Limitations of Infiltration Indices
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Oversimplification of Time-Variable Infiltration Behavior
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start by discussing one of the main limitations of infiltration indices. They tend to oversimplify the time-variable infiltration behavior. Can someone explain what this means?

It means that the indices don’t change even if the rainfall intensity varies during a storm, right?

Exactly! That's a key point. Since runoff and infiltration can change throughout a storm, using a single infiltration index may not reflect the true situation. This can lead to inaccurate modeling.

So, if rainfall suddenly increases, the index wouldn't provide a correct response?

Correct! It can’t adapt to real-time changes. Remember the acronym 'TIME' – Temporal Infiltration Model Error – helps us remember this limitation! Let's move on to the next limitation.
Sensitivity to Accurate Measurement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s discuss the sensitivity of infiltration indices to accurate measurements. Why do you think this is a problem?

If the measurements for runoff or rainfall are wrong, it could lead to completely incorrect indices.

Exactly! This sensitivity is crucial because even minor errors can skew results drastically.

Can you give an example where this would matter?

Certainly! If a storm is underestimated in terms of total rainfall, the runoff calculated might not be accurate, leading to poor flood risk assessments. Always keep in mind: Accurate data equals reliable indices!
Neglect of Spatial Variability
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about spatial variability. Why is it important in the context of infiltration indices?

Different areas like valleys or hillsides might absorb water differently due to soil type or cover.

Exactly! Infiltration varies across catchments due to factors like soil composition and vegetation. Infiltration indices assume uniformity, which leads to inaccuracies in prediction.

So, in cases of diverse land usage, using a single index won’t work as well?

You got it! To remember this point, think of 'VARY' – Variability Across Regions Yields discrepancies. Let's look at the last limitation.
Inapplicability under Certain Conditions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's address situations where infiltration indices simply can't be applied. Can anyone think of an example?

If the rainfall is always less than what the soil can handle, like in sandy areas, right?

Exactly! Such conditions mean there's no runoff, making the use of infiltration indices irrelevant. Remember: if you can’t see the runoff, the index won't be helpful!

That sounds like a situation we should always check before applying these indices!

Correct! Always assess the conditions first. To help remember, think of 'RIVER' – Rain Intensity vs. Viable Effective Runoff, which reminds us to consider rainfall intensity beforehand.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section highlights the limitations of infiltration indices, focusing on their oversimplification of complex infiltration dynamics, sensitivity to accurate data, inability to consider spatial variability, and applicability concerns under specific rainfall conditions.
Detailed
Limitations of Infiltration Indices
Infiltration indices, while useful for estimating runoff and simplifying infiltration analyses, come with significant limitations. These limitations include:
- Oversimplification of Time-Variable Infiltration Behavior: Infiltration indices do not adequately capture the dynamic nature of infiltration over time. Complex infiltration patterns can vary throughout a rain event, and indices might fail to reflect these changes.
- Sensitivity to Accurate Measurement of Runoff and Rainfall: The effectiveness of infiltration indices is highly dependent on the precision of the data collected. Errors in measuring runoff or rainfall can lead to inaccurate calculations of infiltration indices.
- Neglect of Spatial Variability: Infiltration varies significantly across different areas of a catchment due to factors like soil type, land cover, and moisture content. Infiltration indices typically assume uniform conditions, which can misrepresent actual infiltration behavior.
- Inapplicability under Certain Conditions: Infiltration indices become irrelevant in situations where rainfall intensity is consistently lower than the infiltration capacity of the soil, resulting in no surface runoff. This limits their utility in cases of moderate or low-intensity storms where infiltration meets or exceeds the rainfall rate.
Overall, while infiltration indices provide a useful tool for hydrologists, recognizing their limitations is essential for accurate hydrological modeling and flood management.
Youtube Videos
![WRE Module2 [PART02]- Infiltration indices: phi-index and w-index, runoff by infiltration method](https://img.youtube.com/vi/TS6Mem4j-qY/mqdefault.jpg)







