Prenatal Stage
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Prenatal Development
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we are going to talk about the prenatal stage, which is the period from conception to birth. It lasts about 40 weeks and is critically important for human development.

Why is the prenatal stage so important?

Great question! The prenatal stage lays the foundation for physical, cognitive, and emotional growth. It’s affected by various factors, including maternal health, nutrition, and environmental influences.

What happens if the mother isn’t healthy during this time?

If the mother has health issues, it can lead to low birth weight or developmental problems. That's why maternal health is so crucial during this stage!

Remember, we can use the acronym 'TEN' which stands for Teratogens, Environment, and Nutrition. These three factors are critical to understand in prenatal development.

How do these teratogens affect the baby?

Teratogens are harmful agents that can cause birth defects or developmental issues. Common examples include drugs, alcohol, and some infections. They interfere with normal developmental processes.

So, if a mother has a healthy lifestyle, then it helps the baby?

Exactly! A healthy lifestyle, including good nutrition and avoiding harmful substances, supports healthy prenatal development. It's all interconnected.

To summarize, the prenatal stage is essential for setting the stage for the child's future development. Remember the acronym 'TEN' to recall key influencing factors: Teratogens, Environment, and Nutrition.
Impact of Maternal Characteristics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's focus on maternal characteristics. What do you think are some important factors in maternal health during pregnancy?

I think nutrition must be one of them.

Absolutely! Maternal nutrition plays a crucial role. Poor nutrition can lead to low birth weight, which affects the baby's health.

What about the mother's age?

Yes, age is also significant. Younger mothers may face different risks compared to older mothers, including complications during pregnancy.

And what about stress or emotional state?

Good observation! The mother’s emotional state can impact the baby too. High stress levels can lead to negative health outcomes for both the mother and the fetus. Keeping mentally healthy is as important as physical health.

Let's remember the acronym 'MAC' for Maternal Age, Conditions, which emphasizes the key factors influencing prenatal development.

So, taking care of the mother means it's taking care of the baby, right?

Exactly! All these maternal characteristics interconnect to influence the growth and development of the baby.

To summarize, maternal characteristics such as age, nutrition, and emotional state greatly affect prenatal development. Remember 'MAC' for key maternal characteristics.
Understanding Teratogens
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive deeper into teratogens. Can anyone tell me what teratogens are?

Are they harmful substances that can affect the fetus?

That's correct! Teratogens are agents that can cause abnormal fetal development, leading to serious effects.

What are some examples of teratogens?

Common examples include drugs like cocaine or alcohol, infections like rubella, and environmental toxins like lead. Each has different types of development risks associated with them.

Can you explain how alcohol affects fetal development?

Of course! Alcohol can lead to Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD), resulting in physical and mental disabilities. It's crucial that pregnant mothers avoid alcohol entirely.

That sounds really serious! What can we do to help?

Educating communities about the risks of teratogens can help. Encouraging healthy prenatal practices can reduce exposure.

For memory aids, remember 'TAP' for Teratogens, Alcohol, Pollutants. These are key areas to be aware of in prenatal health.

To summarize, teratogens can have serious effects on fetal development, and education on avoiding them is essential. Remember 'TAP' for safety.
Prenatal Care and Its Importance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s shift to discussing prenatal care. Why do you think prenatal care is essential?

I suppose it helps ensure the health of both mother and baby.

Precisely! Regular check-ups can monitor the health of both. It’s essential to address any risks early.

What does prenatal care actually involve?

Prenatal care includes routine check-ups, nutrition advice, and education on what to expect throughout pregnancy. It's an opportunity to discuss any concerns.

How can expectant mothers find good prenatal care?

That's a great point! They should consult healthcare providers for recommendations and look for services that cater specifically to prenatal care.

Sounds like a vital part of having a healthy baby!

Exactly! Remember the three key elements of prenatal care: Monitoring, Nutrition, and Education, which ensure the well-being of both mother and child.

