Matrices
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Matrices
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start by discussing what a matrix is and how it can be used in environmental impact assessments. Who can tell me what they think a matrix does?

Isn’t it a type of table that shows relationships between things?

Exactly! In our case, one axis of the matrix represents project activities while the other represents environmental factors. This way, we can visualize the impacts clearly.

How does that help us figure out the impacts?

By noting interactions in the cells of the matrix, such as using symbols for different impact types, we can identify and scale their significance. Memory aid: Think of 'MAT' - 'Matrix Analyzes Threats'.

What kinds of impacts can we indicate?

Great question! Impacts can be direct, indirect, or cumulative. We can use ticks or numbers in the cells to indicate these types.
Elements of a Matrix
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about how we fill in the matrix. Who remembers what we can put in the cells?

We can put ticks for impact types, and maybe numbers for the severity?

Yes! You can also include qualitative comments to describe each interaction. This contextualizes the numerical data.

How do we determine the severity levels?

Severity can depend on several factors: the scale of the activity, the vulnerability of the environment, and existing regulations. Remember: Think of each cell as telling a little story about the interaction.

Can this matrix be used for all types of projects?

Absolutely! Matrices can be tailored for different types of projects, such as roads or dams, to address specific environmental concerns.
Benefits and Limitations of Matrices
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What are some benefits of using a matrix for impact identification?

It seems it would help organize a lot of information clearly!

Exactly! It allows for quick visual assessments and comparisons. However, what might be a limitation?

Maybe it could oversimplify some complex interactions?

Good point! Matrices can sometimes miss nuanced relationships or failing to capture qualitative data adequately. Always remember to supplement matrix findings with other methods.

What are those other methods?

We may include methods like checklists, networks, and GIS for a more comprehensive analysis. Think of a matrix as one piece in a larger puzzle of impact assessment.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Matrices are a key instrumental tool in environmental impact assessment (EIA) used to succinctly illustrate the interactions of project activities with various environmental factors. They help in the organization and clarification of potential impacts, allowing for an efficient appraisal of severity and types of interactions.
Detailed
Matrices in Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA)
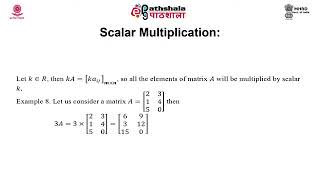
Matrices are grid-like tables that facilitate the identification of interactions between project activities and environmental characteristics in environmental impact assessments. Each axis of the matrix represents either a set of activities or environmental factors, with cells indicating the nature and severity of impacts. This method allows for visual representation, making it easier for stakeholders to comprehend complex interactions. The matrix can include different notations such as ticks for impact types, scales, or textual comments categorizing impacts as direct, indirect, or cumulative. This structured approach to impact identification is pivotal in ensuring that evaluations are comprehensive and that significant indirect effects are noted.
Youtube Videos






![Environmental Science Summer Course in Oxford [Ages 13-15, 16-17, 18-24]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/01SKvc9TiTA/mqdefault.jpg)

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Matrices
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A matrix is a grid-like table that is used to identify the interaction between project activities, which are displayed along one axis, and environmental characteristics, which are displayed along the other axis.
Detailed Explanation
A matrix is essentially a table format with two dimensions. One dimension lists different project activities (like construction, drilling, etc.), while the other lists environmental factors (like air quality, soil, etc.). This layout allows us to visualize how these activities might affect the environment. Each activity can have different effects on various environmental aspects.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a matrix like a menu in a restaurant. The rows might represent different types of dishes (like pizza, pasta, salads) while the columns represent ingredients (like cheese, tomatoes, peppers). By looking at the menu, you can quickly determine which dishes contain which ingredients.
Identifying Interactions
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Using the table, environment-activity interactions can be noted in the appropriate cells or intersecting points in the grid.
Detailed Explanation
Within the matrix, you place 'entries' in the cells where the corresponding activity and environmental characteristic intersect. For example, if construction activities affect air quality, you might mark a cell in the matrix to indicate this interaction. This helps in easily identifying which project activities impact specific environmental factors.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're checking which clothes in your wardrobe match with which accessories. You could create a matrix where one axis lists your clothes and the other lists your accessories. If a particular dress goes well with a specific necklace, you'd mark that cell with a tick or a check mark.
Entries and Impact Severity Indicators
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
‘Entries’ are made in the cells to highlight impact severity or other features related to the nature of the impact, for instance:
• Ticks or symbols can identify impact type (such as direct, indirect, cumulative) pictorially;
• Numbers or a range of dot sizes can indicate scale; or
• Descriptive comments can be made.
Detailed Explanation
The entries in the matrix can take various forms. You could use symbols (like a tick or a star) to show whether an impact is direct (immediate), indirect (long-term), or cumulative (multiple effects over time). Additionally, you might use numbers to represent the severity of impact, such as '1' for low impact and '5' for high impact. This visual organization helps to convey complex information at a glance.
Examples & Analogies
Consider someone using a fitness app. They might use colorful symbols (red for high heart rate, yellow for moderate, and green for low) to indicate intensity levels during their workouts. This quick visualization helps them understand their workout intensity very easily.
Key Concepts
-
Matrix: A visual tool to map interactions between project activities and environmental factors.
-
Impact Types: Various categories of potential impacts that projects can have on the environment.
-
EIA: The systematic process of assessing the environmental impacts of a project.
Examples & Applications
A matrix for a new highway project analyzing its impact on nearby wildlife, water sources, and air quality.
A project involving the construction of a new dam, detailing how it would affect local vegetation, fish populations, and water levels.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When constructing a grid, do not be afraid, using ticks and comments, impacts won't evade.
Stories
Imagine a detective using a grid to track suspects; each cell shows how they might relate to a crime, just like project impacts on the environment.
Memory Tools
Remember 'MICE' for matrices: 'Mapping Interactions Clearly and Effectively'.
Acronyms
MAT - 'Matrix Analyzes Threats' can help you remember its purpose in EIA.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Matrix
A structured grid used to depict relationships between activities and environmental elements.
- Impact Types
Categories of interactions such as direct, indirect, and cumulative impacts from project activities.
- Environmental Characteristics
Features of the environment that can be affected by project activities, like air and water quality.
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)
A process used to evaluate the environmental consequences of proposed projects.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
