Post-Earthquake Performance Considerations
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Structural Monitoring
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's dive into structural monitoring. Why is it important after an earthquake?

To see if the building is still safe to use?

Exactly! We use sensors to assess the performance of the structure during quakes. Can anyone think of the benefits of having real-time data?

It helps identify damages quickly, right?

Yes, it allows for timely decision-making regarding repairs or evacuations. Remember the acronym 'SOAR' – Sensor Observation And Response!

That's a great way to remember it!

So, in summary, structural monitoring is about keeping us informed on building health after seismic events.
Damage Assessment
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's discuss damage assessment. What should we do after an earthquake?

Inspect the building for damage?

Absolutely! We conduct both visual and instrumental inspections. Why do we need both?

Visual inspections are quick, but instrumental ones can detect deeper issues!

Great insight! This methods ensure safety before re-occupying the building. Use the mnemonic 'VIVA' – Visual Inspection, Verify Assessment.

That’s helpful! I think I’ll remember it.

To sum up, thorough damage assessment is critical for safety and function.
Resilience Planning
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s move on to resilience planning. What does that involve?

Planning how to help people evacuate safely and quickly?

Yes! It's about emergency evacuation and ensuring access for repairs. Why is continuity of function critical?

To keep essential services running after a disaster?

Right! Remember the acronym 'CARE' – Continuity And Recovery Efforts. It helps remind us of the key elements in resilience planning.

That makes it easier to recall!

In summary, resilience planning is essential for minimizing the impacts of earthquakes on communities.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Post-earthquake performance considerations involve the use of structural monitoring to assess building performance, conducting thorough damage assessments with visual and instrumental inspections, and developing resilience planning that includes emergency evacuation, repair access, and continuity of function.
Detailed
Post-Earthquake Performance Considerations
In the aftermath of an earthquake, it is crucial for civil engineers and building managers to evaluate the integrity and operational capacity of structures. This section discusses three critical aspects of post-earthquake performance:
- Structural Monitoring: The use of advanced sensors allows for real-time assessment of structural performance during seismic events. This helps in understanding the dynamics of the building under duress and identifying any potential weaknesses.
- Damage Assessment: It is essential to conduct thorough inspections—both visual and instrumental—immediately following a seismic event to evaluate any structural damages. This assessment helps in determining whether a building is safe for occupancy and identifies necessary repairs.
- Resilience Planning: Effective resilience planning incorporates provisions for emergency evacuation, ensuring that repair access is available, and maintaining continuity of function for critical infrastructure and services. This promotes recovery and reduces downtime for building operations, significantly benefiting the community impacted by the earthquake.
Overall, these considerations are vital in ensuring the safety, functionality, and resilience of structures in post-earthquake scenarios.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Structural Monitoring
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Use sensors to assess building performance during quakes.
Detailed Explanation
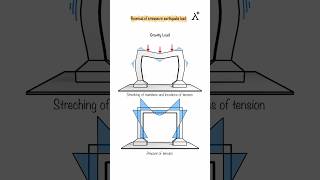
Structural monitoring involves placing sensors on buildings to collect data on how they perform during an earthquake. These sensors can measure vibrations, shifts, and other critical changes in the structure's integrity. The data collected helps engineers understand how well the building has withstood seismic forces and can identify areas that may have sustained damage.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a fitness tracker that monitors your heart rate, steps, and other health metrics during a workout. Just like the tracker provides feedback on your physical health, sensors on buildings give real-time data on their structural health during an earthquake. This information can help engineers assess whether the building is safe for occupancy afterward.
Damage Assessment
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Conduct visual and instrumental inspection post-event.
Detailed Explanation
Damage assessment is the process of evaluating a building after an earthquake to identify any structural harm. This can involve visual inspections, where engineers look for cracks, deformations, or other visible signs of damage, as well as instrumental inspections that utilize technology to detect issues that may not be immediately visible. This comprehensive approach ensures that all potential problems are recognized before the building is used again.
Examples & Analogies
Think of how you would inspect your car after a rough drive. You would look for dents, scratches, or anything that seems out of place. In a similar way, engineers inspect buildings after an earthquake to see what's damaged and what needs repair, ensuring safety before anyone uses the building again.
Resilience Planning
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Include provisions for emergency evacuation, repair access, and continuity of function.
Detailed Explanation
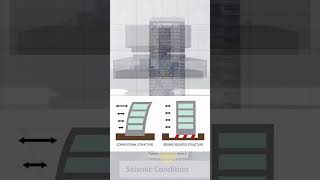
Resilience planning involves creating strategies to ensure that a building can quickly regain its functionality after an earthquake. This includes planning for emergency evacuation routes for occupants, facilitating access for repair crews, and ensuring that critical functions of the building can continue. The goal is to minimize disruption and ensure safety while planning for efficient recovery from seismic events.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the difference between having a fire drill and not having one. If a fire occurs, those who practiced the drill know exactly how to evacuate safely and quickly. Similarly, resilience planning in the context of earthquakes prepares the building and its occupants to respond effectively, ensuring they know how to exit safely and what to do next.
Key Concepts
-
Structural Monitoring: The use of technology to track the performance of structures during seismic events.
-
Damage Assessment: Critical inspections needed to evaluate the extent of structural harm post-earthquake.
-
Resilience Planning: Proactive strategies to ensure buildings can recover and remain operational after a quake.
Examples & Applications
After a moderate earthquake, sensors in a tall building might indicate slight deformations. Engineers would analyze this data to assess safety.
Following an earthquake, a rapid visual inspection might reveal cracks in walls, while a more detailed instrumental inspection could uncover deeper structural issues.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In quakes we say don't look away, monitor structures night and day!
Stories
After an earthquake, Sarah used sensors in her building to check its safety, gathering data to help her community recover swiftly.
Memory Tools
To remember the steps: M - Monitor; A - Assess; P - Plan for resilience.
Acronyms
Use 'DREAM' for Damage assessments
- Determine
- Review
- Examine
- Assess
- Mitigate.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Structural Monitoring
The use of sensors to assess the performance and integrity of structures during and after seismic events.
- Damage Assessment
The process of evaluating and quantifying damages to a structure following an earthquake, involving both visual and instrumental inspections.
- Resilience Planning
Strategies developed to ensure safety, recovery, and operational continuity after an earthquake.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
