Definition and Concept
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Depression Storage
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing depression storage. Can anyone tell me what that might mean?

Is it about how water collects in some areas during rain?

Exactly! Depression storage is the amount of water collected in surface depressions during rainfall, like puddles. Importantly, water in these depressions doesn’t contribute to runoff until the depressions are filled. Think of it this way: until we fill the 'dips’, no ‘spill’ occurs. Who can help me remember the parts of initial abstraction?

Is it like the formula with depression storage, interception, and infiltration?

That's right! We can remember it as 'DII'—Depression, Interception, Infiltration. That way, we can quickly recall what makes up our initial losses. Any questions so far?

What happens to the water when these depressions fill up?

Great question! Once filled, excess water starts to flow and contribute to surface runoff. Let’s summarize: depression storage is vital as it delays runoff. It also helps us understand how rainwater interacts with our landscapes.
Role of Depression Storage in Hydrological Accounting
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s dive deeper into why depression storage is significant. Can someone explain how it fits into hydrological accounting?

I think it plays a part in the initial abstraction losses?

Correct! Initial abstraction includes depression storage, interception, and infiltration—it's all interconnected. So, if we want to estimate effective precipitation, we need to consider how much water we lose to depression storage first. How does this affect flood predictions?

If we underestimate depressions, we might overestimate runoff during a flood?

Exactly! Correct assessment helps us manage resources and prevent flooding. Remember, more storage means less immediate runoff, which gives us time to handle excess water.
Examples of Surface Depressions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s look at some examples of surface depressions that can contribute to depression storage. Can anyone name a few?

Potholes are one example, right?

Absolutely! Potholes, puddles, and even ploughed fields are excellent examples. They all act as storage points. How about farmland? What features there can contribute to depression storage?

Furrows! And maybe any low-lying areas?

Spot on! These features can significantly increase depression storage, especially in agricultural landscapes. So remember, the more complex the topography, the greater the potential for storing water. Let’s recap where depression storage occurs—potholes, furrows, ploughed fields, and low areas.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section introduces the concept of depression storage, highlighting its role in hydrological accounting as part of initial losses, which includes interception and infiltration. Understanding depression storage helps in estimating effective precipitation and managing water resources.
Detailed
Depression Storage: Definition and Concept
Depression storage is defined as the amount of water that collects in surface depressions, such as puddles and potholes, during rainfall. This stored water does not contribute to surface runoff until the depressions are filled. Notably, depression storage is considered part of the initial losses in hydrological accounting, which can be expressed as:
Initial abstraction = depression storage + interception + infiltration.
Typical examples of areas contributing to depression storage include low-lying areas, ploughed fields, and furrows in agricultural landscapes. Understanding this concept is crucial for professionals in hydrology and civil engineering, as it influences infiltration rates, flood peak estimations, and assists in effective water resource management.
Youtube Videos



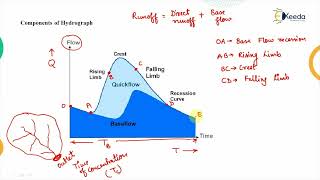






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Depression Storage
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Depression storage is defined as the amount of water that collects in surface depressions during rainfall and does not contribute to surface runoff. It must be filled before any runoff can occur. It is considered part of initial losses in hydrological accounting.
Detailed Explanation
Depression storage refers to the water that accumulates in small surface depressions like puddles, holes, or uneven ground after it rains. Before any water can move into rivers or lakes as runoff, these depressions need to fill up. This concept is crucial in hydrology because it impacts how much water is available for soaking into the ground (infiltration) and how much will be lost before runoff begins. Losses in hydrology include surface water that is intercepted by vegetation, water that seeps into the ground, and the water held in depression storage.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sponge that soaks up water. Before the sponge can overflow, it must fill up completely. Similarly, before rainwater can flow away as runoff into streams or rivers, it first fills the little 'sponge-like' depressions on the ground.
Initial Abstraction in Hydrology
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Initial abstraction = depression storage + interception + infiltration (before runoff starts).
Detailed Explanation
Initial abstraction is a key concept in hydrological studies. It encompasses all the water that is lost in the early stages of a rain event before any excess water begins to flow away as runoff. This includes water stored in depressions, water that gets caught by plants and trees (interception), and water that soaks into the soil (infiltration). Understanding these factors helps in managing water more efficiently and predicting the behavior of water in the environment.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how a sponge can hold onto water before it starts dripping. The amount of water it can hold corresponds to depression storage. Any water that is lost to the sponge (infiltration) or is absorbed by a surface (interception) before it starts dripping out again represents initial abstraction.
Examples of Depression Storage
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Typical examples: water in potholes, ploughed fields, ruts, low-lying areas, etc.
Detailed Explanation
Depression storage can be found in various forms in our environment. For instance, after it rains, potholes on roads can collect water, just like how fields that have been ploughed can hold small amounts of water in their grooves. Low-lying areas are also natural depressions that gather rainwater. Recognizing these examples helps in understanding how water is stored temporarily before it drains away or evaporates.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a child playing in a mud puddle. The puddle represents a depression where rainwater collects. As the child plays, the puddle gets filled with more water until it can no longer hold it, leading to the overflowing of water – this visualizes how natural depressions function in managing water.
Key Concepts
-
Depression Storage: The collection of water in surface depressions during rainfall.
-
Initial Abstraction: Loss of water before reaching surface runoff, made up of depression storage, interception, and infiltration.
-
Effective Precipitation: Rainfall that is available for infiltration and runoff after accounting for initial losses.
Examples & Applications
Potholes and puddles that collect rainwater during a storm contribute to depression storage.
Agricultural fields with furrows retain rainfall in low areas, enhancing depression storage and preventing runoff.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In puddles and holes, rainwater stays, before it runoff and flows away.
Stories
Imagine a thirsty garden after rain; water collects in small dips, nourishing plants before it spills into the pathways.
Memory Tools
Remember 'DII' - Depression, Interception, Infiltration for initial losses in hydrology.
Acronyms
DII can remind you of the parts that contribute to initial losses in rainfall management.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Depression Storage
The amount of water that collects in surface depressions and does not contribute to surface runoff.
- Initial Abstraction
The portion of precipitation that is lost before runoff begins, consisting of depression storage, interception, and infiltration.
- Effective Precipitation
The portion of rainfall that contributes to infiltration and runoff after accounting for initial losses.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
