Density
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Soil Compaction and Admixtures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome class! Today, we’re diving into soil compaction and the role of admixtures. Can anyone tell me what you think admixtures are in the context of soil?

Are they substances we add to improve soil quality?

Exactly, Student_1! Admixtures, especially stabilizing agents, are added to enhance soil properties. They not only help in stabilization but also often accelerate densification. Does anyone know what densification means?

Is it when soil is packed more tightly, reducing voids?

Yes! Densification reduces the voids in the soil by expelling air, increasing the dry density significantly. This process is fundamental in improving the performance of soil for construction. Let’s remember this as 'Densification = Packed Soil'!
Effects of Compaction on Soil Properties
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss the effects of compaction on soil properties. Who can enumerate some properties that compaction affects?

I think it affects density and strength.

And permeability too!

Great answers! Compaction increases density, which strengthens the connections between soil particles — we call this shear strength. What's interesting is that in granular soils, more contacts increase the shear strength significantly. But it’s a bit different in clay soils; various factors influence their shear strength. Anyone know what these might be?

Is it related to moisture content and how we compact it?

Absolutely! The method of compaction and moisture content significantly affect clay's shear strength. Remember: 'Granular Gains' for granular soils and 'Moisture Matters' for clay!
Permeability and Settlement Effects
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s move on to permeability. How does increased compaction affect soil permeability?

It decreases permeability because there’s less void space.

Exactly, Student_2! At the same density, soils compacted dry of optimum moisture content are typically more permeable. This is all about how voids interact with water flow. Now, how does compaction affect settlement?

Compaction decreases both elastic and consolidation settlement!

Yes! Compaction raises density and reduces void ratios, which ultimately minimizes settlement. Great job! Let's remember: 'Compact to Reduce Settlement.'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section highlights the role of stabilizing agents, the effects of compaction on soil density, shear strength, permeability, and other characteristics. Understanding these effects is crucial for optimizing soil performance in construction and engineering applications.
Detailed
Density
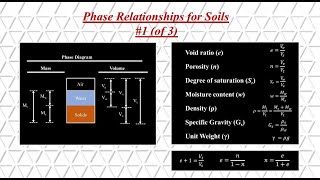
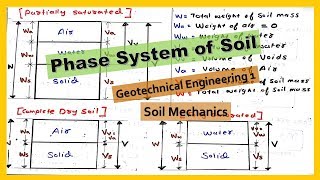
This section explores how the addition of admixtures, particularly stabilizing agents, affects soil density and its fundamental properties. Compaction plays a vital role in reducing voids within the soil, increasing dry density, and enhancing other characteristics such as shear strength and permeability. Key points discussed include:
- Admixtures and Compaction: Admixtures are used to stabilize soil, accelerating densification.
- Influence on Density: Compaction expels air and reduces voids, enhancing dry density.
- Shear Strength: Increased compaction raises the number of contacts between particles, boosting shear strength, especially in granular soils.
- Permeability: Greater compaction decreases void space and thus reduces permeability.
- Bearing Capacity: Enhanced density from compaction leads to increased bearing capacity, vital for construction.
- Settlement: Compaction reduces both elastic and consolidation settlement.
- Soil Structure: Different moisture levels impact the structure of fine-grained soils significantly.
- Pore Pressure: Compaction conditions affect pore water pressure in clayey soils.
- Stress-Strain Characteristics: The behavior of soil during applied stress varies depending on moisture content in relation to optimum compaction.
Youtube Videos


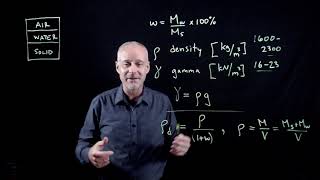




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Effect of Compaction on Density
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The effect of compaction is to reduce the voids by expelling out air. This results in increasing the dry density of soil mass.
Detailed Explanation
Compaction refers to the process of increasing the density of soil by reducing the air gaps (voids) between soil particles. When soil is compacted, air is pushed out of the spaces, allowing the soil particles to come closer together. This densification leads to an increase in the dry density of the soil mass. The higher the dry density, the heavier the soil feels for a given volume, improving its load-bearing capacity and stability.
Examples & Analogies
Think of compacting soil like pressing down a sponge. Initially, the sponge has lots of air trapped in it, making it light and fluffy. When you press down on the sponge, it becomes denser, the air escapes, and it takes up less space, similar to how soil becomes denser when compacted.
Importance of Dry Density
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Increased dry density due to compaction is critical for improving the mechanical properties of the soil.
Detailed Explanation
The dry density of soil is vital in determining its mechanical properties, such as shear strength and bearing capacity. Higher dry density indicates fewer voids and more contact points between soil particles, which enhances stability and resistance to deformation under loads. This means that a densely compacted soil can support heavier structures without undergoing excessive settlement or failure.
Examples & Analogies
Consider building a house. If the foundation is laid on a solid, compacted soil, it will be sturdy and able to support the house’s weight. In contrast, if the soil underneath is loose and has a low dry density, it could shift or settle over time, leading to cracks and structural damage.
Key Concepts
-
Admixtures: Substances that improve soil quality.
-
Compaction: Reduces voids and increases density.
-
Densification: Focused on increasing soil density.
-
Shear Strength: Resistance to shearing forces improved with compaction.
-
Permeability: Influenced by compaction and moisture content.
-
Settlement: Reduction in both elastic and consolidation settlement due to compaction.
-
Moisture Content: Key in compaction effectiveness.
-
Optimum Moisture Content: Ideal moisture level for maximum density.
Examples & Applications
In road construction, compacted granular soil improves stability and load-bearing capacity.
A clay layer compacted at optimum moisture retains less pore water, increasing its stability.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To compact and not to slack, keep the voids fully intact.
Stories
Once there was a soil that yearned to be strong. Admixtures came along, turning its weakness into a thriving bond, allowing it to bear loads generously.
Memory Tools
DPM: Density, Permeability, Moisture - key factors in compaction.
Acronyms
CSD
Compaction = Strength + Density.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Admixture
A substance added to soils to improve their stability and performance.
- Compaction
The process of reducing the volume of soil by expelling air and water, increasing its density.
- Densification
The process of increasing soil density by reducing the voids within the soil.
- Shear Strength
The resistance of soil to shearing forces, which is enhanced through increased contact points between particles.
- Permeability
The ability of soil to allow water to flow through its voids.
- Settlement
The downward movement of soil caused by compressibility or load.
- Pore Pressure
The pressure of water within the soil's voids, which can affect its stability.
- Moisture Content
The amount of water contained in soil, which can influence its mechanical properties.
- Optimum Moisture Content
The moisture level at which soil achieves maximum density upon compaction.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
