Both elastic and consolidation settlements are reduced.
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Soil Compaction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss how soil compaction affects settlement. Can someone tell me what happens when we compact soil?

It becomes denser, right?

Exactly! By expelling air from the soil, compaction increases its dry density. This affects properties like permeability and performance under load. Remember the acronym DENSE to think about Density, Elastic settlement, Number of contacts, Shear strength, and Effective stress.

What do we mean by elastic settlement?

Good question! Elastic settlement refers to the temporary deformation of soil under load. Compacted soil experiences less elastic settlement because of increased density.

And what about consolidation?

Consolidation settlement occurs over time due to the expulsion of pore water from the soil. Both types of settlement are reduced through effective compaction.

So, is reducing void ratio key?

Absolutely! A lower void ratio results in decreased permeability and more compact soil, directly impacting both elastic and consolidation settlements. Let's summarize: effective compaction leads to reduced settlements due to higher density and lower void ratio.
Influence of Admixtures on Soil
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's talk about admixtures. Who can tell me how they impact soil?

They stabilize the soil!

Great! Admixtures like stabilizing agents can increase the density and accelerate the compaction process, thus enhancing soil performance. Remember, STABLE can help you recall Stability, Transformation of structure, Adhesion, Bearing capacity, and Low permeability.

So, do they always make soil better?

Not always. The effectiveness of admixtures depends on the soil type and conditions. Fine-grained soils respond differently than coarse soils when wetted or compacted.

How does moisture content influence this?

Excellent point! Soils compacted dry of optimum moisture content have a different structure compared to those compacted wet of optimum. We'll dive deeper into that next!
Exploring Settlement Reduction Mechanisms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's now focus on how compaction specifically affects both elastic and consolidation settlements.

What mechanism explains the reduction in elastic settlement?

Elastic settlement reduces because compacting soil increases its density and reduces voids. This higher density translates to less deformation under loads.

How does this relate to consolidation?

Good connection! Reduced void ratio also diminishes the potential space for water, so pore water is expelled more effectively when load is applied, decreasing consolidation settlement.

Does that mean we can have a better bearing capacity?

Yes! Higher density results in increased bearing capacity, as the number of contact points among soil particles increases. Engaging with these concepts will help visualize their impact better!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Compaction of soil, particularly when using admixtures, plays a significant role in enhancing soil density and strength. This section highlights the benefits of reduced void ratio leading to lower settlement rates, specifically addressing both elastic and consolidation settlements.
Detailed
Both Elastic and Consolidation Settlements are Reduced
In this section, we explore the various effects of soil compaction and the role of stabilizing agents, known as admixtures. These agents not only help in stabilizing the soil but also in accelerating the densification processes. Compaction effectively increases soil density and decreases the void ratio, which subsequently leads to significant reductions in both elastic and consolidation settlements. This understanding is essential when considering the bearing capacity and overall stability of constructions built on compacted soils. Experiments demonstrate that soils compacted dry of optimum conditions face greater compression compared to those compacted wet of optimum, presenting important considerations for civil engineering and construction practices. Proper application of compaction technologies will help to achieve optimal soil performance.
Youtube Videos
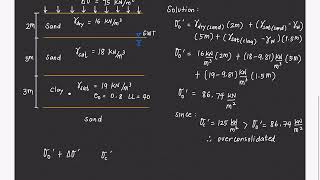






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Impact of Compaction on Settlement
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
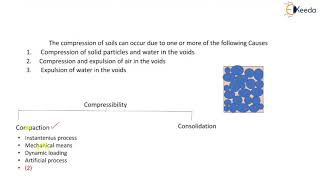
- Compaction increases density and decreases void ratio.
- This results in reduced settlement.
Detailed Explanation
Compaction of soil leads to an increase in its density and a decrease in void ratio. Density refers to how closely packed the particles in the soil are, and void ratio refers to the space between those particles. When soil is compacted, the particles are pushed closer together, reducing the amount of empty space. This reduction in voids means that there is less capacity for the soil to compress under load, which results in reduced settlement. Settlement is the downward movement of the ground due to loads applied over time, often seen in structures built on the soil.
Examples & Analogies
Think of packing a suitcase. When you pack your clothes tightly with not much space between them, less room is left for other items to shift or settle in. If you were to put additional weight (like another jacket), the packed clothes do not compress much because they are already tightly packed. Similarly, when soil is well-compacted, it resists settling under the weight of buildings.
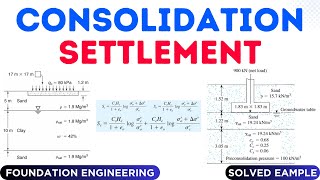
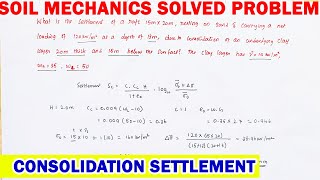
Reduction of Both Elastic and Consolidation Settlements
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Both elastic settlement and consolidation settlement are reduced.
- Soil compacted dry of optimum experiences greater compression than that compacted wet of optimum.
Detailed Explanation
There are two types of settlements that occur in soils: elastic settlement and consolidation settlement. Elastic settlement refers to the immediate deformation of soil when a load is applied, while consolidation settlement refers to the gradual squeezing out of water from the soil pores when a load is applied over time. When soil is compacted, both types of settlements are reduced due to the increase in density and decrease in voids, allowing the soil to handle loads more effectively. Additionally, if the soil is compacted when dry, it will generally compress more than if it is compacted when wet due to the structural differences in soil grains and water's lubricating effect.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sponge soaking in water. When you squeeze it, water comes out as it compresses. If you try to squeeze the same sponge while it’s still very wet, it may compress less because the water acts as a barrier. An optimally compacted (dry) soil behaves like a tightly squeezed sponge, ready to handle more load without settling compared to a wet sponge (wet compacted soil).
Key Concepts
-
Soil Compaction: The mechanical process of increasing soil density.
-
Elastic Settlement: Temporary deformation of soil.
-
Consolidation Settlement: Long-term settlement due to pore water expulsion.
Examples & Applications
Compacting soil for a building foundation reduces both types of settlements, ensuring stability.
An example is a road construction where higher compaction improves the bearing capacity and longevity of the road.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When the soil is tight, it holds on right, both types of settlements take flight.
Stories
Once upon a time in a building project, the foreman discovered that when the soil was compacted using special mixtures, the building stood tall and proud, with no signs of settling!
Memory Tools
PES - Remember how Perfectly Elastic Settlements can be reduced through effective soil compaction.
Acronyms
STEADY
Soil Type
Elastic settlement reduction
Admixtures influence
Density improvement
Yield under load.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Compaction
The process of increasing the density of soil by reducing the voids, typically through mechanical means.
- Admixture
A material added to soil to improve its physical properties.
- Elastic Settlement
Temporary deformation of soil under load that recovers once the load is removed.
- Consolidation Settlement
A gradual settlement due to the expulsion of pore water and decreasing voids over time.
- Void Ratio
The ratio of the volume of voids to the volume of solid soil particles.
- Bearing Capacity
The capacity of soil to support the loads applied to the ground.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
