Structure of the Judiciary
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Supreme Court of India
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will begin by discussing the Supreme Court of India. What do you think is the role of the Supreme Court?

Isn't its role to make the final decisions on legal matters?

Exactly! The Supreme Court is the highest court, and its decisions are binding on all lower courts. Can anyone tell me what other powers the Supreme Court has?

It can transfer judges of High Courts or even move cases from lower courts to itself, right?

Correct! Remember this with the acronym 'ATM': A for Authority over cases, T for Transferring judges, and M for Moving cases. This encapsulates the Supreme Court's key functions.

What happens if a High Court makes a decision that affects a lot of people?

An excellent point! The Supreme Court can also take cases from any High Court if it deems it necessary. What's crucial to remember is its power to maintain the integrity of the law.

So, it seems the Supreme Court has a large responsibility!

Yes, and it's vital for upholding justice. In summary, the Supreme Court's rulings are final, and it has significant control over the judicial system. Don't forget the 'ATM' acronym!
High Court and its Role
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's look at the High Courts. What do you think their main responsibilities are compared to the Supreme Court?

Are they like the local leaders of the judiciary?

That's a very good analogy! High Courts hear appeals from lower courts and also exercise control over them. They have the unique power to issue writs to restore fundamental rights. Who can explain what a writ is?

Isn't it a kind of order issued by a court?

Exactly! High Courts deal with cases within state jurisdiction and maintain oversight. To remember their functions, think 'HAW': H for Hear appeals, A for Authority to issue writs, and W for Wielding control over other courts.

What types of cases do the High Courts generally handle?

They typically handle appeal cases, but they also address significant legal matters of public interest. In summary, High Courts have a pivotal role in individual rights protection and overseeing lower courts. Remember 'HAW'!
District and Subordinate Courts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss District Courts and Subordinate Courts. Who can describe the primary function of District Courts?

They handle local cases from the district, like civil cases and more serious crimes, right?

Spot on! District Courts adjudicate cases that arise within their jurisdiction and also hear appeals from subordinate courts. Can anyone tell me what kinds of cases Subordinate Courts deal with?

They must be dealing with less severe cases, right?

Yes! Subordinate Courts focus on civil and criminal cases of lesser severity. To help remember the role of these courts, think 'D-SAFE': D for District Courts, S for Subordinate Courts, A for Adjudicating cases, F for Fetching appeals from lower ones, and E for Ensuring justice at the local level.

So, their interactions are important for the overall judicial system?

