Tensions and Conflicts
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Post-Soviet Conflicts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re discussing the tensions and conflicts that arose in the former Soviet republics after its collapse in 1991. Can anyone share what they think caused these conflicts?

I think it had to do with nationalism and people wanting independence.

Economic issues also played a big part, right?

Exactly! Nationalism was a big factor. Many groups were previously suppressed and once free, they wanted self-determination. Economic struggles also made the situation volatile, creating profound inequalities. Let’s remember the acronym N.E.C. — Nationalism, Economy, and Conflict — to recall the key causes.

What specific countries were affected by these issues?

Good question! Countries like Chechnya and Dagestan in Russia, and Tajikistan experienced significant unrest and civil conflicts. The diverse ethnic backgrounds contributed to complex dynamics. Want to explore an example?

Yes, I’d like to learn more about Chechnya!

Chechnya is a perfect case study. We’ll dive into its conflict next session!
Case Study: Chechnya
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s examine the Chechen conflict. What do you know about it?

I know it was violent and involved secessionist movements against Russia.

Correct! The Chechen war was marked by brutal fighting and significant human rights violations. The desire for independence was fueled by a longstanding struggle against Russian control. Remember the phrase 'The Fight for Freedom' — it encapsulates many of the republics' sentiments. Can anyone see how this connects to nationalism?

It shows how intense nationalism can lead to violent outcomes.

Absolutely. When marginalized groups feel suppressed, they may resort to violence. It’s a cycle of conflict that we see even today. How does this connect with other republics like Tajikistan?

Tajikistan had civil wars too, right? Similar reasons?

Yes! Economic strife and political instability led to a civil war that lasted years, showcasing how interconnected these issues are.
Economic Challenges Post-Soviet Union
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s now focus on the economic landscape. How did the transition to capitalism affect these republics?

I heard it was quite chaotic and led to many people becoming poor.

That’s a great insight! The term 'shock therapy' describes the rapid transition to a market economy. While intended to revitalize the economy, it often resulted in mass poverty. Can anyone think of a major impact of this economic strategy?

I suppose it created a big wealth gap between people.

Exactly! This economic inequality exacerbated dissatisfaction, fueling conflict. Let's remember the acronym E.C.A. for Economic Challenges and Aftermath. Any questions on how this contrasts with other regions' transitions?

Wasn’t there a difference in how quickly some countries transitioned?

Yes! Some regions fared better than others, which complicates their social and political landscapes. Complex, right?
Role of External Influences
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s look at the role of external powers. How have they affected the dynamics in these republics?

Countries like Russia wanted to maintain influence over their former states.

Very true! Russia viewed these areas as its 'Near Abroad,' leading to interventions in times of conflict. So, they perceived any movement toward independence as a threat. What does this suggest about international relations?

It shows that borders matter, but so do interests in the global arena.

Exactly, the geopolitical landscape became complex. The idea of national security often takes precedence over the sovereignty of states. Keep in mind the phrase 'Influence vs. Independence.'

Did Western nations also get involved?

Absolutely! Beyond the traditional East-West dynamic, Western nations begin to support various regimes or movements. Understanding this helps clarify the conflicts' roots. Would you like more examples from the current situation?
Conclusion: Current Implications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we wrap up, what implications do these tensions and conflicts have for today?

I think they still shape the politics in the region.

Right! The legacies of these conflicts still impact relations and stability today. It’s important to understand history for better future policies. Can anyone see a lesson from our discussion?

Addressing economic inequality seems key to reducing conflict.

Well said! Addressing root causes is essential in promoting peace. Always remember to apply the lessons from history to contemporary issues. Final thoughts?

I’d like to explore more about how external powers affect smaller nations.

