The Significance of Urbanism
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Urban Economies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into urban economies, which are vital to understanding the significance of urbanism. Can anyone explain how an urban economy differs from an agricultural one?

Urban economies include trade and crafts, right? They aren't just about farming?

Exactly! Urban economies are characterized by a range of activities beyond food production. Acronym 'DREAM' can help us remember: Diversification of activities, Resources from trade, Economy built on interaction, Agriculture as a component, and Manufacture of goods. Can someone explain how division of labor fits into this picture?

With division of labor, people specialize in different tasks, like one making tools and another trading them.

Great point! This specialization requires coordination and trade amongst various sectors. It’s a complex web! Let's sum up: Urban economies rely on multiple activities and division of labor.
The Role of Writing in Urban Life
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Writing emerged as a crucial aspect of urban life. Why do you think early writing was so significant for trade?

It helped keep track of goods and transactions, so businesses could manage better!

Exactly! Writing allowed for documentation and record-keeping. Think of the phrase 'Track and Trust'—writing tracks transactions and builds trust in trade relationships. Can anyone share how this led to more complex societies?

With writing, leaders could manage larger communities and resources more efficiently!

Spot on! Writing enabled organized governance, crucial for urban centers. Today, we learned that writing isn't just about communication; it’s a tool for societal growth.
Trade Networks and Urbanization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about trade networks. What role did they play in urbanization?

They connected urban areas with resources they didn’t have, helping cities grow!

Exactly! Think of trade as the lifeblood of a city’s economy, enabling them to thrive by eating beyond local production. Can someone identify examples of resources traded?

Copper and tin for bronze tools, and textiles for wood!

Well done! With these trades, cities became centers of wealth and culture, fostering innovation. Key takeaway: trade not only supplies resources but also shapes urban identity.
Social Structures in Urban Areas
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Urbanism also influenced social structures. How do you think urban life changed social hierarchies?

There were probably more distinct social classes, like rulers, traders, and workers.

Exactly! The emergence of new classes created complexities within societies. Remember the acronym 'CROWN'—Classes, Roles, Organization, Wealth Distribution, and Nobility. Could someone discuss why this was significant?

Different roles meant more organized government and society, plus each class had different responsibilities!

