Determination of the Exchange Rate
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Flexible Exchange Rate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re diving into Flexible Exchange Rates. Can anyone tell me what they think this means?

I believe it means that the currency value changes based on supply and demand?

Exactly! In a Flexible Exchange Rate system, the exchange rate shifts as the demand and supply of currencies fluctuate. For example, if more people want to buy US goods, the demand for dollars increases, pushing its value up.

So, if demand for dollars goes up, does that mean the rupee would become weaker?

Right! This is known as depreciation of the domestic currency. The rupee would buy fewer dollars, showing its reduced value in terms of foreign currency.

Is this the same as appreciation?

Not quite. Appreciation occurs when the domestic currency strengthens against foreign currencies. If the rupee buys more dollars, it indicates appreciation.

How do speculators influence this?

Speculators buy currency based on expected future rates, influencing current demand. If they think the dollar will strengthen, they will buy dollars now, increasing current demand and affecting the exchange rate.

To remember this, think of DEP for Depreciation, Up for Increasing Demand! So, if demand goes up, depreciation happens.
Fixed Exchange Rate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s discuss Fixed Exchange Rates. Who can explain this concept?

I think it’s when the government sets a specific exchange rate and keeps it stable?

Yes! Governments peg their currencies to another, like the dollar, to ensure stability. But this requires constant monitoring and intervention. Can anyone give an example?

Isn't the Chinese Yuan a good example?

Correct! China manages its Yuan's value. However, a risk is that if the market doubts the government's ability to maintain the rate, speculation can ensue, leading to an attack on their currency.

What happens during a devaluation?

Devaluation occurs when a government officially reduces the exchange rate to promote exports. Remember: Government Action = Fixed Rate! AID for action of intervention.
Managed Floating Exchange Rates
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, we have Managed Floating Rates. Can someone explain this?

It's like a hybrid of Flexible and Fixed exchange rates, right?

Exactly! Under a managed floating system, governments can intervene in the market to stabilize their currency as needed. They don’t let it float freely but manage fluctuations responsibly.

Doesn’t this mean central banks buy or sell their own currency?

Correct! This intervention helps smooth out fluctuations and maintain economic stability. It's flexibility with a safety net!

Can this be advantageous during economic crises?

