CIRCULAR FLOW OF INCOME AND METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Circular Flow of Income
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about the circular flow of income. This concept shows how money moves between households and firms. Can anyone explain what we mean by 'circular flow'?

Is it about how money keeps flowing in a cycle between buying and selling?

Exactly! When households earn income through wages, rent, and profits, they spend this income on goods and services produced by firms. So, if households spend all their income on goods, what's the impact on firms?

Firms will see an increase in sales revenue.

Correct! This leads to a sustainable economic cycle. To remember this process, think of 'B-Flow': **B**uying leads to **Flow** of resources. Let's understand how this flow can be quantified.
Methods of Calculating National Income
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss how we can calculate the national income using three different methods. Can you think of any method to measure this?

Could we look at total production value?

Yes! That's known as the Product Method, which focuses on value added at each production stage, ensuring we avoid double counting. What's the second method?

The Expenditure Method? It sums up all spending on final goods.

Right! And remember, it includes consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports. Now who can tell me about the Income Method?

It totals earnings from wages, rent, interest, and profits, right?

Exactly! So whether we calculate using production, expenditure, or income, we obtain the same national income. Understanding these methods helps in analyzing economic health. Keep the acronym ‘PEI’ in mind for Product, Expenditure, and Income.
Significance of Accurate National Income Measurement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do you think it is important to accurately measure national income?

Because it reflects the economy's health?

Absolutely! Accurate measures help in policy-making, understanding economic cycles, and allocation of resources. What might happen if we underreport or overreport national income?

Misallocation of resources could occur, and policy decisions may be flawed.