In summary, prenatal care is crucial for healthy pregnancies. Remember MNE for Monitoring, Nutrition, and Education!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The prenatal stage, lasting about 40 weeks, involves the development of the fetus influenced by maternal characteristics, nutrition, and environmental factors. Teratogens can adversely affect this development, leading to various consequences. Maternal health significantly impacts fetal development, and understanding this stage is crucial for grasping the overall human development process.
Detailed
Detailed Summary: Prenatal Stage
The prenatal period spans from conception to birth and typically lasts about 40 weeks. This stage is crucial for development as it sets the foundation for future physical, cognitive, and emotional growth. During this time, both genetic and environmental factors play significant roles in shaping the development of the fetus.
1. Key Features of Prenatal Development
Prenatal development is significantly influenced by the mother’s characteristics, such as age, nutrition, and emotional health. For instance:
- Maternal Nutrition: Poor maternal nutrition can lead to low birth weight and developmental issues.
- Maternal Health Conditions: Illnesses like rubella or HIV can pose severe risks to fetal development.
2. Teratogens
Teratogens are environmental agents that cause deviations in normal development leading to severe abnormalities or even death. Common teratogens include:
- Drugs and Alcohol: Substance abuse during pregnancy (e.g., cocaine, alcohol) can lead to congenital abnormalities.
- Infections: Conditions like German measles can have harmful effects on the fetus.
- Environmental Pollutants: Exposure to harmful chemicals (e.g., mercury, lead) can impede the healthy development of the fetus.
3. Significance
Understanding the prenatal stage provides crucial insights into the multi-faceted processes of human development and highlights the importance of maternal health and environment in shaping future generations.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Prenatal Stage
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
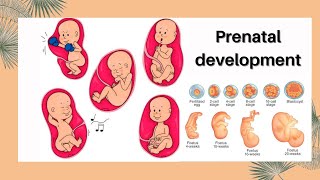
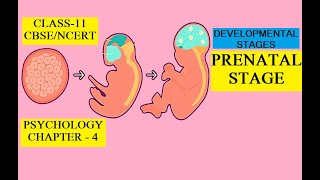
The period from conception to birth is known as the prenatal period. Typically, it lasts for about 40 weeks.
Detailed Explanation
The prenatal stage refers to the time during which a baby develops inside the mother's womb. This begins when the sperm fertilizes the egg, creating a zygote, and continues until the baby is born. This period lasts approximately 40 weeks, which is commonly measured in three trimesters. Each trimester signifies different stages of development and changes in the fetus.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the prenatal stage like a seed growing into a plant. Just as it takes time, nurturing, and the right environment for a seed to grow roots, stems, and leaves, a fetus requires time in the womb to develop vital organs, limbs, and other characteristics before being born.
Influence of Genetic and Environmental Factors
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Both genetic and environmental factors affect our development during different periods of the prenatal stage.
Detailed Explanation
Development during the prenatal stage is significantly influenced by both genetics and the environment. Genetic factors come from the parents' DNA and determine traits such as physical attributes and potential health issues. Environmental factors include everything the mother experiences during pregnancy, such as nutrition, stress, and exposure to toxins, which can affect the fetus’s development.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine baking a cake. The ingredients you choose (genetic factors) will affect how the cake tastes and looks, while the cooking instructions (environmental factors) will determine how well it rises and bakes. If you change the ingredients or don’t follow the instructions, the outcome can be quite different.
Maternal Characteristics Impacting Development
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Prenatal development is also affected by maternal characteristics, which include mother’s age, nutrition, and emotional state.
Detailed Explanation
A mother’s age can influence the health of the pregnancy; younger mothers may have higher risks of complications, while older mothers may face challenges related to genetic anomalies. Proper nutrition is critical because it affects the growth of the fetus. Emotional stress and mental health can also impact fetal development since a stressed mother may produce hormones that affect the baby.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a plant that needs certain nutrients and care. If a gardener is attentive and provides proper nutrition and a nurturing atmosphere, the plant thrives. Conversely, if the gardener neglects it or is too rough, the plant may not grow well. Similarly, a mother who maintains good health and a supportive environment contributes positively to her baby's growth.