That’s an excellent direction for further study!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section elaborates on the aftermath of the Soviet Union's disintegration, examining the civil wars and conflicts within various republics, including Chechnya and Tajikistan, as well as the role of external powers and economic challenges faced by the new states.
Detailed
Tensions and Conflicts
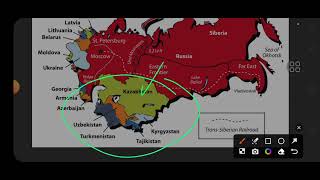
The disintegration of the Soviet Union in 1991 led to significant regional tensions and conflicts. Many of the former Soviet republics were prone to internal instability and civil wars due to a combination of economic inequality, authoritarian governance, and rising nationalist sentiments. For instance, the Chechen and Dagestani uprisings in Russia exemplified violent secessionist movements that emerged in this context.
The new political frameworks established across these republics did not always accommodate the aspirations of diverse ethnic groups, leading to ongoing clashes. In addition, the immediate economic aftermath of ‘shock therapy’ and the transition to capitalism left many people impoverished and created vast disparities between the rich and the poor. Countries like Tajikistan experienced prolonged civil wars, while other regions like Azerbaijan and Georgia witnessed secessionist movements fueled by ethnic tensions.
Moreover, the involvement of external powers compounded these conflicts. Russia’s view of its neighboring republics as its ‘Near Abroad’ influenced its approach to managing dissent within these territories. As the new states navigated their path toward independence, they faced pressures from global powers, resulting in a complex interplay of national identity and international relations that continues to evolve to this day.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Conflicts in Former Soviet Republics
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Most of the former Soviet Republics are prone to conflicts, and many have had civil wars and insurgencies. Complicating the picture is the growing involvement of outside powers.
Detailed Explanation
After the collapse of the Soviet Union, many republics faced internal conflicts and civil wars. This instability was intertwined with the influence of foreign countries, which may have their agendas in these regions. The mix of internal struggles and external interests made the political landscape even more complicated.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a neighborhood where families are fighting over property lines. If another family from a neighboring area moves in and starts giving advice to one side, it adds tension and confusion. Similarly, outside powers in post-Soviet states can escalate conflicts by supporting one faction over another.
Specific Conflicts: Chechnya and Dagestan
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In Russia, two republics, Chechnya and Dagestan, have had violent secessionist movements. Moscow’s method of dealing with the Chechen rebels and indiscriminate military bombings have led to many human rights violations but failed to deter the aspirations for independence.
Detailed Explanation
Chechnya and Dagestan have sought independence from Russia, leading to violent confrontations. The Russian government has responded with military force, which has often resulted in human rights abuses. This approach has not resolved the desire for independence among the local populations, demonstrating how violent methods can sometimes backfire.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a parent trying to stop a child from protesting by yelling or punishing them. Instead of calming the child, the harsh response could make the child more determined to express their feelings or fight back, which is what has happened in Chechnya and Dagestan.
Civil Wars in Central Asia
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In Central Asia, Tajikistan witnessed a civil war that lasted ten years until 2001. The region has many sectarian conflicts.
Detailed Explanation
Tajikistan’s civil war highlighted the fragility of new states formed after the Soviet Union's breakup. Ethnic and sectarian divides, which had been suppressed under Soviet rule, resurfaced and led to prolonged violence. This situation underscores the challenges of nation-building in contexts where historical grievances are deep-seated.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a school where students of different backgrounds are forced to work together on projects. If they were always separated and only learned about each other's differences, when they are put together without guidance, conflicts can arise. Similarly, in Tajikistan, the lack of preparation for diverse ethnic groups to coexist led to conflict.
Economic Inequality and Instability
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
As a result of democratic institutions not being prioritized alongside economic transformation, most countries had a strong executive president with the widest possible powers that rendered elected parliaments relatively weak.
Detailed Explanation
The transition from communism to democracy in former Soviet states often resulted in unbalanced power structures. Many presidents gained excessive powers, leading to authoritarian governance rather than true democracy. This situation frequently leads to public dissatisfaction and can fuel further conflicts.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a classroom where one student is allowed to make all the decisions about the class's activities. While it might be efficient in a small group, eventually, other students might feel frustrated and powerless, leading to disputes. In these countries, the lack of balance in governance has similar effects.
Resource Riches vs. Politics
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Countries like Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Russia, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan are major oil and gas producers. This wealth has attracted attention from outside powers, complicating local politics.
Detailed Explanation
The presence of rich natural resources in some post-Soviet states has made them strategically important to global powers, leading to external influences in their politics. These dynamics can foster corruption and inequality, as locals may not benefit equitably from the resources.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a lucrative lemonade stand suddenly becoming the center of attention in a neighborhood. Everyone wants a piece of it, leading to competition and disagreements among friends. Similarly, when countries have resources, outside interests may vie for control or influence, complicating the local political situation.
Cultural Connections and National Sentiment
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
India maintains good relations with all post-communist countries, but the strongest ties are with Russia, where Indian culture, especially films, remains popular.
Detailed Explanation
India's cultural influence, particularly through films, has helped foster strong connections with former Soviet countries, especially Russia. This cultural bond can serve as a bridge for political and economic partnerships, enhancing ties through shared interest and sentiment.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how fandom for a particular band can unite people across different backgrounds. If two fans of the same band meet, they instantly have something in common, which can lead to lasting friendships. Similarly, shared cultural interests like films can strengthen international relationships, as seen between India and Russia.
Key Concepts
-
Post-Soviet Conflicts: Refers to the various tensions and conflicts that arose following the Soviet Union's dissolution, particularly with nationalism and economic disparities.
-
Economic Struggle: A difficult transition from a planned economy to a market economy, leading to hardships and civil unrest in many states.
-
Nationalism vs. Secessionism: The conflict between the desire for national independence versus the desire to remain part of a larger political entity.
Examples & Applications
The conflict in Chechnya highlighted the violent struggle for independence in regions with significant ethnic diversity after the Soviet Union's disintegration.
Tajikistan experienced a prolonged civil war largely due to economic collapse and rising ethnic tensions, showcasing the repercussions of shock therapy.
Azerbaijan’s conflict in the Nagorno-Karabakh region illustrates ethnic tensions stemming from historical grievances.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
From East to West, nations divided, / In the name of pride, many decided.
Stories
Once upon a time, a land full of promise turned into chaos as people fought for their identity and the right to govern themselves.
Memory Tools
Use 'N.E.C.' for Nationalism, Economic challenges, and Conflict to remember the core issues.
Acronyms
SEC — Secession, Economic Struggle, Conflicts, for understanding the themes.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Nationalism
A political ideology that emphasizes the interests of a particular nation or group, often seeking independence or self-governance.
- Shock Therapy
A sudden and abrupt transition from state-controlled to free-market economics often resulting in economic hardship.
- Secessionism
The action of withdrawing formally from membership of a federation or body, especially a political state.
- Conflict
A serious disagreement or argument, often a prolonged struggle between groups or states.
- Economic Inequality
The unequal distribution of wealth and income within a population.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
