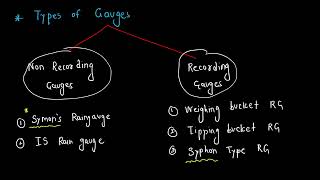
Recording Rain Gauges
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Recording Rain Gauges
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into recording rain gauges! Can anyone tell me how they differ from non-recording rain gauges?

I think recording gauges provide continuous measurements, while non-recording ones only give totals?

Exactly! Recording gauges document rainfall over time, which is crucial for various hydrological analyses. What are some examples of recording gauges?

I've heard of the tipping bucket and weighing bucket gauges.

Great! Remember, to capture rain data accurately, we have the tipping bucket gauge, which assists in remote monitoring.
Weighing Bucket Rain Gauge
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's explore the weighing bucket rain gauge. Can anyone name its key components?

It has a bucket that weighs the rain accumulation?

Correct! It also includes a pen that records data over time. How does it operate?

The weight of rain in the bucket increases, and that causes the pen to write on a chart, showing total rainfall over time.

Exactly right! It's particularly good for accurate measurement, even when dealing with snow. Any questions?
Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about the tipping bucket rain gauge. Can someone explain how it works?

It uses a double bucket system, right? When one bucket fills, it tips and records each tip.

Exactly! Each tip corresponds to a predetermined volume of rain. What are some advantages of using this gauge?

It's great for digital recording and can be used in remote locations.

