Initial density
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Initial Density
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the concept of initial density. Can anyone tell me what initial density refers to in the context of soil?

Is it the weight of the soil before we start compacting it?

Great point! Yes, initial density measures the mass of the soil per unit volume before any compaction efforts. Why do you think this is important?

Because it affects how the soil will behave under load! I remember the acronym DENSITY - 'D' for Density, 'E' for Elasticity... that's how important it is!

Exactly! Density is critical for determining the stability of the soil. Let's discuss how grain size and shape affect initial density.
Grain Size and Shape
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

So, why do you think grain size influences the initial density of soil?

Finer particles can fit more tightly together, which would mean a higher density, right?

Absolutely! Finer particles fill the voids between larger grains. This leads us to consider how particle shape might also play a role. What do you think?

If particles are angular, they could interlock better compared to round particles, resulting in higher density!

Right! So the combination of size and shape drives the initial density. And what's the connection to water content?
Water Content
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Water content plays a vital role in achieving optimal initial density. Can someone explain how?

At the right moisture level, the soil can be compacted more effectively. Water helps fill in the voids, increasing density!

Exactly! At optimal water content, soil achieves maximum density. How do construction procedures relate to this?

Procedures like the number of passes the compactor makes can also affect how well the soil is compacted, right?

Yes, that's right! Each pass can significantly affect the density achieved. Let's summarize this session.
Construction Procedures Impact
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Last session, we touched on construction procedures. What are the main factors that influence initial density during construction?

The number of passes and the thickness of the lift are significant factors!

And the frequency of the compactor's operation can also change the outcome.

Excellent! Remembering these aspects is critical—try the mnemonic 'PASS' for Passes, Amplitude, Speed, and Soil moisture, which are key factors affecting initial density!

That's helpful for remembering! Can we have a quick recap before we end?

Sure! We discussed how grain size, shape, and water content impact initial density, alongside important construction procedures. Understanding these aspects ensures effective soil compaction.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Initial density is a crucial parameter in soil compaction processes. This section examines the characteristics that impact a soil's initial density, including particle size, water content, and the role of construction procedures in achieving desired compaction levels.
Detailed
Initial Density
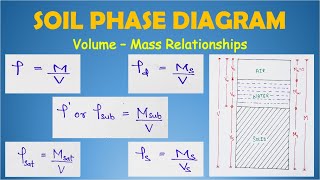
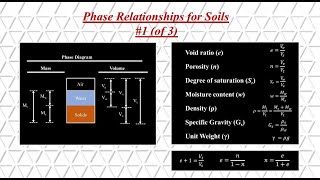
The initial density of soil refers to the mass of soil per unit volume before any compaction processes are applied. This characteristic plays a pivotal role in engineering applications, especially in construction and infrastructure projects, as it affects the soil's stability, strength, and behavior under loads.
Key Characteristics of Initial Density
- Grain Size and Shape: The distribution of grain sizes within the soil can significantly influence its initial density. For instance, finer particles tend to pack more densely than coarser ones. Likewise, the shape of soil grains—whether they are rounded or angular—affects how they interlock and thus their density.
- Water Content: The amount of water in the soil also plays a critical role. At optimal moisture content, soil particles can achieve maximum density as they fill the voids between the grains, enhancing stability.
- Construction Procedures: Initial density is influenced by various construction methods, such as the number of passes made by compacting machinery, the thickness of lifts in soil layers, and the operational frequency of vibrators used in the compaction process. Understanding these procedures allows for effective management of soil compaction to obtain desirable density levels.
In summary, various characteristics impact a soil's initial density, including its physical properties and the methods used during construction, which are critical to achieving desired compaction levels and ensuring structural integrity.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Initial Density
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Initial density refers to the mass of the soil per unit volume before any compaction process occurs.
Detailed Explanation
Initial density is a crucial factor in understanding soil properties. It essentially measures how much soil material is present in a given volume before compaction happens. Higher initial density can indicate that the soil is already densely packed, while lower initial density suggests that the soil is loose and has more air spaces.
Examples & Analogies
Think of initial density like the difference between a fully packed suitcase and an empty suitcase. The packed suitcase is like high initial density with items tightly fitted in, while the empty suitcase represents low initial density with a lot of space available.
Importance of Initial Density
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Initial density affects the effectiveness of the compaction process and the final density achieved after compaction.
Detailed Explanation
The initial density of the soil is significant because it influences how much further the soil can be compacted. If the soil starts with a low initial density, it means that there's a lot of air and space between soil particles, making it easier to compress. This can lead to great improvements in the soil's overall strength once compaction is completed. Conversely, if the initial density is already high, there may be less improvement possible after compaction.
Examples & Analogies
Consider blowing up a balloon. If you start with a deflated balloon (low initial density), it's easy to inflate it to a larger size. But if the balloon is already partially inflated (high initial density), it takes more effort to blow it up further.
Measuring Initial Density
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Initial density can be determined using the ratio of the mass of the soil to its volume.
Detailed Explanation
To measure the initial density of soil, you can use a simple formula which is density = mass/volume. By weighing a known volume of soil and then dividing its mass by that volume, you can calculate the initial density. This measurement helps engineers assess how suitable the soil is for construction purposes.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have a container filled with sand. You can weigh the sand to find out its mass and divide it by the container’s volume to get the initial density. This is similar to how the construction teams work with soil to ensure they have the correct density for their projects.
Key Concepts
-
Initial Density: The measure of soil mass per volume before compaction; crucial for stability.
-
Grain Size and Shape: Characteristics of soil particles affecting how they fit and interact.
-
Water Content: The key factor enhancing the effectiveness of soil compaction.
-
Construction Procedures: The methods shaping the compaction outcome including passes and lift thickness.
Examples & Applications
For example, clay particles are smaller in size compared to sand particles, allowing them to fill voids better and achieve a higher initial density when wet.
When a roller compactor makes several passes over the same area of soil, it can considerably increase the soil's initial density.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In soil's realm where particles lay, Density's the key for compaction today.
Stories
Imagine building a castle. The sand grains have to fit snugly to support the towers. Water helps them pack just right, making the castle strong against the night.
Memory Tools
Remember 'GROW' for Grain size, Relative density, Optimal water content, and construction procedures.
Acronyms
DENSITY - Density, Elasticity, Numerics, Size, Texture, Yield.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Initial Density
The mass of soil per unit volume before compaction, crucial for determining soil stability.
- Grain Size
The size of individual soil particles which affects how they pack together.
- Grain Shape
The geometric configuration of soil particles that influences how they interlock.
- Water Content
The amount of water within the soil which plays a critical role in achieving optimal compaction.
- Construction Procedures
Methods and techniques employed in the construction process that influence soil compaction.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