Yes, it provides more control during economic instability. Just remember: M for Managed means Mitigate risks!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section elaborates on the various methodologies countries use to determine exchange rates, emphasizing the roles of demand, supply, and economic indicators like interest rates and income levels. It also describes the implications of these exchange rate systems for the economy.
Detailed
In this section, we explore the determination of exchange rates under different systems including Flexible, Fixed, and Managed Floating Exchange Rates. The Flexible Exchange Rate is influenced by market forces of demand and supply, allowing the rate to fluctuate freely. As market conditions change, such as an increased demand for foreign goods, the equilibrium exchange rate will adjust, leading to depreciation or appreciation of the domestic currency. The teacher highlights how speculative actions and interest rate differences also impact exchange rates. In contrast, a Fixed Exchange Rate is set by the government and maintained through monetary intervention, creating stability. However, this system can be prone to speculation if the market perceives the government's capacity to maintain the rate as weak. Furthermore, Managed Floating Exchange Rates blend both approaches, enabling governments to moderate exchange rate fluctuations through intervention while allowing market-driven movements as well. Understanding these systems allows one to grasp their economic implications, particularly relating to trade balances and international competitiveness.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Methods of Determining Exchange Rates
Chapter 1 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
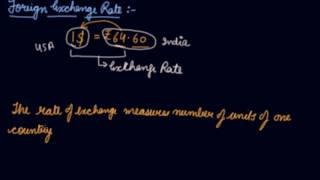
Different countries have different methods of determining their currency’s exchange rate. It can be determined through Flexible Exchange Rate, Fixed Exchange Rate or Managed Floating Exchange Rate.
Detailed Explanation
There are three primary methods for determining exchange rates: flexible, fixed, and managed floating. Each method affects how a country's currency is valued in relation to others. A flexible exchange rate fluctuates based on supply and demand in the market. In contrast, a fixed exchange rate remains constant with values set by the government. Managed floating is a hybrid, where the government intervenes occasionally to stabilize currency fluctuations.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a flexible exchange rate like a seesaw that moves up and down based on how heavy the weights (supply and demand) are on either side. Conversely, a fixed exchange rate is like a plank held horizontally at a fixed height above the ground, regardless of how many kids want to play on either end; it only changes if a teacher (the government) decides to raise or lower the plank.
Flexible Exchange Rate
Chapter 2 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
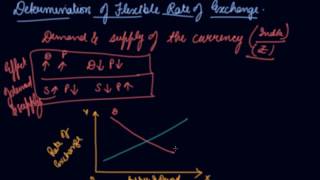
Flexible Exchange Rate is determined by the market forces of demand and supply. It is also known as Floating Exchange Rate.
Detailed Explanation
A flexible exchange rate is determined by the interaction of supply and demand in the foreign exchange market. When demand for foreign currency increases, the exchange rate rises, meaning it becomes more expensive to buy foreign currency. Market dynamics thus dictate the currency value rather than government controls.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a farmer's market where the price of apples rises whenever there are more buyers than sellers. Similarly, in the foreign exchange market, if many people want to buy dollars, the price in terms of rupees (the exchange rate) goes up, just like the price of apples does when they are in higher demand.
Impact of Increased Demand for Foreign Goods
Chapter 3 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Suppose the demand for foreign goods and services increases (for example, due to increased international travelling by Indians), then...the demand curve shifts upward and right to the original demand curve.
Detailed Explanation
When the demand for foreign goods increases, more people require foreign currency to make their purchases. This leads to an upward shift in the demand curve for that currency, causing the exchange rate to rise. Consequently, it costs more rupees to purchase the same amount of foreign currency. This phenomenon illustrates how consumer behavior impacts currency valuation.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine if a new blockbuster movie is released that everyone wants to see. The cinemas are packed, and tickets are hard to get. As more people try to buy tickets, the price goes up. In foreign exchange, if many people want dollars for shopping abroad, the price of dollars also rises.
Speculation and Its Effects
Chapter 4 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Money in any country is an asset. If Indians believe that British pound is going to increase in value relative to the rupee, they will want to hold pounds.
Detailed Explanation
Speculation refers to the practice where people anticipate future changes in currency values. If investors think that a currency, like the pound, will appreciate against the rupee, they will buy pounds now to profit later. This increased demand for pounds can cause the current exchange rate to rise, effectively becoming a self-fulfilling prophecy as more people buy pounds, thus driving up its price.
Examples & Analogies
It’s similar to investing in stocks. If everyone believes a particular tech stock will increase in value, more and more investors will buy it, driving the price up. Currency speculation works in much the same way.
Interest Rates and Currency Value
Chapter 5 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In the short run, another factor that is important in determining exchange rate movements is the interest rate differential.
Detailed Explanation
Interest rate differentials between countries can greatly affect currency values. If a country offers higher interest rates, investors will prefer to invest there, increasing demand for its currency as they need it to make investments. As demand rises, the value of that currency appreciates while the value of the investors' original currency depreciates.
Examples & Analogies
Think about it like a savings account. If one bank offers a significantly higher interest rate than another, you'd want to deposit your money there. Thus, many people will exchange their current currency for the bank's currency to take advantage of the higher interest rates, driving up its value.
Income Levels and Exchange Rates
Chapter 6 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
When income increases, consumer spending increases. Spending on imported goods is also likely to increase.
Detailed Explanation
As people's incomes rise, they tend to spend more on goods, including imports. This increase in demand for foreign goods results in a higher demand for foreign currency. Consequently, this can lead to a depreciation of the domestic currency as more currency is needed to purchase the same amount of foreign goods.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a family that gets a raise. With more money available, they decide to eat out more frequently at their favorite foreign cuisine restaurant. As their demand for those foreign meals increases, they need more of foreign currency to pay their bills, which can influence the exchange rate due to the increased demand for that currency.
Purchasing Power Parity in Exchange Rates
Chapter 7 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The purchasing Power (PPP) theory is used to make long-run predictions about exchange rates.
Detailed Explanation
The Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) theory suggests that exchange rates should adjust to equalize the price levels of identical goods in different countries. Long-term changes in exchange rates often reflect differences in inflation rates between countries. If inflation rises in one country but not another, the currency of the country with higher inflation will depreciate.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how prices change over time. If a hamburger costs $5 in the US and the same in India equivalent to Rs 250, the exchange rate should reflect this difference. If inflation in India grows but stays stable in the US, soon a burger in India might cost Rs 300, suggesting the rupee's value relative to the dollar should adjust accordingly.
Fixed Exchange Rates and Government Control
Chapter 8 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In this exchange rate system, the Government fixes the exchange rate at a particular level.
Detailed Explanation
Fixed exchange rates are set by the government and do not fluctuate based on market conditions. This can lead to stability in international transactions, but requires a government to maintain the set rate, often using its foreign reserves. If a government sets the exchange rate too high, it may need to sell foreign currency; if set too low, it may create an excess demand for foreign currency.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a price control on gas set by the government. If gas prices are kept artificially low, people will flock to buy more of it, leading to shortages—just like if a rupee is set too low against a dollar. The government must keep a close watch on the supply and demand to prevent a crisis.
Key Concepts
-
Flexible Exchange Rates: Currency values fluctuate based on market demand and supply, allowing for real-time adjustments.
-
Fixed Exchange Rates: A monetary policy tool stabilizing currency values by government intervention to maintain fixed rates.
-
Managed Floating Exchange Rates: A combination of market-determined rates with selective government intervention.
-
Depreciation and Appreciation: Terms used to describe currency value decline and rise, impacting trade and investment.
-
Speculation in Exchange Rates: Concept where traders make currency transactions based on predicted future movements.
Examples & Applications
If the demand for U.S. cars increases in India, the demand for dollars rises, causing the rupee to depreciate.
China's Yuan is intentionally kept at a specific level against the dollar, demonstrating a fixed exchange rate approach.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When rupees drop and dollars rise, it's depreciation, no surprise!
Stories
Imagine a ship sailing on unpredictable waves. The waves symbolize market forces that determine currency values, reflecting the journey of Flexible Exchange Rates.
Memory Tools
Remember 'Fried Dough' for Flexible, Depreciation, and Managed — the three systems of exchange determination!
Acronyms
FMM for Flexible, Managed, and Monetary policies in exchange rates!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Flexible Exchange Rate
An exchange rate determined by market forces of supply and demand.
- Fixed Exchange Rate
An exchange rate that is set by the government and maintained through intervention.
- Managed Floating Exchange Rate
A system where exchange rates are largely determined by market forces, but central banks may intervene.
- Depreciation
A decrease in the value of a currency relative to other currencies.
- Appreciation
An increase in the value of a currency relative to other currencies.
- Speculation
Taking a position in the currency market based on expected future movements.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
