Classification of Drainage Systems
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Surface Drainage Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll start with surface drainage systems. These systems are crucial for removing excess water from the land's surface to prevent crop loss. Can anyone tell me why managing water on the surface is important?

I think if there's too much water, it can cause waterlogging.

Exactly, waterlogging can damage crops. Surface drainage systems include open ditches, random drainage, parallel drainage, and cross-slope drainage. Let’s break these down. What is one of the methods?

Open ditches allow water to flow away, right?

That’s correct! Think of open ditches as channels for water to escape. Now, remember the term 'CROSS' for surface drainage: C for Channels, R for Random, O for Open, S for Slope, and S for Surface. This acronym can help you remember the key types.

That's a neat way to remember them!

Great! In summary, surface drainage systems are essential for managing excess water to protect our crops.
Subsurface Drainage Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s move on to subsurface drainage systems. These are designed to manage water beneath the soil surface. What do you think are some examples?

Maybe they use pipes underground?

Correct! Those pipes are perforated and help transport excess water. This is called tile drainage. Recall the acronym 'PIPE' for subsurface systems: P for Pipes, I for Interceptor drains, P for Perforated, and E for Efficiency. Who can tell me about mole drainage?

Mole drainage creates channels in the soil, right?

Yes! It’s a technique best suited for clay soils. Remember, subsurface systems are key to maintaining an ideal water table for crop health. In summary, tile drainage and mole drainage help prevent root problems caused by excess water.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The classification of drainage systems is essential for effective agricultural practices. Surface drainage systems, which include methods like random drainage and cross-slope drainage, help remove water from land surfaces, while subsurface systems, such as tile drainage and mole drainage, target water below the soil surface, ensuring optimal conditions for crop growth.
Detailed
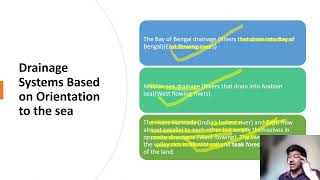
In the classification of drainage systems, we categorize them into two main types: surface drainage systems and subsurface drainage systems.
Surface Drainage Systems
- Open Ditches: These are straightforward channels designed to remove excess water from the land surface.
- Random Drainage: Involves strategically placed ditches to address specific low areas.
- Parallel or Bed Drainage: Comprises parallel ditches constructed at regular intervals for efficient water runoff.
- Cross-Slope Drainage: Utilized primarily in sloped areas, this drains water perpendicularly to the slope.
Subsurface Drainage Systems
- Tile or Pipe Drainage: Composed of perforated pipes buried below the ground, which collect and transport excess water from the root zone.
- Mole Drainage: Formed using mole ploughs to create unlined channels in clay soils.
- Vertical Drainage (Tube Wells): Involves pumping groundwater out to reduce water table levels.
This classification helps in designing effective drainage systems tailored to specific agricultural conditions, enhancing soil health and crop yield.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Drainage Systems
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Drainage systems are classified based on their function and layout:
Detailed Explanation
Drainage systems are crucial for managing water in agricultural land. They help remove excess water from the soil or surface, which can happen because of heavy rainfall or irrigation. The classification helps in understanding the design and implementation based on the specific needs of the land.
Examples & Analogies
Think of drainage systems like the plumbing in your house. Just as pipes carry excess water away from your sinks or bathrooms to prevent flooding, drainage systems do the same for agricultural fields.
Surface Drainage Systems
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Surface Drainage Systems
These systems remove excess water from the surface of the land and include open ditches, land grading, and shaping.
• a. Random Drainage: Ditches are placed randomly to remove surface water from low spots.
• b. Parallel or Bed Drainage: Shallow parallel ditches constructed at regular intervals.
• c. Cross-Slope Drainage: Used for sloping lands; ditches run perpendicular to the slope.
Detailed Explanation
Surface drainage systems focus on managing water that collects on the soil's surface. Various designs improve efficiency. Random drainage helps in low areas, while parallel drainage works well with flat land, and cross-slope drainage is specifically for hilly areas, helping to channel water away effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a playground after it rains. Surface drainage is like the sloping design of the ground that allows water to flow down and away from the swings, keeping the play area dry so kids can play safely.
Subsurface Drainage Systems
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Subsurface Drainage Systems
These systems remove water from the root zone and lower layers of the soil. They are also known as tile drainage systems.
• a. Tile or Pipe Drainage: Perforated pipes placed below ground to collect and transport excess water.
• b. Mole Drainage: Unlined channels made using mole ploughs in clay soils.
• c. Vertical Drainage (Tube Wells): Groundwater is pumped out to lower the water table.
Detailed Explanation
Subsurface drainage systems work below the soil surface, targeting water that accumulates in the root zone, which is critical for crop health. Tile drainage uses pipe systems that remove water effectively from deep within the soil, mole drainage creates channels to facilitate water movement, and vertical drainage involves pumping water out to maintain ideal moisture levels.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine using a sponge to soak up water – subsurface drainage systems are like the sponge that removes excess water from the soil's deeper layers, helping plants thrive without drowning.
Key Concepts
-
Surface Drainage Systems: Key for removing excess surface water to prevent crop loss.
-
Subsurface Drainage Systems: Manage water below the soil surface, allowing for better root health.
-
Tile Drainage: A method using perforated pipes to collect and drain excess water.
-
Mole Drainage: An efficient drainage method for clay soils using unlined channels.
Examples & Applications
An example of surface drainage is a farmer digging open ditches in their field to guide excess water away from crops during heavy rains.
A practical instance of subsurface drainage is the installation of perforated pipes in agricultural fields to manage the water table level.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For drainage to gain, open ditches we maintain!
Stories
Once upon a time, in a farm filled with crops, rain would come pouring down. The clever farmer built ditches to save the day, guiding water away to make his crops sway!
Memory Tools
'CROSS' systems help with surface drainage: Channels, Random, Open, Slope, Surface.
Acronyms
'PIPE' systems for subsurface
Pipes
Interceptor
Perforated
Efficient.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Surface Drainage Systems
Systems designed to remove excess water from the surface of the land.
- Subsurface Drainage Systems
Systems that remove water from the root zone and lower layers of soil.
- Tile Drainage
A method that involves perforated pipes placed below ground to collect excess water.
- Mole Drainage
Unlined channels made using mole ploughs primarily in clay soils.
- CrossSlope Drainage
A drainage technique where ditches are placed perpendicular to the slope.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