Correct! Just remember it may underreport lightly falling rain due to water loss during tipping. Let’s review!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Recording rain gauges automatically document rainfall over time, utilizing various mechanisms such as tipping buckets and weighing buckets to capture both cumulative and intensity data. These instruments play a crucial role in meteorological studies and water resource management.
Detailed
Recording Rain Gauges
Recording rain gauges are sophisticated instruments used to measure and record precipitation automatically over time. Unlike non-recording rain gauges, which only collect total rainfall amounts, these gauges provide continuous readings, making them vital for accurate weather monitoring and hydrology studies.
Key Types of Recording Rain Gauges
- Weighing Bucket Rain Gauge: Utilizes a bucket weighed on a mechanism to measure rain; it records changes in weight, reflecting the accumulated water on a time chart. This type is accurate, even in snow conditions, and provides both cumulative and intensity data.
- Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge: Comprising a funnel and dual buckets that tip when a fixed volume of rain is collected (e.g., 0.25mm), it effectively captures rainfall data digitally, making it suitable for remote monitoring.
- Float Recording Rain Gauge: Utilizes a float chamber and pen mechanism to trace rainfall levels on a rotating chart but is typically found in older meteorological systems.
Each of these gauges has distinct advantages, such as improving data collection for weather forecasts and better understanding precipitation patterns, which are crucial for flood management, agriculture, and urban planning.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Recording Rain Gauges
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Recording rain gauges automatically record rainfall as it occurs, providing a continuous graphical or digital record of precipitation with respect to time.
Detailed Explanation
Recording rain gauges are sophisticated devices that track rainfall data automatically. Unlike non-recording gauges that only measure total rainfall over a period, recording gauges provide ongoing updates about precipitation levels. This feature allows us to see not just how much rain falls, but also when it falls, which is crucial for various applications such as flood forecasting and water resource management.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a recording rain gauge like a fitness tracker that measures not just how far you've run in a week, but also how fast you ran each mile. Just as the fitness tracker provides a detailed output of your performance over time, the recording rain gauge provides a detailed record of rainfall over time, allowing for better analysis and planning.
Weighing Bucket Rain Gauge
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
6.3.1 Weighing Bucket Rain Gauge
This type measures the weight of accumulated precipitation.
Components:
• A bucket mounted on a weighing mechanism.
• A pen attached to the mechanism records data on a chart.
Working Principle:
• As rain falls into the bucket, its weight increases.
• The increased weight causes the pen to deflect on a time-chart, giving cumulative rainfall over time.
Detailed Explanation
A weighing bucket rain gauge works by measuring the weight of the rain that falls into it. As rain collects, the weight increases, which is detected by a weighing mechanism. This change in weight causes a pen to move along a chart, visually displaying how much rain has fallen over a particular time period. This method is particularly accurate, as it accounts for varying amounts of rain and is effective even in snowy conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a scale that measures the weight of water as you pour it in. Just like you can see how much weight you've added each time, the weighing bucket rain gauge tracks the added weight of rain. It’s similar to tracking how much water you drink over a day—every glass you pour into your bottle increases your total amount, giving you a clear record of your intake.
Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
6.3.2 Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge
One of the most commonly used automatic gauges, especially in remote weather stations.
Components:
• A funnel leads rain into a small double-bucket system.
• Each bucket tips when filled with a fixed volume (e.g., 0.25 mm).
• A magnetic switch records each tip electronically.
Working Principle:
• Each tip corresponds to a known volume of rainfall.
• A data logger records the number and timing of tips.
Detailed Explanation
The tipping bucket rain gauge is an efficient device used widely in automatic weather stations. As rain enters through a funnel, it fills one of two buckets until it reaches a specified volume (for example, 0.25 mm). When this volume is reached, the bucket tips over, emptying itself and allowing the second bucket to fill. Each time a bucket tips, it sends an electronic signal that tracks the amount of rain over time. This method efficiently gives instant rainfall measurement in a digital format.
Examples & Analogies
Consider it like a game where you add marbles to a container until it tips over. Each time the container tips, you know you added a specific number of marbles. In the case of the tipping bucket, every tip corresponds to a certain amount of rainfall collected. It's a simple, yet effective way of measuring rain continuously, just like counting how many times you refill a glass throughout the day.
Float Recording Rain Gauge
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
6.3.3 Float Recording Rain Gauge
Used in older meteorological setups.
Components:
• A float chamber that rises with collected rainfall.
• A pen linked to the float traces the rainfall on a rotating chart.
Working Principle:
• The float rises as the water level increases.
• The pen moves over a time-chart, producing a mass curve of rainfall.
Detailed Explanation
The float recording rain gauge is an older method used to track rainfall. It comprises a float that rises with the water level in a chamber. As the level rises, the float lifts, and this movement is transferred to a pen that marks a chart rotating at a constant speed. The resulting marks create a graphical representation of rainfall over time, showing both total and changes in rainfall amounts.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a swing floating on a body of water. As more water fills the basin, the swing goes higher and higher. Just as you can see how high the swing goes to understand how much water is in the basin, the float records how high the water gets in relation to the duration, giving a clear view of rainfall patterns.
Key Concepts
-
Recording Rain Gauge: Instruments that continually measure precipitation.
-
Weighing Bucket: A gauge type measuring the weight of collected rain.
-
Tipping Bucket: Commonly used for automatic measurement, tips when filled to a set amount.
Examples & Applications
The tipping bucket rain gauge provides data for agricultural irrigation planning by offering hourly rainfall readings.
Weather stations utilize weighing bucket gauges to create more accurate cumulative rainfall charts.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Recording rain gauges catch the wet, measuring rain with no regret.
Stories
Imagine a backyard with a weighing bucket gauge. It fills with rain, and as it gets heavier, a little pen dances across a chart, plotting the rainfall history!
Memory Tools
Remember WRFT: Weighing, Recording, Float, Tipping - the different types of recording rain gauges.
Acronyms
TIGER for Tipping Bucket Gauge
Tipping
Intensity
Gathers
Easily
Records.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Recording Rain Gauge
An instrument that automatically measures and records precipitation over a given period.
- Weighing Bucket Rain Gauge
A recording gauge that measures precipitation based on the weight of the collected water in a bucket.
- Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge
A type of automatic rain gauge that collects rain in a bucket which tips over when filled to a set volume.
- Float Recording Rain Gauge
An older type of recording gauge using a float mechanism to measure rainfall levels on a graph.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