Absolutely! They function under the supervision of the District Courts, forming a structured chain. In summary, 'D-SAFE' helps you remember that both District and Subordinate Courts play a crucial role in the justice system.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
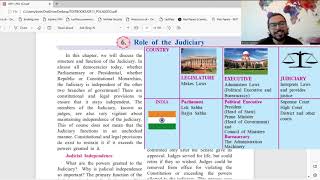
The judiciary in India is structured in a pyramidal manner, with the Supreme Court at its apex, followed by High Courts, District Courts, and Subordinate Courts. Each level of court has specific powers and responsibilities, maintaining checks and balances within the judicial framework.
Detailed
Structure of the Judiciary
The Constitution of India provides for a single integrated judicial system, differentiating it from other federal systems that may have separate state courts. The structure is hierarchical:
- Supreme Court - This is the highest court, whose decisions are binding on all other courts. It has the authority to transfer judges of High Courts, move cases from any court to itself, and transfer cases between High Courts.
- High Court - Positioned below the Supreme Court, High Courts hear appeals from lower courts, can issue writs to protect fundamental rights, manage cases pertaining to state jurisdiction, and have supervisory power over lower courts.
- District Court - These courts deal primarily with cases arising within a district, hear appeals on decisions made by subordinate courts, and adjudicate cases involving serious criminal offenses.
- Subordinate Courts - These include various civil and criminal courts that handle lower-level cases. They operate under the supervision of the District Court.
The structured nature of the judiciary ensures direct oversight and regulatory control across different levels, reinforcing the legal framework's integrity and efficiency.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding the Structure of Indian Judiciary
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Constitution of India provides for a single integrated judicial system. This means that unlike some other federal countries of the world, India does not have separate State courts. The structure of the judiciary in India is pyramidal with the Supreme Court at the top, High Courts below them and district and subordinate courts at the lowest level. The lower courts function under the direct superintendence of the higher courts.
Detailed Explanation
The judiciary in India is organized in a hierarchical structure, meaning it has different levels working together effectively. At the apex is the Supreme Court, which holds the highest authority. Below it are the High Courts, which oversee state legal matters, and at the base are the District Courts and Subordinate Courts. This integrated system ensures that all legal disputes can be handled uniformly and fairly across the country, without the complications of separate state systems.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Indian judiciary as a pyramid, where the Supreme Court is the top tier responsible for important decisions affecting the whole country. The High Courts are like regional managers handling local issues, and the District Courts are akin to local branches dealing with everyday legal matters. This hierarchy helps maintain order and clarity in the legal system.
Roles of the Supreme Court
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Supreme Court of India
– Its decisions are binding on all courts.
– Can transfer Judges of High Courts.
– Can move cases from any court to itself.
– Can transfer cases from one High Court to another.
Detailed Explanation
The Supreme Court has several powerful functions. Firstly, its decisions must be followed by all lower courts in India, meaning it sets a legal precedent. Secondly, it can transfer judges between High Courts to ensure balance and continuity. Additionally, it can accept cases from any court if it deems that those cases require higher scrutiny. Finally, it is empowered to move cases from one High Court to another to maintain fairness and efficiency in the judicial process.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the Supreme Court as the captain of a sports team. Just as the captain's play dictates the team’s strategy and direction, the Supreme Court’s decisions guide how other courts interpret laws. If a particular match (case) needs special attention, the captain can choose players (judges) from different teams (High Courts) to play together for a better outcome.
Functions of the High Court
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
High Court
– Can hear appeals from lower courts.
– Can issue writs for restoring Fundamental Rights.
– Can deal with cases within the jurisdiction of the State.
– Exercises superintendence and control over courts below it.
Detailed Explanation
High Courts serve multiple critical functions. They review decisions made by lower courts, which ensures that justice is administered fairly. They also have the authority to issue writs, legal orders that can protect individuals' fundamental rights when they are threatened. Furthermore, High Courts handle cases related to state jurisdiction and oversee the functioning of lower courts to ensure they operate appropriately and fairly.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the High Court as a regional supervisor at a large company. Just as a supervisor reviews the work of their team and ensures that all employees (the lower courts) are adhering to company policies (constitutional laws), the High Court checks the legality of decisions made by lower courts and helps restore rights if they are infringed.
District and Subordinate Courts
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
District Court
– Deals with cases arising in the District.
– Considers appeals on decisions given by lower courts.
– Decides cases involving serious criminal offences.
Subordinate Courts
– Consider cases of civil and criminal nature.
Detailed Explanation
District Courts are pivotal as they address a range of legal matters within a specific district, including appeals from lower-level courts and serious criminal cases. Subordinate Courts handle more routine civil and criminal cases, ensuring that everyday legal issues can be dealt with promptly. This structure allows justice to be more accessible to the general public, addressing local concerns effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the District Court as a local office where residents can report issues or disputes, whether it’s about a serious crime or a simple contract disagreement. The Subordinate Courts are like small help desks that assist with day-to-day problems. This setup ensures there’s little friction and people can get help nearby without having to go to the top-level offices.
Jurisdiction of the Supreme Court
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Jurisdiction of Supreme Court
– Original: Settles disputes between Union and States and among States.
– Appellate: Tries appeals from lower courts in Civil, Criminal and Constitutional matters.
– Advisory: Advises the President on matters of public importance.
Detailed Explanation
The Supreme Court operates with three types of jurisdiction: Original jurisdiction allows it to resolve disputes involving union and state matters directly. Through Appellate jurisdiction, it hears appeals, ensuring thorough review of legal decisions. Lastly, it possesses Advisory jurisdiction, meaning it can provide legal guidance to the President on pressing constitutional or public matters.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Supreme Court’s jurisdictions like different departments in a company. For instance, the Original jurisdiction acts like the HR department resolving conflicts between employees (States), while the Appellate jurisdiction is like the review board handling appeals on crucial decisions. The Advisory jurisdiction can be compared to having an experienced consultant who advises the CEO (President) on key business decisions.
Key Concepts
-
Single Integrated Judicial System: India does not have separate state courts; all courts serve under a unified judiciary.
-
Hierarchy of Courts: The Supreme Court is at the top, followed by High Courts, District Courts, and Subordinate Courts.
-
Binding Decisions: The Supreme Court's rulings are mandatory for all other courts.
-
Writ Power of High Courts: High Courts can issue writs to protect fundamental rights.
Examples & Applications
An example of a case handled by the Supreme Court is the 'Shayara Bano case,' which challenged the constitutionality of instant triple talaq.
A District Court may adjudicate a serious criminal offense like theft resulting in significant punishment.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Supreme, High, District too, Judiciary’s structure helps us through.
Stories
In the Kingdom of Law, the Supreme Court was the king, ruling all below. The High Court gave justice to the tales of the land, while the District and Subordinate Courts helped each hand in hand.
Memory Tools
Remember 'D-SAFE' for District and Subordinate Courts: D for District Courts, S for Subordinate Courts, A for Adjudicating cases, F for Fetching appeals and E for Ensuring justice.
Acronyms
Use 'ATM' for Supreme Court functions
for Authority over cases
for Transferring judges
for Moving cases.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Supreme Court
The highest court in India, whose decisions are binding on all lower courts.
- High Court
A court that hears appeals from lower courts and can issue writs for protecting fundamental rights.
- District Court
A court that deals with cases arising within a district and hears appeals from subordinate courts.
- Subordinate Courts
Courts that handle cases of civil and criminal nature under the jurisdiction of higher courts.
- Writ
An order issued by a court directing a party to perform or refrain from performing a specific act.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
