Definition of Precipitation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Defining Precipitation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re diving into 'precipitation'. Can anyone tell me what they think precipitation means?

Is it just rain?

Great starting point! Precipitation includes all forms of water that fall from the atmosphere, not just rain. We classify it into liquid forms like rain and solid forms like snow and hail.

So, it’s not only rain, but also snow and hail?

Exactly! Remember the acronym RSHSD: Rain, Snow, Hail, Sleet, and Drizzle. This helps us recall these main types of precipitation.

What is the importance of understanding precipitation?

Understanding precipitation is vital for hydrological modeling, flood estimation, and designing water-related infrastructures. It impacts groundwater and surface runoff.

In summary, precipitation is vital for water systems and includes various forms: rain, snow, hail, sleet, and drizzle.
Mechanism of Precipitation Formation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss how precipitation forms. Can anyone tell me what conditions must be met?

It probably has to do with water vapor in the air?

Yes! The air must be saturated with water vapor, which usually happens when the temperature drops.

What about those particles you mentioned? What are they again?

Good question! These are often called condensation nuclei, like dust or salt. They act as surfaces for the vapor to condense on.

What comes after that, teacher?

Once the droplets of water condense on these nuclei, they need to coalesce or grow larger to fall as precipitation. That's how rain, snow, and other forms occur!

So to summarize: Precipitation formation requires saturated air, condensation nuclei, and coalescence of droplets.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section defines precipitation as a result of atmospheric water vapor condensation, encompassing various forms such as rain, snow, hail, and sleet. Understanding precipitation is crucial for hydrology and water resource planning.
Detailed
Definition of Precipitation
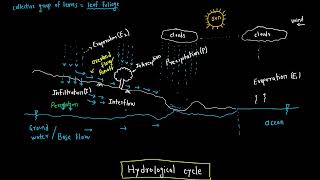
Precipitation is a fundamental aspect of the hydrological cycle and is defined as the product of condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls to the Earth’s surface due to gravitational forces. It manifests in various forms including rain, snow, hail, sleet, and drizzle, each with its unique characteristics and implications for hydrology and civil engineering. The comprehension of these forms is essential for hydrologists and water resource engineers since it influences surface runoff, groundwater recharge, soil moisture, and infrastructure design. This section hence emphasizes the significance of understanding precipitation's definition and its various forms.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Precipitation
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Precipitation is defined as the product of condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls to the Earth’s surface under gravitational force.
Detailed Explanation
Precipitation refers to any form of water that originates from the atmosphere, condenses, and then falls to the ground due to the force of gravity. This process starts with water vapor in the air, and when conditions are right, this vapor cools and condenses into water droplets or ice crystals. These droplets or crystals then become heavy enough to fall to the Earth's surface.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a cold glass of water on a hot day. As the moisture from the air comes into contact with the cool glass, water droplets form on its surface. This is similar to how water vapor in the air can condense into precipitation when it cools. When these droplets get large enough, they fall, just like rain from the sky.
Forms of Precipitation
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It includes all forms of water, both liquid and solid, that originate in the atmosphere and fall to the surface. Common forms include rain, snow, hail, sleet, and drizzle.
Detailed Explanation
Precipitation can take on various forms depending on temperature and atmospheric conditions. The main types include rain (liquid water), snow (frozen ice crystals), hail (large balls of ice), sleet (frozen raindrops), and drizzle (light rain with small droplets). Each type has different characteristics and plays unique roles in the environment and weather patterns.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a weather report. When it says 'rain,' you know it’s liquid water falling; this is useful for watering plants but can also lead to flooding if too much falls too quickly. In contrast, if it says 'snow,' we might prepare for fun activities like skiing, but it can also affect travel and safety. Each form of precipitation has its own impact on our daily lives.
Key Concepts
-
Precipitation: Refers to water in various forms falling from the atmosphere to Earth.
-
Condensation Nuclei: Particles that facilitate the condensation of water vapor.
Examples & Applications
Rain: Liquid droplets larger than 0.5 mm, common in temperate climates.
Snow: Ice crystals forming snowflakes, occurring at temperatures below freezing.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Precipitation falls down from the sky, whether liquid or solid, oh my, it can be rain or snowflakes too; when you see it, you know it's true.
Stories
Imagine a cloud as a cotton ball, filled with tiny water droplets. When it gets too heavy, it decides to drop them as rain, snow, or hail, giving life to rivers and plants below.
Memory Tools
RSHSD: Remember Rain, Snow, Hail, Sleet, and Drizzle for the main forms of precipitation.
Acronyms
PVA - Precipitation = Vapor + Atmosphere.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Precipitation
Any form of water, liquid or solid, that falls from the atmosphere to the Earth's surface.
- Condensation Nuclei
Minute particles in the atmosphere, such as dust or salt, that serve as surfaces for water vapor condensation.
- Coalescence
The process where smaller droplets combine to form larger ones.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
