Introduction to Communication Protocols for Embedded Systems
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Communication Protocols
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore the importance of communication protocols in embedded systems. Can anyone tell me why these protocols are crucial?

They help in data exchange between microcontrollers and other devices.

Exactly! They enable communication that allows sensors to send data to microcontrollers. Let’s remember: Protocols = Communication!

What protocols are commonly used?

Great question! The two most common protocols are I2C and SPI. Both are vital for sensor integration. I’ll explain further in our next session!
Overview of I2C and SPI
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s delve into I2C and SPI. Who can share what they know about I2C?

I think it uses two wires for communication?

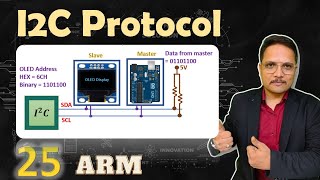
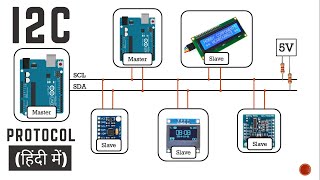
Correct! I2C uses two wires: SCL for the clock and SDA for data. Now, does anyone know how many devices can it connect?

Multiple devices!

Yes! It allows multiple masters and slaves. Now, transitioning to SPI, it uses four wires and supports full-duplex communication, which means it can send and receive data simultaneously.
Pros and Cons of I2C and SPI
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s analyze the pros and cons of each protocol. What are some advantages of I2C?

It’s simpler with just two wires?

Absolutely! And it’s ideal for lower-speed devices. However, what about the downsides?

It’s slower than SPI?

Yes, that's right! Now for SPI, its advantages include faster data transfer. Can anyone mention a disadvantage?

It requires more wires?

Exactly! So remember, speed vs. simplicity: I2C for simplicity, SPI for speed!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section introduces the importance of communication protocols like I2C and SPI in embedded systems. These protocols facilitate data transfer between microcontrollers and external devices, enabling sensor integration and control of various peripherals.
Detailed
In embedded systems, communication protocols play a pivotal role in enabling data exchange between microcontrollers and external devices such as sensors, actuators, and peripherals. These protocols facilitate seamless interaction, allowing sensors to transmit data to the microcontroller and enabling control over various devices. Among the most widely used protocols for sensor integration are I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) and SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface). Both protocols are designed for efficient data transfer with simple wiring. This chapter offers an in-depth overview of these communication protocols, detailing their operation, differences, and practical applications in interfacing with sensors in embedded systems.
Youtube Videos
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Communication Protocols
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In embedded systems, communication protocols are crucial for enabling data exchange between microcontrollers and external devices like sensors, actuators, and peripherals.
Detailed Explanation
Communication protocols are like the languages that microcontrollers and external devices use to talk to each other. These protocols ensure that data can smoothly flow from a sensor to a microcontroller, or from the microcontroller to an actuator. In embedded systems, these protocols are essential because they allow devices to interact and function together effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Think of communication protocols like the set of rules and signs used in traffic systems. Just as traffic lights and road signs guide cars safely through intersections, communication protocols guide data between devices to ensure they don't collide and function correctly.
Functions of Communication Protocols
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These protocols allow sensors to transmit data to the microcontroller and enable the microcontroller to control or interface with other devices.
Detailed Explanation
Communication protocols serve two main functions: they allow sensors to send data to the microcontroller and let the microcontroller send commands to other devices. This back-and-forth data exchange is essential for the system to respond to sensor inputs and control actuators or peripherals based on that data.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a school classroom where a teacher (the microcontroller) instructs students (the sensors) to perform tasks. The students report back to the teacher about their tasks, enabling the teacher to make decisions and give further instructions based on the information received. This dynamic interaction is similar to how communication protocols work.
Overview of Common Protocols: I2C and SPI
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
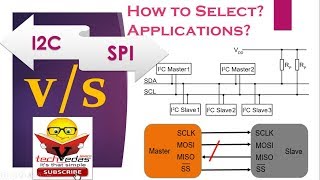
Two of the most widely used communication protocols for sensor integration are I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) and SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface). Both of these protocols are designed for connecting multiple devices to a microcontroller with relatively simple wiring and efficient data transfer.
Detailed Explanation
I2C and SPI are the two dominant communication protocols in embedded systems. I2C uses two wires for communication and allows multiple devices to connect to the same lines, making it very efficient for low-speed data transfer. SPI, on the other hand, uses more wires but offers faster data transfer rates and supports simultaneous communication. Understanding the differences and applications of both protocols helps in deciding which one to use in a project.
Examples & Analogies
Think of I2C and SPI like public transportation systems. I2C is like a bus that can carry many passengers on a single route, making it easier but slower. In contrast, SPI is like a series of taxis that can take each passenger directly to their destination quickly, ideally suited for those who need faster service.
Purpose of the Chapter
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This chapter provides an overview of I2C and SPI communication protocols, including how they work, their differences, and how to use them to interface with sensors in embedded systems.
Detailed Explanation
This chapter aims to equip readers with a foundational understanding of the I2C and SPI protocols. It details how to implement these protocols in real-world applications, specifically in sensory data collection and actuator control. By understanding the nuances of both protocols, students can make informed decisions when designing their embedded systems.
Examples & Analogies
Consider this chapter as the syllabus for a cooking class focused on Italian and Mexican cuisines. It will cover the ingredients, cooking techniques, and cultural significance of each dish, preparing students to create their own culinary masterpieces effectively.
Key Concepts
-
Communication Protocols: Essential for data exchange between microcontrollers and devices.
-
I2C: A two-wire protocol ideal for multiple device integration.
-
SPI: A four-wire protocol suitable for high-speed communication.
Examples & Applications
Using I2C to read a temperature sensor data.
Using SPI for interfacing with high-speed ADCs.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
SPI is fast, I2C is neat; if you like more speed, SPI can't be beat.
Stories
Imagine a busy post office; I2C is like a fixed delivery route for many small packages, while SPI is a speedy courier who delivers large boxes quickly.
Memory Tools
I2C (Two for communication, Clocks come after) - remember SDA and SCL!
Acronyms
SCP - Speed, Communication, Precision for SPI.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- I2C
Inter-Integrated Circuit, a synchronous multi-master, multi-slave communication protocol using two wires.
- SPI
Serial Peripheral Interface, a synchronous communication protocol using separate lines for input and output.
- Microcontroller
A compact integrated circuit designed to govern a specific operation in an embedded system.
- SDA
Serial Data Line, used for data transmission in I2C.
- SCL
Serial Clock Line, provides the clock signal for synchronization in I2C.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
