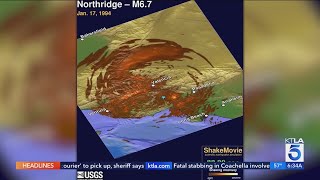
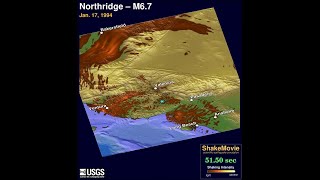
The 1994 Northridge Earthquake, USA
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of the Northridge Earthquake
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss the Northridge earthquake that struck on January 17, 1994. Can anyone tell me its magnitude?

Was it around 6.7?

That's correct! It registered a magnitude of 6.7. What do you think were some consequences of such a significant quake?

I remember it caused a lot of damage.

Exactly, it resulted in over 9,000 injuries and a staggering economic loss of about $44 billion. Let's remember the acronym 'NICE': Northridge, Injuries, Costs, and Engineering insights.

That’s a good way to remember the key points!

Yes! And it helps to recall the event's significance in terms of engineering practices.
Engineering Observations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's explore the engineering observations from the Northridge earthquake. What do you think 'blind thrust faulting' means?

Is it when a fault moves without causing ground movement on the surface?

Exactly! That’s what makes it particularly dangerous. The fault in Northridge didn’t rupture the surface, which contributed to its severity. What kind of buildings were mostly affected?

I think soft-story buildings were impacted significantly.

That’s correct! They were vulnerable, and the strong ground motions were beyond what designs anticipated at that time. Can anyone recall a lesson learned from the event?

They had to revise the seismic codes afterward.

Exactly! New codes now focus on retrofitting older buildings to better withstand such quakes.
Impact and Lessons Learned
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s wrap up by discussing the impacts and lessons learned from the Northridge earthquake. What do we know about the human and economic toll?

57 people died, and there were over 9,000 injuries.

Very true! The economic losses were also estimated at $44 billion. What can these figures tell engineers about building practices?

It shows that we need to prepare better and enforce stricter building codes.

Exactly right! The tragedy of the Northridge earthquake highlighted the crucial need for retrofitting older buildings, enforcing seismic design codes, and enhancing public safety measures in vulnerable structures. Remember, LUCA: Losses, Understanding engineering, Codes, and Awareness.

