Importance in Hydrological Studies
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Design of Hydraulic Structures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why is it important to consider precipitation when designing structures like dams or culverts?

To handle the water flow properly and prevent failures?

Exactly! We must assess precipitation patterns to determine the necessary water handling capacities. Remember: 'Plan Precipitation for Perfect Prevention.'

That's a great way to remind myself of this along with flood risks!

Great! To conclude, we see how understanding precipitation is foundational to designing effective hydraulic structures that can manage water flow safely.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
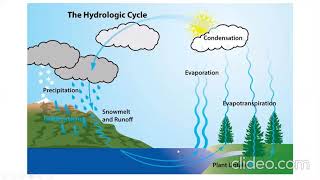
Understanding different forms of precipitation is vital for hydrologists and water resource planners. It plays a crucial role in runoff estimation, watershed behavior, flood forecasting, soil erosion, and the design of hydraulic structures. Properly assessing these factors ensures effective management of water resources.
Detailed
Importance in Hydrological Studies
Different forms of precipitation such as rain, snow, sleet, and hail significantly impact various hydrological elements. The precision in understanding and measuring these forms is integral for important predictions and modeling in hydrology.
Key areas affected by precipitation include:
- Runoff Estimation: Accurate computation of runoff helps in managing water resources effectively.
- Watershed Behavior: Understanding how different types of precipitation interact with the watershed is crucial for environmental management.
- Flood Forecasting: Proper precipitation analysis aids in anticipating and mitigating floods.
- Soil Erosion: Different forms can cause varying levels of soil erosion, which impacts land productivity and stability.
- Design of Hydraulic Structures: Knowledge of precipitation patterns is essential for designing structures like culverts, dams, and spillways to ensure they can handle expected precipitation rates.
Understanding the type, intensity, and spatial distribution of precipitation is thus essential in accurate hydrological modeling and sustainable water resource planning.
Youtube Videos







![Introduction to Engineering Hydrology and its Applications [Year - 3]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/Sds3dB-hA8E/mqdefault.jpg)
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Impact on Hydrological Processes
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Different forms of precipitation affect:
- Runoff estimation
- Watershed behavior
- Flood forecasting
- Soil erosion
- Design of hydraulic structures (culverts, dams, spillways)
Detailed Explanation
This chunk highlights the critical impact that various precipitation types have on hydrology. Each form of precipitation can influence runoff — which is the flow of water that occurs when excess rainwater, meltwater, or other sources flow over the ground. This is vital for understanding how water moves through watersheds, which are the land areas that drain into a river or lake. Accurate runoff estimation is also essential for predicting potential flooding, as heavy rain can lead to increased water levels in rivers and lakes. Additionally, precipitation influences soil erosion processes and is a key factor in the design of hydraulic structures, ensuring they can handle specific water flow rates.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the effects of precipitation like a sponge that absorbs water. If it rains lightly, the sponge soaks up slowly, but if it rains heavily, the sponge becomes overloaded and water spills out. Similarly, different precipitation patterns can either saturate the ground or lead to excess runoff, which can either be helpful for irrigation or create floods, requiring careful planning for drains or dams.
Significance in Hydrological Modeling
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Understanding the type, intensity, and spatial distribution of precipitation is essential in accurate hydrological modeling and sustainable water resources planning.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk emphasizes the necessity of comprehending how different types of precipitation behave — including their intensity (how much rain falls) and distribution (where it falls) — for modeling water systems effectively. Hydrological modeling involves using data to predict water movement and availability within a landscape. Without accurate models, it is difficult to plan for water usage, manage supply in arid regions, or design infrastructure capable of managing storm runoff. Effective water resource planning is crucial for ensuring that communities have sufficient water supplies even during droughts or unanticipated floods.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to create a map for a treasure hunt in a city that experiences different types of weather. If you know where and when it rains or snows heavily, you can predict where the best hiding spots may be, or where floods might wash away clues. Similarly, in hydrology, knowing about precipitation allows scientists and engineers to better understand where and how to manage water resources effectively, ensuring that water remains available where it's most needed.
Key Concepts
-
Runoff Estimation: The assessment of water flow following precipitation events.
-
Watershed Behavior: How different precipitation types influence the behavior of a watershed.
-
Flood Forecasting: Predicting potential flooding based on precipitation data and patterns.
-
Soil Erosion: The impact of precipitation on soil stability and loss.
-
Hydraulic Structures: The importance of precipitation in the design of structures to manage water.
Examples & Applications
Heavy rain can lead to immediate runoff and potential flooding, necessitating careful assessment for urban planning.
Snowpack in mountainous regions provides delayed runoff essential for maintaining river flow during dry months.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Snow Stows, Rain Flows—a way to remember how snow and rain differ in runoff timing.
Stories
Picture a spring thaw in a mountain range: the snow melts slowly providing water to rivers, while heavy rains cause them to rush over rocks wildly.
Memory Tools
FLOOD: Fast Lakes or Overly Deep—reminder about how heavy rain leads to flooding.
Acronyms
HERO
Hydrology & Erosion Reduction with Observations—what we do through studying precipitation.
Flash Cards
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
