Foreign Exchange Rate
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Foreign Exchange Rate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome class! Today, we are exploring the Foreign Exchange Rate. Can anyone tell me what they think the Foreign Exchange Rate is?

Isn't it how much one currency is worth in terms of another?

Exactly! It's the price of one currency in terms of another. For instance, if it takes Rs 50 to buy $1, that is our exchange rate.

Why is it important to know this rate?

Great question! It helps us understand international prices and costs. Let's remember it with the acronym PACE: Price of currency, Allows comparison, Changes over time, Exchange of goods.

How do we know the rates fluctuate?

The rates can change based on demand and supply for foreign exchange. Let's move on to that.
Demand for Foreign Exchange
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive into the demand for foreign exchange. Why do you think people demand it?

To buy things from other countries, right?

Absolutely! People demand forex to purchase foreign goods, send gifts, or invest abroad. Now, what happens if the price of foreign exchange goes up?

It gets more expensive to buy those foreign goods.

Exactly! This reduces the demand for imports, which in turn decreases the demand for foreign exchange. Remember the word 'DOLLAR' for Demand: Decreases as Outlay rises, so Less Amount Required!

What if we need to import more?

Then the demand for foreign exchange would increase again, despite the higher rate. This leads us to the next topic: the supply of foreign exchange.
Supply of Foreign Exchange
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's shift gears to the supply of foreign exchange. Can anyone share how foreign currency comes into a country?

Through exports and remittances?

Exactly! Exports create demand for domestic goods overseas, bringing in foreign currency. Also, foreigners sending gifts or investments adds to this supply. What's the magic word to retain these concepts?

How about 'EASY' for Supply: Exports, Assets bought by foreigners, and Yields in currency?

Very clever! Now, if the price of foreign exchange rises, what happens to the supply?

It could increase because it's cheaper for foreigners to buy more from us.

Exactly right! The supply could increase, but it also depends on many factors like the elasticity of demand for exports. Let’s summarize what we discussed today.

In summary, the Foreign Exchange Rate is crucial for international trade, influenced by demand for imports and supply from exports. Remember our acronyms for quick recall!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explains the concept of Foreign Exchange Rate, detailing how demand and supply for foreign exchange influence the costs of goods and services between countries. It highlights the impact of exchange rates on imports and exports, using India and the USA as an example.
Detailed
Foreign Exchange Rate
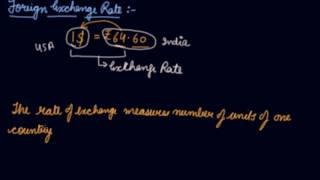
The Foreign Exchange Rate, often referred to as the Forex Rate, is defined as the price of one currency expressed in terms of another currency. This rate is crucial for linking the currencies of various countries, thereby enabling the comparison of costs and prices in international trade.
For example, if one needs to pay Rs 50 for $1, then the exchange rate is Rs 50 per dollar. This section focuses on the factors that influence both the demand for and supply of foreign exchange.
Demand for Foreign Exchange
People require foreign exchange for various reasons:
1. Purchasing goods and services from other countries.
2. Sending gifts abroad.
3. Investing in foreign financial assets.
An increase in the price of foreign exchange will make foreign goods more expensive in domestic currency terms, thus decreasing demand for imports and subsequently reducing the demand for foreign exchange itself.
Supply of Foreign Exchange
Foreign currency enters a home country for several reasons:
1. Exports, leading foreigners to purchase domestic goods.
2. Transfers and gifts sent by foreigners.
3. Foreign investments in domestic assets.
If the price of foreign exchange rises, it decreases the cost for foreigners buying products from India, potentially increasing India's exports and thus influencing the supply of foreign exchange. However, whether the supply indeed increases depends on several factors, notably the elasticity of demand for both exports and imports.
Youtube Videos







![Balance of Payments and Foreign Exchange | [ISC ECONOMICS Class 12] | ISC EXAMS 2025](https://img.youtube.com/vi/wbgH4FrCXiw/mqdefault.jpg)