I’ll definitely use that to remember the key implications!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
On January 17, 1994, a 6.7 magnitude earthquake struck Northridge, California, resulting in 57 fatalities and over 9,000 injuries, along with economic losses estimated at $44 billion. Key engineering insights from this event highlighted the need for improved seismic codes.
Detailed
The 1994 Northridge Earthquake
The 1994 Northridge earthquake occurred on January 17, with a magnitude of 6.7. Its epicenter was located in Northridge, California, at a depth of 18.4 km. This earthquake caused significant devastation, with 57 lives lost and over 9,000 individuals injured. The economic impact was enormous, with losses reaching approximately $44 billion.
Engineering Insights
The Northridge earthquake was characterized by blind thrust faulting, which did not produce surface rupture. Its damage was particularly severe in soft-story buildings and welded steel moment-frame structures, showcasing vulnerabilities in existing engineering practices. Strong ground motions were recorded that exceeded design levels, leading to a thorough reevaluation of seismic design practices, culminating in revised codes to address the previously overlooked vulnerabilities of certain construction types, chiefly soft-story and steel frame structures.
The lessons learned from the Northridge earthquake emphasized the importance of retrofitting older buildings to ensure greater resilience to such seismic events in the future.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Location and Magnitude
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Date: January 17, 1994
• Magnitude: 6.7
• Epicenter: Northridge, California
• Depth: 18.4 km
Detailed Explanation
The Northridge Earthquake occurred on January 17, 1994, with a magnitude of 6.7 on the Richter scale. This earthquake was centered in Northridge, California, at a depth of 18.4 kilometers. Understanding the epicenter and magnitude helps assess the potential impact and damage, as these factors determine how energy is released during an earthquake and where the most severe effects will be felt.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the magnitude of an earthquake like the volume of music. A louder volume (higher magnitude) can cause greater disturbance (more damage) in a room (the environment) compared to softer music. Here, Northridge’s deep ‘volume’ made it powerful enough to cause significant destruction, even at that distance underground.
Damage and Impact
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• 57 people killed, over 9,000 injured
• Economic losses estimated at $44 billion
• Major freeway overpasses and buildings collapsed
Detailed Explanation
The Northridge Earthquake resulted in devastating consequences: 57 fatalities and over 9,000 injuries, along with extensive property damage leading to an estimated economic loss of $44 billion. Major freeway overpasses and various buildings collapsed, highlighting the vulnerabilities in infrastructure design and emergency preparedness at that time.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a large group of people at a concert; if a sudden loud sound interrupts, not only might some people get hurt in the chaos, but the event (like the concert) loses a lot — tickets, food sales, and future events. Similarly, the Northridge Earthquake not only caused loss of life but led to huge financial losses and disrupted services in Los Angeles.
Engineering and Geological Observations
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Blind thrust faulting without surface rupture.
• Damage concentrated in soft-story buildings and welded steel moment-frame structures.
• Strong ground motions recorded exceeding design levels.
Detailed Explanation
This earthquake was primarily caused by 'blind thrust faulting,' which means the fault did not visibly rupture the ground surface. The damage was particularly severe in soft-story buildings (structures with parking or open floors below) and welded steel moment-frame structures, which were not designed to withstand the forces generated by the earthquake. Strong ground motions occurred that exceeded what many buildings were designed to handle, leading to severe structural failures.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a multi-layer cake, where the bottom layer is significantly weaker than the layers above it. If you place heavy decorations on top, the weak layer might collapse under the weight. Similarly, buildings not designed for heavy shaking can fail when an earthquake hits, especially if their base isn’t strong enough.
Lessons Learned
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Revised seismic codes to address vulnerability of soft-story and steel frame structures.
• New emphasis on retrofitting older buildings and infrastructure.
Detailed Explanation
The Northridge Earthquake led to significant changes in engineering practices and building codes. Following the disaster, there was a focus on revising seismic codes to improve the safety of soft-story and steel frame structures. There was also a heightened emphasis on retrofitting older buildings to better withstand future earthquakes, which has become integral in protecting life and property.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a school learning from a fire drill. If students notice a weakness in the fire exit routes during practice, they will improve those routes to ensure safety during a real emergency. The same goes for buildings — after the Northridge event, engineers reassessed and improved structures to prepare for the chance of future earthquakes.
Key Concepts
-
Magnitude 6.7: The earthquake's strength, indicating significant energy release.
-
Blind Thrust Faulting: A seismic event with no surface rupture, presenting unique hazards.
-
Economic Loss: Financial toll on infrastructure, estimated at $44 billion.
Examples & Applications
The Northridge earthquake's impacts led to revisions in building codes, focused especially on soft-story structures.
Economic losses of $44 billion highlight the importance of disaster preparedness and resilient infrastructure.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Northridge shook with a mighty quake, safety codes we must remake.
Stories
Imagine a city where buildings wobble and sway; Northridge taught us to design them better each day to keep everyone safe.
Memory Tools
Use 'NICE' (Northridge, Injuries, Costs, Engineering) to remember the key implications of the earthquake.
Acronyms
LUCA (Losses, Understanding engineering, Codes, Awareness) helps recall the lessons learned from the Northridge event.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Blind Thrust Faulting
A type of faulting where a fault does not rupture the earth's surface.
- SoftStory Buildings
Buildings with weak ground levels, often failing in earthquakes.
- Seismic Codes
Regulations set to ensure structures can withstand seismic activity.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
