Solid Waste Treatment
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Impact of Pesticides
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to talk about the impacts pesticides have on our environment. Can anyone tell me what pesticides are used for?

They're used to kill pests affecting crops.

Exactly! However, pesticides like DDT can persist in the environment and even biomagnify up the food chain. What do you think this means for animals higher in the food web?

It could harm them, maybe leading to population declines?

Right. For example, DDT led to eggshell thinning in birds of prey. Remember the acronym 'BEE'—Bioaccumulation, Exposure, and Effects, to remember these concepts. Can someone tell me what bioaccumulation means?

It's when substances build up in organisms over time.

Great! In the long run, this accumulation can severely affect ecosystems.
Types of Solid Waste
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's delve into what comprises solid waste. Can anyone name some common sources of solid waste?

There’s household garbage and industrial waste.

Exactly! It also includes materials like plastics and hazardous waste from industries. What kinds of hazards might these materials pose?

They can pollute groundwater and harm wildlife.

Yes! To combat these issues, we can utilize the 'Three R’s'—Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle. What do you think is the importance of recycling?

It helps reduce the volume of waste and can save natural resources!

Spot on! Recycling not only helps manage waste, but it also conserves the environment.
Control Measures of Soil Pollution
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's explore how we can control soil pollution. What do you think are some effective measures we can take?

We could reduce the use of harmful pesticides!

That's one! What else can we do to manage waste better?

Implementing proper waste management systems!

Absolutely! By neutralizing hazardous waste before disposal and promoting practices like composting, we can significantly cut down pollution. Remember 'TRACT'—Treat waste, Recycle, Adopt eco-friendly practices, Create awareness, and Test waste quality. Can anyone give an example of composting?

Using kitchen scraps to create nutrient-rich soil!

Perfect! This not only minimizes waste but enriches our soils too.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the impacts of solid waste, such as the indiscriminate use of pesticides and the problems associated with solid waste disposal. It highlights the effects on soil and public health, and presents control measures for preventing soil pollution and solid waste mismanagement.
Detailed
Solid Waste Treatment
Solid waste treatment is critical due to the increasing generation of waste from urban, agricultural, and industrial sources. Pesticides and herbicides used indiscriminately can contaminate soil and food crops, affecting humans and wildlife. With the rise of solid waste—chiefly composed of paper, plastics, and hazardous materials—effective management practices are necessary to mitigate soil and water pollution. The impacts of soil pollution include reduced fertility and health risks, prompting the need for measures such as reusing materials, recycling, and implementing sound waste treatment practices to neutralize hazardous wastes. Key strategies in solid waste management include reducing chemical usage and improving waste disposal protocols.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Solid Waste Management
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
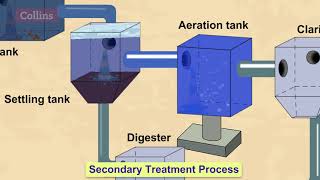
Proper methods should be adopted for management of solid waste disposal. Industrial wastes can be treated physically, chemically and biologically until they are less hazardous.
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, we focus on the importance of managing solid waste properly. Solid waste includes various types of refuse from homes, industries, and agriculture. The management of this waste is crucial for protecting the environment and public health. Techniques such as physical treatment (which can involve sorting and shredding), chemical treatment (which uses chemical reactions to neutralize harmful substances), and biological treatment (which may use microorganisms to break down organic waste) are employed to make industrial waste less hazardous. These steps are vital in ensuring that waste does not pose a danger to the environment or human health.
Examples & Analogies
Think of solid waste management like maintaining a clean house. Just as you sort, discard, or recycle items to keep your home tidy and safe for your family, proper management of industrial waste involves treating and sorting materials to keep our environment clean and safe.
Neutralization of Waste
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Acidic and alkaline wastes should be first neutralized; the insoluble material if biodegradable should be allowed to degrade under controlled conditions before being disposed.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk discusses the process of neutralization in waste management. Acidic and alkaline industrial wastes can be harmful if released into the environment. Neutralization involves adding substances to these wastes to balance their pH levels, making them less reactive and harmful. Additionally, if any materials are biodegradable, they should be allowed to decompose in a controlled manner before disposal, which helps reduce environmental impact and facilitates easier handling of waste materials.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you spill lemon juice (acidic) on your kitchen floor. To make it less acidic and neutralize it, you might sprinkle baking soda (an alkaline substance) over it. This is similar to how we neutralize industrial waste to ensure it is safe for disposal.
Key Concepts
-
Pesticides: Chemicals used to control pests that can lead to environmental risks.
-
Solid Waste: Composed of various disposables from households, industries, and agriculture.
-
Biomagnification: The process by which toxins increase in concentration in organisms at higher trophic levels.
Examples & Applications
DDT affecting bird populations by causing eggs to have thinner shells.
Proper waste management of electronic goods to prevent heavy metals from polluting the groundwater.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Reuse, reduce, recycle it's true, helps the earth, and you too!
Stories
Once there was a town that used pesticides carelessly until one day their beloved birds began to vanish. This spurred a change, leading them to recycle and compost instead!
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym 'PES': Pesticides cause Environmental issues, Soil fertility loss.
Acronyms
BEE
Biomagnification
Environmental impact
Ecosystem health.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Pesticides
Substances used to kill or control pests, including insects and weeds.
- Biomagnification
The increasing concentration of substances, such as pesticides, in the tissue of organisms at each successive level of the food chain.
- Solid Waste
Any discarded materials that are not liquid or gas, often classified as municipal, industrial, and agricultural waste.
- Hazardous Waste
Waste that poses a significant risk to human health or the environment due to its toxic, ignitable, corrosive, or reactive properties.
- Three R's
Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle; principles aimed at minimizing waste and conserving resources.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