Effects of Diseases and Infections
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Disease or infection carried by the mother can adversely affect prenatal development. For example, rubella (German measles), genital herpes, and Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) are believed to cause genetic problems in the newborn.
Detailed Explanation
If a mother contracts certain diseases or infections during pregnancy, they can be passed to the fetus, leading to serious health issues or congenital disabilities. For instance, rubella can cause heart defects, deafness, or blindness, while HIV can lead to the infant being born with the virus, affecting their health and development.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a factory producing toys. If the production process gets contaminated, every toy produced could have defects. Just like the factory needs to be free from hazards to produce quality toys, a healthy pregnancy environment is essential for the development of a healthy baby.
Understanding Teratogens
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Another source of threat to prenatal development is teratogens, environmental agents that cause deviations in normal development that can lead to serious abnormalities or death.
Detailed Explanation
Teratogens refer to substances that can cause malformations in a developing fetus. These can include drugs, medications, alcohol, tobacco, and environmental toxins. Teratogens might lead to birth defects or other developmental issues that can affect a child's physical or mental health.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sponge soaking up water from a dirty puddle. Just as the sponge absorbs both clean and harmful substances, a developing fetus can take in both beneficial nutrients and harmful chemicals, which can impact its development. Being careful about what a pregnant mother is exposed to is crucial for the baby's health.
Impact of Lifestyle Choices
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Intake of drugs (marijuana, heroin, cocaine, etc.), alcohol, tobacco, etc. by women during pregnancy may have harmful effects on the foetus and increase the frequency of congenital abnormalities.
Detailed Explanation
Lifestyle choices made by a pregnant woman can greatly impact fetal health. Substances like alcohol and drugs can disrupt normal developmental processes, potentially resulting in fetal alcohol syndrome or neonatal abstinence syndrome, among others. Avoiding harmful substances is crucial for ensuring the fetus has the best chance for healthy development.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a child trying to build a structure with blocks. If the blocks are sturdy and well-made, the structure will be strong. But if the blocks are weak or broken, the structure may fall apart. Similarly, a fetus needs healthy conditions to develop properly – unhealthy choices can compromise that foundation.
Key Concepts
-
Prenatal Development: Development from conception to birth, crucial for future growth.
-
Maternal Characteristics: Factors like age, nutrition, and emotional health influencing fetal health.
-
Teratogens: Harmful agents affecting fetal development, including drugs and environmental toxins.
-
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD): Issues arising from maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy.
-
Prenatal Care: Important routine care during pregnancy to monitor health and support fetal development.
Examples & Applications
If a pregnant woman smokes or consumes alcohol, the baby may face serious health problems, highlighting the importance of avoiding teratogens.
A well-nourished expectant mother with regular prenatal care is more likely to give birth to a healthy baby compared to one who doesn't receive such care.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Prenatal care, a health affair; Healthy moms make babies fair.
Stories
A mother named Daisy discovered that eating healthy and visiting her doctor regularly helped her baby grow strong and smart during the prenatal months.
Memory Tools
'TEN' reminds us of Teratogens, Environment, and Nutrition when studying prenatal health.
Acronyms
'MAC' for Maternal Age and Conditions influencing fetal health.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Prenatal Stage
The period from conception to birth, lasting about 40 weeks, critical for development.
- Teratogens
Environmental agents that can cause deviations in normal fetal development resulting in abnormalities.
- Maternal Characteristics
Aspects of the mother's health, nutrition, and emotional state that influence fetal development.
- Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD)
A range of effects that can occur in a person whose mother drank alcohol during pregnancy.
- Prenatal Care
Routine medical care provided during pregnancy to ensure the health of the mother and fetus.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
