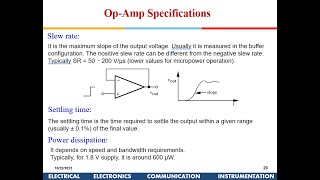
Slew Rate
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Slew Rate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the concept of slew rate in operational amplifiers. Can anyone tell me what they think slew rate means?

Is it about how quickly the output can change based on the input?

Exactly! The slew rate represents how fast the output voltage of an op-amp can change in response to a rapid change in the input signal. It's crucial for high-speed applications.

How is it measured?

Good question! It's typically measured in volts per microsecond, V/μs. Now, can anyone think of why this might be important?

If the slew rate is too low, the op-amp won't be able to accurately follow fast signals!

That's right! A low slew rate can lead to distortion in high-frequency signals.
Factors Affecting Slew Rate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand what slew rate is, let's discuss what affects it. Can anyone think of what might limit the slew rate?

Maybe the current from the output stage?

Exactly! The output stage's current limits how quickly the output can change. If we try to move the output too quickly, it may not be able to keep up.

And the load capacitance, right?

Correct! A higher load capacitance will also slow down the output's response times because more charge needs to be moved to change the output voltage.
Applications of Slew Rate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

How might a low slew rate impact real-world applications?

In audio applications, it could lead to distortion in the sound signal!

Yes, that's a great example. It could also affect how well an op-amp works in feedback systems too. What about in high-speed data conversion?

If the slew rate isn't fast enough, we could lose data integrity!

Exactly! Accurate signal following is critical in such applications. Understanding the slew rate helps engineers select the right op-amp.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Slew rate, expressed in volts per microsecond (V/μs), is essential for op-amps in high-speed applications as it determines the speed at which the output can follow the input signal changes. It is primarily limited by the output stage current and load capacitance.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Slew Rate
The slew rate is a significant performance indicator for operational amplifiers, particularly for those used in high-speed applications. It measures how quickly the output voltage of the op-amp can respond to a rapid input signal change. The slew rate is expressed in volts per microsecond (V/μs).
Key Concepts
- The slew rate is critical because it affects the dynamic response of an op-amp in circuits such as audio amplification, signal conditioning, and data conversion.
- It is influenced mainly by two factors: the amount of current that can be sourced or sunk by the output stage and the load capacitance connected to the op-amp output.
Understanding the slew rate helps in selecting the appropriate op-amp for specific applications and ensures optimal performance in signal processing tasks.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Slew Rate
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The slew rate defines how quickly the output voltage of the op-amp can change in response to a fast change in the input signal. It is an important metric for high-speed applications.
Detailed Explanation
The slew rate is an essential parameter when assessing the performance of an operational amplifier (op-amp). It measures the speed at which an op-amp can respond to rapid changes in input signals. The faster the output voltage can change, the better the op-amp can handle high-frequency signals without distortion. In high-speed applications, like audio processing or fast signal conditioning, having a suitable slew rate ensures that the output accurately reflects rapid variations in the input without delay or distortion.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a water faucet. If you turn it on quickly, the water pressure increases and reaches its peak instantly, similar to a high slew rate where the output voltage quickly adjusts. If the faucet takes time to respond and build pressure, it represents a low slew rate. In an audio amplifier, a high slew rate ensures that rapid sound signals are reproduced clearly without any lag, similar to how fast-moving water delivers a consistent flow.
Measurement of Slew Rate
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Slew Rate: It is typically expressed in volts per microsecond (V/μs) and is limited by the current available in the output stage and the load capacitance.
Detailed Explanation
Slew rate is quantified in units of volts per microsecond (V/μs). This metric indicates how many volts the output can change per microsecond. For example, a slew rate of 1 V/μs means the op-amp can change its output by 1 volt every microsecond. However, the ability of the op-amp to achieve a certain slew rate is not unlimited. It is primarily constrained by the current available in the output stage of the op-amp; higher output current capability allows for a faster change. Additionally, the load capacitance affects the slew rate. A higher capacitance requires more current to charge or discharge, thereby slowing the output response.
Examples & Analogies
Think of charging your smartphone battery. If you try to charge it (increase voltage) using a 5-watt charger, it will take longer than if you use a 20-watt charger. Similarly, in an op-amp, a higher current available at the output can increase the slew rate. Additionally, if your battery is large (analogous to higher load capacitance), it may take longer to charge, which represents a slower response in changing voltage.
Key Concepts
-
The slew rate is critical because it affects the dynamic response of an op-amp in circuits such as audio amplification, signal conditioning, and data conversion.
-
It is influenced mainly by two factors: the amount of current that can be sourced or sunk by the output stage and the load capacitance connected to the op-amp output.
-
Understanding the slew rate helps in selecting the appropriate op-amp for specific applications and ensures optimal performance in signal processing tasks.
Examples & Applications
In audio applications, a high slew rate ensures that fast transients in sound are accurately reproduced without distortion.
In data conversion applications, a fast slew rate is crucial for accurate representation of high-frequency signals.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Slew rate is the name of the game, keep it fast to avoid distortion’s claim.
Stories
Imagine an op-amp at a race, needing to keep pace with a fast signal. If it can't change quickly, the sound gets distorted—just like a car falling behind in a race.
Memory Tools
SLEW - Speed Limits Every Output Wave.
Acronyms
S.R.=S (speed) R (rate) for responding to signals.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Slew Rate
The maximum rate of change of the output voltage of an op-amp, typically expressed in volts per microsecond (V/μs).
- OpAmp
An operational amplifier, a key analog component used for signal conditioning, amplification, and filtering.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