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Oversimplification of Infiltration Behavior
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Oversimplify time-variable infiltration behavior.
Detailed Explanation
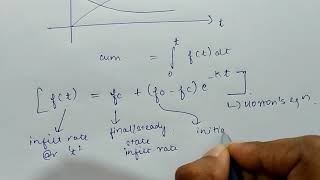
Infiltration indices are designed to simplify complex processes. However, this simplification often means that they do not accurately reflect how infiltration rates can change over time due to various factors such as soil properties and weather conditions. This can lead to inaccurate predictions, particularly in situations where rainfall intensity fluctuates significantly during a storm.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sponge that absorbs water at different rates depending on how dry or wet it is. If we only look at the average absorption rate over time, we might miss peak times when the sponge could absorb much more water. Just like with the sponge, the indices oversimplify the reality of how water infiltrates soil.
Sensitivity to Measurement Accuracy
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Sensitive to accurate measurement of runoff and rainfall.
Detailed Explanation
The accuracy of infiltration indices relies heavily on precise measurement of both rainfall and runoff. If there are errors in measuring either, this can lead to significant discrepancies in the calculated indices. Such inaccuracies can arise from various sources, such as faulty equipment or estimating runoff volumes incorrectly.
Examples & Analogies
Think of trying to weigh ingredients for a recipe. If you incorrectly measure flour or sugar, the final dish won't turn out right. Similarly, if the rainfall or runoff measurements are off, the infiltration indices won't provide a reliable estimate of water movement.
Neglecting Spatial Variability
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Do not account for spatial variability within a basin.
Detailed Explanation
Infiltration indices treat a catchment area as a single unit, overlooking the fact that different parts of a basin can have varying infiltration characteristics. This spatial variability can result from differences in soil type, vegetation cover, or land use, which means that a single index may not accurately represent infiltration across the entire area.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a farmer trying to grow crops in a field with different soil types — some sections may be sandy and drain quickly, while others are clay-heavy and retain water. The farmer can't use one strategy for the whole field successfully. Like the farmer, hydrologists need to recognize these differences to understand infiltration properly.
Inapplicability in Low-Intensity Conditions
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Inapplicable where rainfall intensity is always less than infiltration capacity (i.e., no runoff generated).
Detailed Explanation
Infiltration indices assume that runoff will occur when rainfall exceeds infiltration capacity. However, if the rainfall intensity is consistently lower than the soil's ability to absorb water, no runoff is generated. In these situations, infiltration indices become less relevant since they are designed to quantify runoff performance.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a sponge placed in a shallow dish of water. If water only drips in slowly, the sponge can absorb it all without any overflow. Here, the indices wouldn't provide useful information because there's no runoff to measure, just like there’s no need for a runoff measurement in this scenario.
Key Concepts
-
Oversimplification - Infiltration indices do not effectively account for the dynamic changes in infiltration during rainfall.
-
Data Sensitivity - Accuracy in runoff and rainfall measurements is crucial for reliable infiltration estimates.
-
Spatial Variability - Infiltration behavior can differ across regions within a catchment, which indices do not account for.
-
Condition Reliance - Infiltration indices may be irrelevant in low-intensity rainfall scenarios.
Examples & Applications
An area with heterogeneous soil types may exhibit varying infiltration rates, making a single index ineffective.
In low to moderate rainfall conditions, where infiltration meets or exceeds the rainfall rate, runoff may not occur, resulting in an index that does not apply.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To model flow and see it clear, Infiltration rates must be near. Check your data, check it twice; Accurate is key, don't think it twice!
Stories
Imagine a storm meter measuring rainfall; it could represent a flood or just a drizzle. If the meter isn't accurate, lives can be at risk. This shows how vital accuracy is in interpreting infiltration.
Memory Tools
Remember 'DOST' for the limitations: Data accuracy, Oversimplification, Spatial variability, and Time relevance.
Acronyms
VARY
Variability Across Regions Yields discrepancies in infiltration assessments.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Infiltration Indices
Empirical tools used to represent average infiltration characteristics over a specified period.
- Infiltration Capacity
The maximum rate at which soil can absorb water at any given moment.
- Runoff
The portion of rainfall that flows over the surface rather than infiltrating into the ground.
- Spatial Variability
The differences in infiltration behavior across various areas within a catchment.
- TimeVariable Infiltation Behavior
Changes in the rate of infiltration over the course of a rainfall event.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
