Air Quality Assessment
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Air Quality Assessment
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, everyone! Today, we will explore air quality assessment. Can anyone tell me why it's important to monitor air quality?

I think it's important for protecting health and the environment.

Exactly! Poor air quality can lead to serious health problems. Can someone name the three main ways humans can be exposed to pollutants?

Inhalation, ingestion, and dermal contact.

Great job! Remember the acronym I-D-I for these exposure pathways. Let's dive deeper into how these pollutants enter our bodies.
Types of Pollutants
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss types of pollutants. What are some examples of hazardous materials that we might encounter?

Things like carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and heavy metals?

Correct! And these can come from various sources. Any thoughts on where they might originate?

They might come from vehicles, factories, and even agricultural activities.

Absolutely. Remember, the source of a pollutant helps us understand its route through air, soil, and water. This brings us to the importance of monitoring.
Monitoring Air Quality
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Monitoring air quality is crucial for public health. Does anyone know what parameters might be measured?

Concentrations of specific pollutants?

Yes! We should measure the concentration of hazardous materials in the air. This data helps us determine health risks associated with exposure. Can someone explain why understanding these concentrations is vital?

Because it helps us evaluate if the levels are above safe limits!

Exactly! This evaluation leads to effective health risk assessments and policy making. Let's move to case studies in air quality assessment.
Health Effects of Air Pollution
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s talk about the health effects caused by poor air quality. What kind of health issues can poor air quality lead to?

Respiratory problems and cardiovascular diseases?

Correct. And this highlights the importance of assessing air quality. We need to discuss how we can intervene. Any suggestions?

We could promote cleaner technologies or stricter emissions regulations.

Great examples! Effective air quality assessment leads to better health outcomes. Today’s session wraps up our discussion on air pollution.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Air Quality Assessment is crucial for understanding the impact of environmental pollutants on human health. It delves into how hazardous materials enter the body through exposure pathways, the types of pollutants, and how monitoring air quality can help assess risks associated with health effects from these pollutants.
Detailed
Air Quality Assessment
Understanding air quality is essential for ensuring public health and safety. Air pollutants can come from various sources and enter the human body via different exposure pathways: inhalation, ingestion, and dermal contact. Monitoring these pollutants helps in identifying their concentrations and understanding their toxicity.
The section explores the classification of pollutants and emphasizes the need for systematic monitoring to assess their impacts on health. Key terms and concepts include:
- Hazardous Materials: Chemicals or substances that can pose a significant risk to health.
- Exposure Pathways: The routes through which pollutants can enter the human body—primarily inhaled air, ingested food or water, or through skin contact.
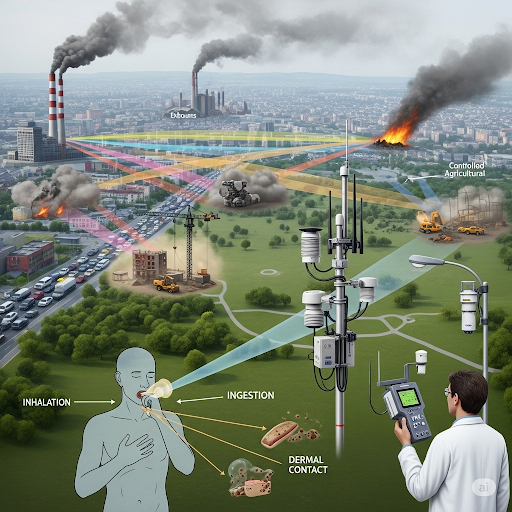
Monitoring pollutants in various environmental compartments such as air, water, and soil is necessary for risk assessment. It helps to identify sources of pollution, such as industrial, vehicular, or agricultural, and facilitates strategic responses to mitigate risks to health associated with air quality. In summary, effective air quality assessment requires an understanding of the relationship between emissions, human exposure, and health outcomes.
Youtube Videos










Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Air Quality Assessment
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Air quality refers to the condition of air within our environment and how it is affected by pollutants. Assessing air quality is crucial for human health and environmental protection.
Detailed Explanation
Air quality assessment involves measuring and evaluating the presence of pollutants in the air. This can include substances like carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter, which can adversely affect health. By assessing air quality, we can determine if the air meets health standards and protect public health.
Examples & Analogies
Think of air quality as the freshness of the air you breathe. Just like you would check if milk is fresh before consuming it, air quality assessments help determine if the air is safe to breathe. If the air contains too many pollutants, it becomes 'spoiled,' similar to milk past its expiration date.
Pollutants in the Air
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Common air pollutants include nitrogen oxides, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter. Each type of pollutant has different sources and health impacts.
Detailed Explanation
Different pollutants come from various sources. For instance, nitrogen oxides are often released from vehicles and industrial processes, while VOCs can emit from products like paints and cleaners. Particulate matter consists of tiny particles that can penetrate deep into the lungs and even enter the bloodstream, causing serious health issues. Understanding these pollutants helps in creating effective regulations to improve air quality.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to breathe in a kitchen filled with smoke. The smoke is similar to air pollutants; just as it makes it hard to breathe and can make you cough, air pollutants can harm lung function and overall health when they accumulate in high concentrations in the atmosphere.
Health Impacts of Poor Air Quality
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Exposure to poor air quality can lead to respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, and can worsen existing health conditions. Children and elderly populations are particularly vulnerable.
Detailed Explanation
Poor air quality can lead to a range of health issues. For example, high levels of particulate matter can irritate the lungs and lead to conditions like asthma and bronchitis. Vulnerable groups such as children, who have developing lungs, and the elderly, who may have pre-existing health conditions, are particularly affected by air pollution. This emphasizes the importance of monitoring air quality to protect these at-risk populations.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how smoke from a bonfire can make it difficult to breathe. Children playing nearby might cough or find it hard to run around. Similarly, air pollution acts like that smoke and can make it challenging for sensitive groups, like children and the elderly, to breathe comfortably.
Methods of Air Quality Assessment
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Air quality can be assessed through direct monitoring, dispersion models, and public health studies. Each method provides valuable information for understanding air pollution.
Detailed Explanation
Several methods are used to assess air quality. Direct monitoring involves using tools to measure levels of specific pollutants in the air, while dispersion models help predict how pollutants spread in the atmosphere based on weather and topography. Public health studies can show correlations between pollution levels and health outcomes in the population, which can inform policy decisions regarding air quality management.
Examples & Analogies
Think of air quality assessment methods like using different types of kitchen tools for cooking. Just as having a thermometer, timer, and taste tester can help you make a perfect dish, different assessment methods together help us understand air quality and ensure a healthy environment.
Regulations and Standards
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Governments and organizations establish regulations and standards for air quality to protect public health. These guidelines help manage pollution sources and ensure clean air.
Detailed Explanation
Regulatory standards, such as the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) in the United States, set limits on the concentration of specific pollutants to safeguard public health. These regulations encourage industries to adopt cleaner technologies and reduce emissions, helping to improve air quality and protect the health of the population.
Examples & Analogies
Regulations for air quality are like traffic laws. Just as speed limits and stop signs keep drivers safe on the road, air quality standards keep communities healthy by limiting harmful pollutants in the air.
Key Concepts
-
Hazardous Materials: Substances posing health risks due to toxicity.
-
Exposure Pathways: Routes of exposure including inhalation, ingestion, and dermal contact.
-
Monitoring: Systematic evaluation of pollutants to assess air quality and health risks.
-
Health Effects: Outcomes of exposure like respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
Examples & Applications
Airborne lead particles are a hazardous pollutant primarily from industrial emissions.
Carbon monoxide from vehicles is an example of a hazardous material that can lead to significant health issues.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Air so clean helps us breathe right, pollutants lurk out of sight.
Stories
A town decided to monitor air quality and found pollutants from factories, leading to healthier living conditions.
Memory Tools
Use 'I-D-I' to remember the exposure pathways: Inhalation, Ingestion, and Dermal contact.
Acronyms
A-P-E - Air Pollutants Exposure pathways.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Air Pollutants
Substances in the air that can cause harm to human health and the environment.
- Exposure Pathways
The routes through which individuals can come into contact with pollutants, including inhalation, ingestion, and dermal contact.
- Hazardous Materials
Substances that pose a significant risk to health due to their toxicity.
- Emission Sources
Origin points of pollutants, such as vehicles, industrial plants, and agricultural activities.
- Health Risk Assessment
A systematic process for evaluating the potential health effects of exposure to hazardous materials.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