Exactly! This showcases the importance of reliable data. Remember, if our measures are 'off,' it can impact everybody, so always 'Audit First, Decide Next'!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we learn how the circular flow of income describes the continuous movement of income and expenditure through households and firms in an economy. It discusses methods for calculating national income, emphasizing the importance of accurate measures and the interconnections between income, consumption, and production.
Detailed
Circular Flow of Income
In a simplified model of the economy without external trade, government activities, or savings, households earn their income from productive contributions and spend this income on goods and services produced by firms. The income circulates between households and firms, creating a continuous flow of expenditure and income. This section illustrates this relationship through the concept of circular flow of income, where every income earned is spent entirely on domestic goods and services, resulting in no leakage from the system.
Methods of Calculating National Income
The section details three primary methods for calculating national income:
1. Product Method: This method calculates national income through the sum total of value added at each production stage, preventing double-counting by deducting the costs of intermediate goods.
2. Expenditure Method: This method sums all final expenditures made by households, businesses, and the government, adjusting for net exports (exports minus imports).
3. Income Method: This method totals all incomes earned by factors of production—wages, rent, interest, and profits.
Through these methods, the aggregate income reflects the overall economic activity and supports further analysis of how shifts in consumption or production can influence income levels.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Basic Structure of the Economy
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In this section, we describe how we can view the aggregate income of the entire economy going through the sectors of the economy in a circular way. The households receive their payments from the firms for productive activities they perform for the latter. As we have mentioned before, there may fundamentally be four kinds of contributions that can be made during the production of goods and services: (a) contribution made by human labour, remuneration for which is called wage; (b) contribution made by capital, remuneration for which is called interest; (c) contribution made by entrepreneurship, remuneration of which is profit; (d) contribution made by fixed natural resources (called ‘land’), remuneration for which is called rent.
Detailed Explanation
The economy can be understood as a system where households and firms interact continually. Households provide labor and resources to firms and receive wages, interest, profits, and rent in return. Each of these payments represents a flow of income that fuels consumption. This flow creates a cycle: households spend their income on the goods and services produced by firms, which in turn allows firms to pay households for more labor and resources. The four types of contributions reflect the different roles within the economy—labor for wage, capital for interest, entrepreneurship for profit, and land for rent.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an ecosystem in nature: just as plants convert sunlight into energy and provide it to herbivores, which in turn feed carnivores, households and firms provide and consume resources in a continuous cycle. This analogy illustrates how each component (households/firms) plays a critical role in giving and receiving energy (income/payment) in the economic system.
Flow of Income Without Leakage
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In this simplified economy, there is only one way in which the households may dispose off their earnings – by spending their entire income on the goods and services produced by the domestic firms. The other channels of disposing their income are closed: we have assumed that the households do not save, they do not pay taxes to the government – since there is no government, and neither do they buy imported goods since there is no external trade in this simple economy.
Detailed Explanation
In our simplified model, all income generated within the economy circulates back into the economy without any losses or 'leakages.' Households spend the entirety of their income, thereby ensuring that firms receive equal payments for all goods produced. The lack of government taxation, saving, or imports stabilizes this flow, making it easier to visualize and understand the circular income flow.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a closed-loop water system in a garden: every drop of water that leaves the tank gets used by the plants, and every bit of moisture that evaporates is either captured and returned or self-renewed through natural cycles. In this case, the constant recycling of water equates to the full use of income in the economy.
Circular Flow Model Representation
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
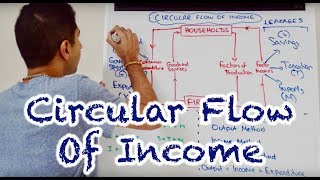
Hence, year after year we can imagine the aggregate income of the economy going through the two sectors, firms and households, in a circular way. This is represented in Fig. 2.1. When the income is being spent on the goods and services produced by the firms, it takes the form of aggregate expenditure received by the firms.
Detailed Explanation
The circular flow of income visually illustrates how money circulates between firms and households. Households spend money on goods and services, which produces revenue for firms. Firms, in turn, use this revenue to pay for labor and resources, thus enabling the continued cycle of production and consumption. The aggregated nature of this flow means that all money spent and earned can be accounted for, reinforcing the relationship between producers and consumers.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a food market where customers buy fruits and vegetables. As shoppers pay for their items, the sellers use that money to stock their stalls and pay their workers. If customers keep returning and spending, this establishes a continuous cycle of income that can be marked as flowing around in a circle within the economy.
Methods of Calculating National Income
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
If we want to estimate the aggregate value of goods and services produced during a year we can measure the annual value of the flows at any of the dotted lines indicated in the diagram. We can measure the uppermost flow (at point A) by measuring the aggregate value of spending that the firms receive for the final goods and services which they produce. This method will be called the expenditure method. If we measure the flow at B by measuring the aggregate value of final goods and services produced by all the firms, it will be called product method. At C, measuring the sum total of all factor payments will be called income method.
Detailed Explanation
National income can be calculated using three different methods: the expenditure method (A), the product method (B), and the income method (C). Each method focuses on a different aspect of the economy's performance. The expenditure method aggregates total spending on finished goods and services. The product method sums the value added by all firms, avoiding double counting of intermediate goods. Lastly, the income method summarizes all income earned from production. Importantly, all three methods ultimately yield the same national income figure, despite their differing perspectives.
Examples & Analogies
Think of these methods as different ways to measure a marathon. The first method counts the total distance when runners complete their laps (expenditure), the second measures how many laps (product), and the third tallies each runner's individual time contributions (income). All three approaches ultimately tell the same story about the marathon's outcome but from unique angles.
Conclusion of Circular Flow of Income
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
We may note here that in the circular flow model, the aggregate spending of the economy must be equal to the aggregate income earned by the factors of production. Observe that the aggregate income must equal the aggregate expenditure. Now let us suppose that at a particular period of time the households decide to spend more on the goods and services produced by the firms...
Detailed Explanation
In concluding the circular flow model, it is essential to emphasize that overall expenditure and income dynamics are inherently balanced. When households increase spending, it drives demand, encouraging firms to produce more and consequently hire more labor. This response influences aggregate income positively, allowing the cycle to continue. Thus, the model indicates that targeting higher spending can elevate overall economic performance.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a busy restaurant where every customer order motivates the staff to prepare more meals. If patrons decide to order twice as much food, the kitchen gears up to meet demand, which not only increases sales (income for the restaurant) but also enables the restaurant to pay its employees more and hire additional staff to manage the increased flow of orders.
Key Concepts
-
Circular Flow of Income: Describes the movement of money within an economy between households and firms, creating continuous economic activity.
-
National Income: The total income earned by a nation’s factors of production.
-
Product Method: Measures national income by adding the value added at each stage of production.
-
Expenditure Method: Measures national income through total spending on final goods and services.
-
Income Method: Calculates national income by summing incomes received by factors of production.
Examples & Applications
In a simple economy, households receive income through wages and spend it on goods produced by firms, creating a cycle where total income equals total spending.
If households increase their expenditure, firms respond by increasing production, leading to a rise in income for the factors of production.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the economy’s flow, income takes its course, through households and firms, like a river's force.
Stories
Once in a village, every job was tied to an income source. Each farmer's hard work led to a happy flow of coins back to their homes.
Memory Tools
Remember 'PEI' for calculating National Income: Product, Expenditure, Income.
Acronyms
B-Flow
Buying leads to Flow of income in a circular way.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Circular Flow of Income
A model that illustrates how money moves through an economy between households and firms.
- National Income
The total income earned by a country's residents and businesses, including wages, profits, rents, and taxes, minus subsidies.
- Product Method
A method of calculating national income that sums up the value added at every stage of production.
- Expenditure Method
A method that measures national income by calculating the total expenditure on final goods and services.
- Income Method
A method for calculating national income that summates all incomes received by factors of production.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
