Definition and Scope of Hydrology
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition of Hydrology
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, class! Today we'll explore hydrology, the science that focuses on water's journey through our planet. Can anyone tell me what they think hydrology entails?

I think it has to do with rivers and lakes, right?

That's part of it! Hydrology looks at water's occurrence, circulation, and properties, both on the surface and underground. It’s vital for understanding our environment. What are some properties of water you can name?

Water is necessary for life and it can exist in different forms like liquid, ice, and vapor.

Exactly! Water's properties are crucial for many processes. Remember, we can summarize hydrology as involving the 'Four C's': Circulation, Occurrence, Conservation, and Chemistry. What do you think these imply?

Circulation must mean how water moves?

Right, it encompasses everything from rainfall to river flow!
Scope of Hydrology in Engineering
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know what hydrology is, let's delve into its various applications in engineering. How do you think engineers use hydrology?

They probably use it to design dams and irrigation systems, right?

Exactly! Hydrology plays a key role in water resources engineering, influencing flood prediction, irrigation system design, and even urban drainage systems. How about we remember these applications with the acronym 'P-F-I-D-U-H', which stands for Planning, Flood control, Irrigation, Dam operations, Urban drainage, and Hydro-power?

That's helpful! So engineers consider all aspects of water, including where it comes from and where it goes?

Absolutely! Understanding these concepts allows engineers to manage water resources sustainably.
Impact of Hydrology on Daily Life
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Think about our daily lives. How does hydrology impact us?

Water supply for drinking and farming?

Exactly! Without understanding hydrology, we couldn't supply fresh water or manage resources effectively. What would happen if we didn't plan for things like flood control?

It could lead to disasters, right? Like floods affecting homes and agriculture?

Spot on! Thus, the scope of hydrology is not just academic; it directly relates to our safety and sustainability.

So, it’s not just about the big projects; it's about every drop of water in our lives?

Absolutely correct! The understanding of hydrology equips us to make informed decisions regarding our water usage.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section defines hydrology, outlining its significance in understanding the water cycle and its applications in engineering for effective water resource management, including flood control, irrigation, and hydropower.
Detailed
Definition and Scope of Hydrology
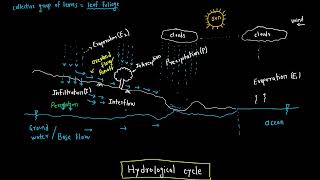
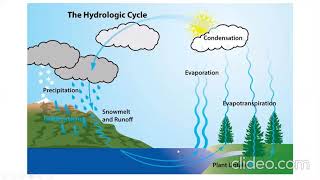
Hydrology is defined as the science that deals with the occurrence, circulation, distribution, and properties of water in various forms across the Earth. This includes both surface water and groundwater, making it essential for various applications in water resources engineering. The scope of hydrology in engineering is vast and pivotal, encompassing:
- Planning and management of water resources projects.
- Flood prediction and control to mitigate natural disasters.
- Designing irrigation systems to optimize agricultural productivity.
- Operating dams and reservoirs for water supply and energy generation.
- Planning for urban drainage systems to handle runoff.
- Generating hydropower as a renewable energy source.
Understanding hydrology is foundational for analyzing and managing water resources effectively.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Hydrology
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Hydrology is defined as the science that deals with the waters of the Earth, including their occurrence, circulation, and distribution, both on the surface and underground, and their physical and chemical properties.
Detailed Explanation
Hydrology is the scientific study of water. It focuses on understanding where water is found on Earth (like in rivers, lakes, and underground), how it moves (like soaking into the ground or flowing in streams), and its physical and chemical characteristics (like temperature and pollutants). This branch of science is vital because it helps us manage water resources effectively and understand their role in the environment.
Examples & Analogies
Think of hydrology like being a detective for water. Just as a detective gathers clues to solve a mystery, hydrologists gather data about water to understand its behavior and find solutions to water-related issues, such as drought or flooding.
Scope of Hydrology in Engineering
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Scope in Engineering:
– Planning and management of water resources projects.
– Flood prediction and control.
– Irrigation system design.
– Dams and reservoir operation.
– Urban drainage system planning.
– Hydropower generation.
Detailed Explanation
The scope of hydrology in engineering encompasses a wide range of applications. Engineers use hydrology to plan and manage projects that involve water, such as designing irrigation systems to ensure crops get enough water or creating flood prediction models to protect communities. It also involves the operation of dams and reservoirs to store water and generate hydropower, and designing urban drainage systems to prevent flooding in cities.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine planning a big city. Just like you’d need to lay out the streets, you also need to plan how water flows into and out of the city. Engineers treat water like a vital resource that needs careful management, similar to how a chef ensures every ingredient is used in the right amount for a perfect dish.
Key Concepts
-
Hydrology: The study of water movement and properties.
-
Surface Water: Water that is found on the Earth's surface.
-
Groundwater: Water located underground within soil or rock formations.
-
Water Resources Engineering: The application of hydrology and related sciences to civil engineering and environmental management.
Examples & Applications
Engineers design flood control systems based on hydrological data to prevent damage during heavy rains.
Urban planners use hydrology to strategize stormwater management in towns and cities.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Water isn't just for drinking; it serves functions that are linking.
Stories
Imagine a raindrop falling from the sky, passing through rivers, lakes, and into the ground, helping ecosystems thrive, then rising again. This journey symbolizes hydrology's endless cycle.
Memory Tools
To remember hydrology aspects, think: 'C-C-D-P'. Circulation, Chemistry, Distribution, Properties.
Acronyms
Remember 'P-F-I-D-U-H' for hydrology applications
Planning
Floods
Irrigation
Dams
Urban drainage
and Hydropower.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Hydrology
The science that deals with the occurrence, circulation, distribution, and properties of water in various forms on Earth.
- Surface Water
Water that collects on the surface of the ground, such as rivers, lakes, and streams.
- Groundwater
Water that is located beneath the Earth’s surface in soil pore spaces and fractures of rock formations.
- Water Resources Engineering
A field of engineering that focuses on the collection, management, and use of water resources.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
