptists
Radical reformers advocating for adult baptism and social equality.
- Jesuits
Members of the Society of Jesus, founded to promote education and combat Protestantism.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
