Signal Detection and Matching
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Correlation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore the concept of correlation and its role in signal detection. Can anyone tell me what correlation means in the context of signals?

Isn't it a way to measure how similar two signals are?

Exactly! Correlation measures the similarity between two signals as a function of time shift. This means we can see how one signal aligns with another over time.

So, it helps us find patterns in signals?

Precisely! It's used to detect specific waveforms within larger signals. Let’s remember the keyword 'similarity' when we think about correlation.
Cross-Correlation Explained
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss cross-correlation. Can anyone explain what cross-correlation is?

Isn't that when we correlate two different signals?

Yes, cross-correlation specifically compares two different signals. This technique is crucial for identifying the similarity or time delays between them.

How is it different from regular correlation?

Great question! Regular correlation can involve one signal being correlated with itself, while cross-correlation involves comparing two different signals. Remember, cross-correlation is vital in applications like detecting echoes in audio processing.
Applications of Signal Detection
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s turn to applications. Who can share an example where signal detection might be important?

In audio processing, we need to detect speech patterns!

Correct! Detecting specific patterns in audio signals is a critical application. Signal detection helps in identifying keywords in voice recognition technologies.

What about in communications?

Absolutely! Signal detection is essential for identifying and extracting information from transmitted signals over various media. Remember, detection leads to efficiency in communication systems!
Summary and Recap
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, we’ve discussed correlation and its role in signal detection. Can someone summarize what we learned?

We learned that correlation measures how similar two signals are, and cross-correlation allows us to compare them.

Also, it has real-world applications in audio processing and communication systems!

Excellent summary! Remember, detecting and matching signals visually and auditorily helps us understand signal processing better.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, the focus is on how correlation is utilized for signal detection and pattern matching. It explains the concept of cross-correlation as a method for comparing two signals, helping to identify delays or similarities between them, and highlights its applications in various fields of signal processing.
Detailed
Signal Detection and Matching
This section delves into the concept of signal detection and matching through correlation, detailing how it applies to identifying specific patterns within larger datasets. Correlation is a crucial tool in various applications, enabling the comparison of signals by measuring their similarity across different time lags. The concept of cross-correlation is notably highlighted, which is instrumental in determining the degree of similarity between two signals, facilitating tasks such as delay detection and feature recognition.
Key Points:
- Correlation serves as an essential technique in pattern matching and signal detection, where the goal is to find a particular waveform within a larger signal.
- Cross-correlation helps compare two signals to identify similarities or delays, vital in practical applications such as audio processing and data analysis.
The ability to effectively detect and match signals can lead to advancements in technology and improved signal processing methodologies.
Youtube Videos
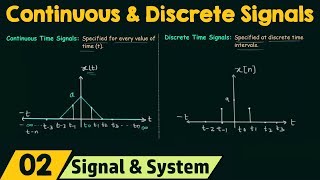

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Signal Detection
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Correlation is used in signal detection and pattern matching. For example, finding a specific waveform within a larger signal can be achieved by correlating the signal with a reference template.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the concept of signal detection, emphasizing the role of correlation in this process. Correlation helps to find a specific waveform or pattern within a larger dataset or signal by comparing it to a predefined template. When these two signals are aligned, their correlation value will be higher, indicating a matching pattern.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're at a crowded concert and trying to find your friend. You might shout their name and listen for their voice. If they respond (the correlation of your voice and their voice), you know you've detected them in the crowd. In a similar way, correlation helps to detect specific patterns in signals.
Cross-Correlation for Signal Comparison
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Cross-correlation is particularly useful for comparing two signals, like detecting delays or similarities between them.
Detailed Explanation
Cross-correlation is a technique used to compare two different signals to identify differences such as time delays and similarities. When applying cross-correlation, one signal is shifted over time against another, allowing us to observe where the two signals align best. This is crucial in applications where timing is essential, such as in communications or audio processing.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like two people playing catch. If one person throws the ball to another, the timing of the throw and the catch can be crucial. If they throw at just the right moment, the catch happens smoothly. In signal processing, cross-correlation helps identify those moments when two signals 'throw' and 'catch' at the right time.
Key Concepts
-
Correlation: Measurement of similarity between two signals.
-
Cross-Correlation: Comparing two different signals to find delays.
Examples & Applications
Example of correlation can be detecting specific vocal patterns in music signals.
An application of cross-correlation might involve analyzing time delays in a radar system.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When signals align, it's correlation divine, matching them by time, so their patterns combine.
Stories
Imagine two friends trying to find a common beat in a song—they listen at different times until they sync their tunes; this is like correlation in action!
Memory Tools
C for Comparison, C for Cross—remember, cross-correlation measures the comparison of distinct signals.
Acronyms
CC stands for 'Compare and Contrast' for Cross-Correlation.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Correlation
A measure of similarity between two signals as a function of the time-lag applied to one of them.
- CrossCorrelation
A technique used to compare two different signals to identify similarities or time delays.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
