Sources of Thermal Pollution
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Thermal Pollution
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, everyone! Today, we're going to explore thermal pollution. Can anyone tell me what thermal pollution means?

I think it has to do with heat being released into the environment.

Exactly! Thermal pollution occurs when excess heat is released into water or air due to human activities or natural events. Can you think of any sources of thermal pollution?

Maybe power plants? They use a lot of water for cooling, right?

Yes! Thermal power plants and nuclear plants are significant sources. They discharge heated water after using it for cooling. Let's remember that with the acronym 'P-N' for 'Power and Nuclear plants'.

What about industries? Do they contribute too?

Absolutely! Industries like steel and paper mills also contribute by releasing hot water back into rivers and lakes. To sum it up, sources are primarily related to energy and industrial production.
Effects of Thermal Pollution
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we’ve covered the sources, let's discuss the effects of thermal pollution. What do you think happens to fish and other aquatic animals when the water temperature increases?

The fish might die, right?

Good point! Warmer water reduces dissolved oxygen levels, which is vital for fish survival. This can lead to decreased life expectancy among aquatic animals. Can anyone remember the term we can associate with this impact?

Is it 'metabolic rate?'

Exactly! Increased temperatures accelerate metabolic rates, meaning fish have to work harder to survive. Remember, higher temperatures equal more stress for aquatic life.

So, it affects the whole ecosystem?

Absolutely! Thermal pollution can disrupt entire ecosystems, affecting food chains and biodiversity. We often call this disruption 'ecological imbalance.'
Management of Thermal Pollution
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To mitigate thermal pollution, various control methods are employed. Can anyone name a method used to manage thermal discharge?

Cooling towers?

Correct! Cooling towers are designed to dissipate heat before water is returned to natural bodies. There's also the use of cooling ponds. What is their function?

They help cool heated water by exposing it to the air, right?

Exactly! Cooling ponds maximize heat dissipation. Lastly, can anyone explain what artificial lakes do regarding thermal management?

They take heated water at one end and allow cooler water to be drawn from the other end?

Exactly! This method helps maintain temperature stability in the larger water body. Great work today, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores the major sources of thermal pollution, such as power plants and industrial facilities, which release excess heat into the environment. It also discusses the effects of thermal pollution on aquatic life and emphasizes the importance of managing and mitigating these impacts through various cooling methods.
Detailed
Thermal Pollution: Sources and Effects
Thermal pollution, also known as heat pollution, occurs when excessive heat is released into water or air, causing adverse effects on living organisms. It can result from natural phenomena like forest fires or volcanic activity, but most often, it stems from human activities. Key sources of thermal pollution include:
- Thermal Power Plants: Coal-fired plants are the primary contributors, releasing hot water used for cooling back into surrounding water bodies.
- Nuclear Power Plants: These facilities not only discharge excess heat but can also release toxic radioactive substances into the environment.
- Industrial Operations: Plants like petroleum refineries, steel mills, and paper mills use large volumes of water for cooling, subsequently discharging heated water, which disrupts aquatic ecosystems.
The increase in water temperature leads to a reduction in dissolved oxygen levels, which negatively affects aquatic species. For example, higher temperatures speed up the metabolism of fish, reducing their life expectancy. This section stresses effective management practices, such as the use of cooling towers, ponds, and artificial lakes, to control thermal pollution and preserve aquatic life.
Youtube Videos







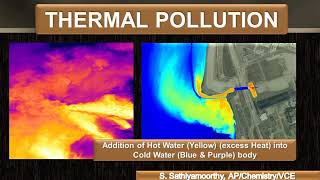


Key Concepts
-
Thermal Pollution: The release of excess heat into water or air, causing harmful effects.
-
Cooling Towers: Structures designed to dissipate heat before water is discharged back into nature.
-
Dissolved Oxygen: Oxygen levels crucial for aquatic life, often diminished by increased water temperatures.
-
Ecological Imbalance: The disruption of ecological equilibrium due to thermal pollution's effects on species.
Examples & Applications
Thermal power plants release hot water into rivers, leading to reduced oxygen levels.
Nuclear power facilities can discharge radioactive waste along with thermal effluents, posing further risks to aquatic ecosystems.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Heat in the water, fish start to bother, oxygen's lost, their lives tossed.
Stories
Once, a power plant dumped hot water into a lake. The fish, struggling for breath, realized their home was becoming too warm. They had to swim to cooler waters, but not all could escape the heat.
Memory Tools
P-N for Power Plants and Nuclear plants, sources of heat their discharge grants.
Acronyms
HEAT stands for Heat Emitted Affecting Temperatures (in aquatic life).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Thermal Pollution
The increase in water or air temperature due to human activities or natural phenomena that adversely affects living organisms.
- Metabolic Rate
The speed at which an organism carries out metabolic processes, influenced by temperature.
- Dissolved Oxygen
Oxygen that is dissolved in water, essential for the survival of aquatic organisms.
- Ecological Imbalance
Disruption of the natural balance within an ecosystem due to changes such as thermal pollution.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