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Foreign Exchange Rate
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Foreign Exchange Rate (also called Forex Rate) is the price of one currency in terms of another. It links the currencies of different countries and enables comparison of international costs and prices. For example, if we have to pay Rs 50 for $1 then the exchange rate is Rs 50 per dollar.
Detailed Explanation
A foreign exchange rate is essentially how much of one currency you need to spend to buy another currency. It allows us to determine what a currency is worth in relation to another, facilitating international trade and investment. In our example, if the exchange rate is Rs 50 for 1 dollar, it indicates that if you want to buy a dollar, you need to spend 50 rupees.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like shopping in two different stores that have different prices for the same item. If a shirt costs 50 rupees in one store and 1 dollar in another, you would need to know how many rupees equals a dollar to assess which option is cheaper for you.
Demand for Foreign Exchange
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
People demand foreign exchange because: they want to purchase goods and services from other countries; they want to send gifts abroad; and, they want to purchase financial assets of a certain country.
Detailed Explanation
The demand for foreign exchange arises when individuals or businesses need to acquire foreign currency to engage in international transactions. This could involve buying goods, such as electronics from abroad, sending money to family or friends in another country, or investing in foreign financial markets. Essentially, whenever there is a desire to spend money in another country, foreign exchange is needed.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a traveler going to Japan who needs yen to pay for a hotel or food. To get yen, they must exchange their home currency, so they approach a currency exchange service to buy yen, demonstrating the demand for foreign exchange.
Supply of Foreign Exchange
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Foreign currency flows into the home country due to the following reasons: exports by a country lead to the purchase of its domestic goods and services by the foreigners; foreigners send gifts or make transfers; and, the assets of a home country are bought by the foreigners.
Detailed Explanation
The supply of foreign exchange available in a country comes from various activities. When a country sells goods to other nations (exports), it receives foreign currency as payment. Additionally, when people in other countries send money as gifts or for transactions, it adds to the currency supply. Moreover, if foreign investors buy assets, such as stocks or real estate, in the country, this also increases the supply of foreign currency in that nation.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a café that sells delicious pastries and gets orders from a foreign customer. When the customer pays with their foreign currency, the café owner now has that currency, adding to the café's foreign exchange supply. This currency can then be sold or converted back into local currency.
Effect of Exchange Rate Changes
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A rise in price of foreign exchange will increase the cost (in terms of rupees) of purchasing a foreign good. This reduces demand for imports and hence demand for foreign exchange also decreases, other things remaining constant.
Detailed Explanation
When the exchange rate increases, it means that it takes more local currency to buy a unit of foreign currency. For instance, if the rate rises from Rs 50 to Rs 70 for 1 dollar, any local consumer wishing to buy products from abroad would need to spend significantly more rupees. Consequently, this can lead to a decrease in imports and thus reduce the overall demand for foreign exchange.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a popular band from another country that you wish to attend a concert by. If ticket prices in dollars increase due to a higher exchange rate, you might reconsider attending because it will cost you more in rupees, leading to a drop in ticket purchases from the international market.
Key Concepts
-
Foreign Exchange Rate: The price of one currency in terms of another currency.
-
Demand for Foreign Exchange: The need for foreign currencies arises from the purchase of goods, services, and investments.
-
Supply of Foreign Exchange: Currency comes into a country from exports, gifts, and investments from foreigners.
-
Elasticity of Demand: Influences how demand reacts to price changes.
Examples & Applications
If the exchange rate is Rs 50 for $1, a foreign product costing $100 will cost Rs 5000.
When the price of foreign exchange increases, the cost for purchasing foreign goods also increases, reducing the number of imports.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Forex rates can fluctuate, making imports feel like a heavy weight.
Stories
Imagine a busy market where currency traders exchange dollars for rupees, adjusting prices as demand changes!
Memory Tools
For the demand: 'DOLLAR' - Decreases as Outlay rises, Less Amount Required.
Acronyms
PACE
Price of currency
Allows comparison
Changes over time
Exchange of goods.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Foreign Exchange Rate
The price of one currency expressed in terms of another currency.
- Demand for Foreign Exchange
The desire to acquire foreign currencies to purchase goods, services, or investments from other countries.
- Supply of Foreign Exchange
The influx of foreign currencies into a country, driven by exports, gifts, and foreign investments.
- Elasticity of Demand
A measure of how sensitive the quantity demanded is to changes in price.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
