Top-Down Approach
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Top-Down Approach
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're discussing the top-down approach in CMOS op-amp design. This method starts systematically by specifying the overall performance parameters like gain and bandwidth. Can anyone tell me why starting from a high-level view is beneficial?

I think it helps ensure that all parts of the design will work together effectively.

Yeah, and it allows for adjustments early in the process.

Exactly! This high-level specification guides the entire design. We focus on main attributes first. What performance parameters do you think are most critical?

Gain and bandwidth seem really important for performance.

Correct! Gain and bandwidth are crucial. Now, let's explore how we refine each stage after establishing these parameters.
Iterative Design Process
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we design, we iteratively refine each stage. What do you think is the first stage we begin with?

It must be the input stage, right? The differential pair?

Yes! The differential pair is essential for amplifying the input signal.

Great observations! We need to ensure that the input stage meets our gain specifications. Once that's set, we can proceed to the next stages. How does this iterative process help us?

It allows us to test performance at every step, making it easier to catch issues.

Absolutely! Each iteration helps fine-tune the design, promoting efficiency and accuracy.
Performance Parameters Focus
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

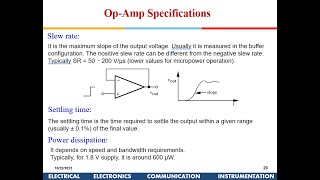
Let's dive deeper into the performance parameters. Why do you think performance metrics like slew rate and unity gain bandwidth are vital for op-amps?

They determine how well the op-amp can handle fast incoming signals.

If they aren't met, the op-amp won't function effectively in its intended application.

Exactly! Metrics like slew rate help us gauge how responsive our design will be. Remember that these specifications guide our design choices.
Final Thoughts on Top-Down Approach
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, the top-down approach is an integral strategy in op-amp design. By specifying and focusing on performance parameters first, we can create a robust design. Any final questions?

How does this differ from the bottom-up approach?

Great question! While the top-down approach specifies goals first, the bottom-up focuses on the components first before assembling them into a system. Each has its benefits depending on the design requirements.

Thanks for clarifying that!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, the top-down approach is discussed as a methodology for CMOS operational amplifier design where designers first define performance metrics such as gain, bandwidth, and slew rate. The design evolves iteratively from the input stage to the output stage, ensuring that each component aligns with the final design goals.
Detailed
Top-Down Approach in CMOS Op-Amps
The top-down approach is a strategic method in designing CMOS operational amplifiers (op-amps) that starts with identifying the essential performance metrics like gain, bandwidth, and slew rate. This method focuses on establishing the overall architecture before delving into specific components. Designers iteratively refine each stage, transitioning from the input stage (often a differential pair) through to the output stage. By emphasizing performance at each level, designers can optimize the op-amp's characteristics for applications that demand high precision and minimal power consumption, aligning the final product with the prescribed specifications.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of the Top-Down Approach
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A top-down design approach involves specifying the required performance parameters (e.g., gain, bandwidth, slew rate) and iteratively designing each stage of the op-amp, starting from the input stage (differential pair) to the output stage.
Detailed Explanation
The top-down design approach starts with defining what performance the operational amplifier (op-amp) needs to deliver, such as how much gain it should provide, its bandwidth capabilities, and the maximum rate at which its output can change (slew rate). After these specifications are established, the design progresses through the various stages of the op-amp from the input to the output. Each stage is designed iteratively, meaning adjustments are made based on how the design performs in relation to the set specifications.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're planning a road trip. Before setting off, you decide your destinations (performance parameters like gain and bandwidth) and map out your route (the design stages). You might start with the first leg of the journey (the input stage), checking and adjusting your plan as you travel towards your final destination (the output stage), ensuring you stay on course to meet your goal.
Key Concepts
-
Performance Specification: Establishing the required parameters before beginning design.
-
Input Stage Design: Starting with the differential amplifier to meet specified gain.
-
Iterative Refinement: Revising each design stage, ensuring alignment with overall goals.
Examples & Applications
Designing a CMOS op-amp for an audio application where high performance is due to top-down specifications.
Iteratively refining a design to meet a target bandwidth of 100kHz.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Top-down we go, define it fast, refine every stage, ensure it will last.
Stories
Imagine a chef crafting a multi-layered cake. First, they decide on the flavors (performance specs), then they layer frosting and cake iteratively, adjusting height and consistency until perfect.
Memory Tools
Think 'GIVE' for performance goals: Gain, Input stage, Verify, and Engage each component.
Acronyms
Remember 'TISP' for the top-down method
Target
Input design
Specify
Perform iteratively.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- TopDown Approach
A design methodology that starts from high-level specifications and iteratively refines each component of the design.
- Performance Parameters
Metrics such as gain, bandwidth, and slew rate that define the effectiveness of an operational amplifier.
- Iterative Process
A method of design where components are revised and improved through repeated cycles.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
