Active Control Systems
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Active Control Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss active control systems. Can anyone tell me what an active control system is?

Is it a system that counteracts vibrations in structures?

Exactly! Active control systems apply external energy to negate vibrations. The key components include sensors, controllers, and actuators. Who can explain what each component does?

Sensors detect vibrations!

Controllers process the signals from the sensors.

And actuators apply forces to counteract the vibrations!

Great job! Remember the acronym SCA, which stands for Sensors, Controllers, and Actuators, to help you recall these components universally.

In summary, Active Control Systems combine these elements to manage vibrations effectively.
Control Algorithms in Active Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive into the control algorithms used in active control systems. Who knows any?

I believe PID is one of them.

Correct! PID stands for Proportional-Integral-Derivative. It’s widely used due to its simplicity. Does anyone know another algorithm?

What about the Linear Quadratic Regulator?

Yes, the LQR helps design optimal control strategies while minimizing energy usage. Another important algorithm is H-infinity, used for robust control. Can anyone remind us what robustness means in this context?

It means the system can function under varying conditions.

Exactly! To remember, think R for Robustness and LQR for Linear Quadratic Regulator! In summary, these control algorithms play vital roles in enhancing performance in active control systems.
Applications and Challenges of Active Control Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's look at where active control systems are typically applied. Can anyone think of some applications?

They are used in laboratories, where precision is key.

Correct! They are also used in precision equipment buildings and even in space structures. But what challenges do these systems face?

High cost and complex maintenance?

And they need a constant power supply!

Precisely! These factors can limit their implementation. Just remember the acronym PCL – Power, Cost, and Maintenance – when considering the drawbacks of active control systems.

In summary, while active control systems are effective, we must be mindful of their challenges when implementing them in real-world scenarios.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Active control systems are designed to counteract vibrations by applying external energy through sensors, controllers, and actuators. These systems are effective in certain applications, though they come with challenges such as high costs and reliance on power.
Detailed
Active Control Systems
Active control systems are crucial in reducing vibrations in structures subjected to dynamic loads, such as those induced by seismic activity. They operate by utilizing a combination of sensors, controllers, and actuators that apply external energy to counteract unwanted movements. The main components include:
- Sensors: Detect motion and provide feedback on vibration levels.
- Controllers: Process sensor data to determine the necessary adjustments.
- Actuators: Apply forces to counteract negative vibrations.
Control algorithms, such as PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative), Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR), and H-infinity, guide the system's response and control dynamics effectively.
Applications and Limitations
Active control systems find their applications in environments requiring high precision, like laboratories, precision equipment buildings, and space structures. However, they face several challenges, including:
- High Cost: Implementation and maintenance can be expensive.
- Power Dependence: Systems often require continuous power to function.
- Complex Maintenance: The operational complexities necessitate ongoing maintenance and expertise.
In summary, while active control systems provide innovative solutions for vibration control, their limitations must be carefully weighed against their benefits.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Principles of Active Control
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Function: Apply external energy to counteract vibrations using actuators and sensors.
• Components:
– Sensors (to detect motion)
– Controllers (to process signals)
– Actuators (to apply forces)
• Control Algorithms: PID, Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR), H-infinity, etc.
Detailed Explanation
Active control systems work by using energy to oppose vibrations in a structure. They do this using three key components: sensors, controllers, and actuators. Sensors detect the motion caused by vibrations, sending this information to controllers which process the signals. Based on the processed data, actuators apply forces to counteract the detected vibrations, stabilizing the structure. The algorithms used to determine how these components interact include methods like PID (Proportional, Integral, Derivative) controls, LQR (Linear Quadratic Regulator), and H-infinity control.
Examples & Analogies
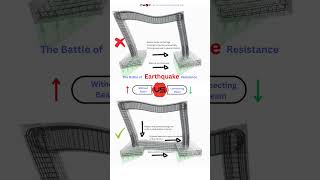
Imagine a person standing on a small boat in the water. As the waves rock the boat, they use paddles to push against the waves, trying to stabilize themselves. Just like the paddles, actuators in an active control system push back against the vibrations to keep a building steady during an earthquake.
Applications and Limitations
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Applications:
– Laboratories
– Precision equipment buildings
– Space structures
• Challenges:
– High cost
– Power dependence
– Complex maintenance
Detailed Explanation
Active control systems are particularly useful in environments where precision is crucial. They are commonly found in laboratories, buildings housing sensitive equipment, and structures in space. Despite their effectiveness, they come with significant challenges, such as high installation and operational costs. Additionally, they require a constant power supply, and maintaining these systems can be complex and costly.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a high-tech research laboratory that requires extremely stable conditions for experiments. Like using a very expensive laser that needs precise adjustments constantly, active control systems allow for intricate adjustments to counteract unwanted vibrations. However, just as these lasers need regular maintenance and can be costly, active control systems also require significant resources and expertise.
Key Concepts
-
Active Control Systems: Systems that use energy inputs to counteract vibrations.
-
Sensors: Devices that detect and measure vibrations.
-
Controllers: Components that process sensor data for system adjustments.
-
Actuators: Mechanisms that exert forces to reduce vibrations.
-
Control Algorithms: Methods to determine system responses and strategies.
Examples & Applications
Active control systems are applied in seismic-resistant buildings where they mitigate the effects of earthquakes.
High-precision laboratories use active control systems to ensure sensitive equipment remains stable despite external vibrations.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Sensors sense the shake, Controllers make no mistake, Actuators take a stand, To keep our structures grand!
Stories
Imagine a team of engineers battling excessive vibrations during an earthquake. The Sensors detect the tremors, Controllers outline a strategic plan, and Actuators spring into action, binding the team together to ensure structural stability and safety.
Memory Tools
Remember SCA: Sensors, Controllers, Actuators to keep vibrations at bay.
Acronyms
Use the acronym PCL (Power, Cost, Limitations) to recall the challenges that active control systems face.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Active Control Systems
Systems that utilize external energy to counteract vibrations in structures through actuators and sensors.
- Sensors
Devices that detect motion and provide data on vibration levels.
- Controllers
Components that process signals from sensors to determine necessary adjustments.
- Actuators
Devices that apply forces to counteract vibrations based on controller signals.
- Control Algorithms
Mathematical strategies used to determine how systems respond, including PID and LQR.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