Right again! This organization allowed cities to function more effectively, solidifying their status.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The emergence of cities and urban economies transformed human societies. Urbanism is not merely defined by population density, but by the diversification of economies beyond food production, including trade, crafts, and governance. This led to complex social structures and necessitated organizational systems, which were supported by early writing methods.
Detailed
In this section, the significance of urbanism is explored through the lens of early societies, particularly in Mesopotamia. Urban centers grew as economies transitioned from purely agricultural to diversified forms of trade, craft manufacturing, and services. The division of labor became essential, as individuals specialized in specific trades, necessitating interaction among different sectors of society. Trade routes were developed to import resources that were scarce in urban areas, prompting the establishment of organized trade networks and the need for written records to manage regulations and transactions. This interconnectedness fostered the emergence of complex social hierarchies and governance structures. The ability to write down transactions and histories correlates with the cultural and intellectual evolution of urban societies, as literacy spread and became essential for administration and societal functions.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Urbanism
Chapter 1 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Cities and towns are not just places with large populations. It is when an economy develops in spheres other than food production that it becomes an advantage for people to cluster in towns.
Detailed Explanation
Urbanism refers to the way of life and economic practices found in cities. Unlike rural areas where most people rely on agriculture, urban areas thrive due to diverse economic activities such as trade, manufacturing, and services. This diversification encourages people to live closely together, as they depend on each other's goods and services rather than being self-sufficient like in a farming community.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a farmer living in a remote village who produces all his food. He may lead a solitary life, but in a city, you have cooks, craftsmen, shopkeepers, and bankers, all reliant on each other. Just like a smartphone is made up of components manufactured far and wide, a city relies on various skills and services to function efficiently.
Specialization and Division of Labor
Chapter 2 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
City people, thus, cease to be self-sufficient and depend on the products or services of other (city or village) people. There is continuous interaction among them.
Detailed Explanation
In urban settings, jobs become more specialized. For instance, a stone seal carver will focus on creating intricate designs but will need bronze tools made by another specialist. This reliance fosters constant interaction and trade between various skilled workers, creating a network that sustains the urban economy.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a modern city where you have different professionals: doctors, teachers, bus drivers, and chefs. Each one specializes in their field, and no one can do all the jobs. This is why cities grow; everyone contributes something valuable, meaning people need each other.
Trade and Organized Systems
Chapter 3 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
There must be a social organisation in place. Fuel, metal, various stones, wood, etc., come from many different places for city manufacturers. Thus, organised trade and storage is needed.
Detailed Explanation
For cities to thrive, they must have organized systems to manage trade and resources. Goods need to be delivered from various locations (like wood for building or metal for tools), and cities require storage facilities to keep supplies. An organized system manages these resources efficiently, ensuring that manufacturers have everything they need to produce goods.
Examples & Analogies
Picture a supermarket: it doesn't grow its own food. Instead, it relies on farmers, manufacturers, and suppliers to stock shelves. Without a robust supply chain (the organization of trade and storage), the supermarket would quickly run out of products.
The Role of Writing
Chapter 4 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Urban economies often require the keeping of written records.
Detailed Explanation
In a bustling city, as various transactions occur, it becomes important to keep accurate records. Writing plays a crucial role in documenting trades, deliveries, and agreements, ensuring accountability and organization within the urban economy. This is an essential part of how cities manage complex interactions.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how businesses today use accounting software to keep track of their sales and expenditures. Just like modern businesses need records to function smoothly, ancient cities relied on written texts for their trades and dealings.
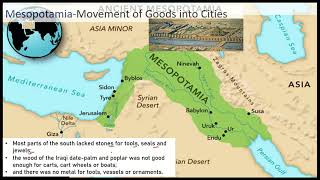
Movement of Goods
Chapter 5 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
However rich the food resources of Mesopotamia, its mineral resources were few. Most parts of the south lacked stones for tools, seals and jewels; the wood of the Iraqi date-palm and poplar was not good enough for carts, cart wheels or boats.
Detailed Explanation
Even with abundant food, Mesopotamian cities faced resource limitations. They lacked stones for making tools and precious materials, which meant that trade was essential to acquire these resources. This interconnectedness of trade and resource gathering is central to urban development, as cities needed to import goods from other areas to survive and thrive.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how modern countries often rely on imports for natural resources. For example, oil-rich nations may import food and textiles because their environment does not provide for those commodities. Similarly, Mesopotamian cities had to obtain essential materials through trade.
Importance of Transport
Chapter 6 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Efficient transport is also important for urban development.
Detailed Explanation
Transportation systems are vital for city growth. If trade goods cannot be moved efficiently, it hampers economic activity. Rivers and roads serve as trade routes, and ease of transport influences the city's ability to thrive. Cities grew strategically near these routes to facilitate trade.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how major cities today are often built around highways or ports. For example, New York City thrives as a port city because it allows ships to bring goods efficiently, just like ancient Mesopotamian cities depended on waterways for trade.
The Development of Writing Systems
Chapter 7 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The first Mesopotamian tablets, written around 3200 BCE, contained picture-like signs and numbers.
Detailed Explanation
The advent of writing in Mesopotamia marked a significant shift in communication and record-keeping. These early tablets represented goods and transactions, allowing Mesopotamians to keep track of trade efficiently. The pictographic writing evolved into a more complex system as needs grew.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a café that starts with a chalkboard menu; as it grows, it increasingly relies on printed menus and digital ordering systems. Just like the café needed to adapt its communication with growth, Mesopotamian writing evolved with the complexities of urban life.
Writing as a Necessity for Urban Life
Chapter 8 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Writing was used not only for keeping records but also for making dictionaries, giving legal validity to land transfers, narrating the deeds of kings.
Detailed Explanation
Writing served multiple functions in urban life. It allowed people to document laws, transfers, and important stories, establishing stability and continuity in city governance and culture. Writing facilitated administration and allowed cities to maintain order and offer a framework for legal matters.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how laws in modern societies are codified in legal texts. Just like legal documents today outline rights and responsibilities, ancient writing did the same for the people in Mesopotamian cities.
Legacy of Urbanism
Chapter 9 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
None of these momentous Mesopotamian achievements would have been possible without writing and the urban institution of schools.
Detailed Explanation
The interplay of urbanism and writing created a framework that allowed for advanced ideas, laws, and social structures to flourish. Schools emerged, and literacy became an aspiration, facilitating knowledge transfer and the continuity of culture. This legacy of urban thought and organization shaped future civilizations.
Examples & Analogies
Just like universities today act as hubs for knowledge and innovation, the schools in ancient Mesopotamia were essential for training scribes who would keep the city functioning and preserve its achievements for future generations.
Key Concepts
-
Urban Economies: Defined by diverse activities beyond food, such as trade and manufacturing.
-
Division of Labor: Critical for urban life, allowing individuals to specialize and create efficient production systems.
-
Importance of Writing: Facilitates record-keeping and communication, crucial for managing urban complexities.
-
Trade Networks: Essential for sourcing resources, goods, and services that bolster urban development.
Examples & Applications
Trade facilitated the exchange of metals, such as copper and tin, essential for tool-making which was a critical aspect of urban growth.
Writing was first used to document transactions and keep records of grain deliveries and other goods in Mesopotamian cities.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Urban life is not just a hive, with trades and jobs, we all thrive.
Stories
In a bustling ancient city, each worker had a unique role, from the potter making wares to the merchant trading goods. They depended on each other to survive.
Memory Tools
Remember 'T.W.E.E.L.' for Trade, Writing, Economy, Labor, and Life; together they form urban existence.
Acronyms
DREAM
Diversification
Resources
Economy
Agriculture
Manufacturing symbolizes urban development.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Urbanism
The way of life characteristic of cities and towns, especially as it relates to society, culture, and commerce.
- Division of Labor
The assignment of different tasks to different people or groups to improve efficiency and productivity.
- Trade Networks
Systems of trade that link different regions and markets, facilitating the exchange of goods and services.
- Cuneiform
The writing system used in ancient Mesopotamia, characterized by wedge-shaped signs.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
