Necessity of Drainage in Irrigated Lands
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Waterlogging and Its Impacts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's explore how waterlogging affects crops. Waterlogging occurs when excess irrigation saturates the soil. Can anyone tell me how this affects plants?

It can drown the roots and reduce oxygen availability.

Exactly! And when roots cannot get enough oxygen, they can rot. This leads to poor crop yields. Remember, W-A-R - Waterlogging Affects Roots!

But how does that relate to irrigation?

Great question! Over-irrigating without proper drainage causes this issue. Let's think of good drainage as a hero that saves crops from drowning!

So are there ways to prevent waterlogging then?

Absolutely, that’s where drainage systems come in. We'll discuss those next!
Salinity Control
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's discuss salinity. In places with high evaporation, salts can rise to the surface. What do you think happens to the soil?

It becomes salty, making it hard for plants to grow.

Right! If the salts build up, it leads to salinization. Remember: High Salts = Low Growth! How do we avoid this?

By having proper drainage to wash the salts away?

Correct! Well-designed drainage systems help control salinity levels, ensuring healthy soil.
Soil Structure Maintenance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about soil structure. Why is it important for crops?

Good soil structure helps roots grow better.

Exactly. Saturated soils lose their structure and aeration. S-A-D - Saturation Affects Drainage! What role do we think drainage plays here?

It keeps the soil from being too wet and helps microbes!

That's right! Drainage systems help maintain aeration and microbial activity, crucial for soil health.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Effective drainage is essential in irrigated lands to prevent negative consequences such as waterlogging and salinity that can harm crops. Proper drainage maintains soil health and supports infrastructure, ultimately leading to higher crop yields and agricultural productivity.
Detailed
Necessity of Drainage in Irrigated Lands
Drainage in irrigated areas plays a vital role in sustainable agriculture. It helps in:
- Prevention of Waterlogging: Excess water can saturate the root zone, which leads to stunted growth and even crop failure due to root rot.
- Control of Salinity and Alkalinity: In arid regions, unchecked groundwater can transport salts to the surface. Without drainage, these salts accumulate, harming soil quality and crop productivity.
- Maintenance of Soil Structure and Aeration: Efficient drainage helps preserve optimal soil moisture levels and soil aeration for microbial activity necessary for healthy cropping.
- Protection of Civil Structures: High groundwater tables can threaten foundations and infrastructure; proper drainage maintains necessary depths for structural stability.
- Increasing Crop Yield and Diversity: Well-drained lands enable diverse crop growth and timely agricultural practices, significantly improving productivity.
Youtube Videos
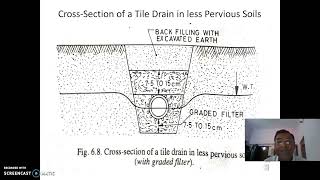



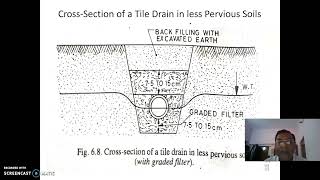



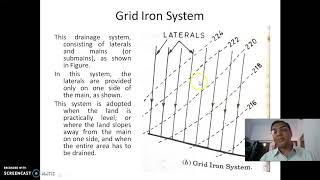

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Prevention of Waterlogging
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Waterlogging occurs when excess irrigation water accumulates in the root zone, saturating the soil and reducing oxygen availability to plant roots. This condition stunts plant growth and may cause root rot or even complete crop failure.
Detailed Explanation
Waterlogging happens when too much water collects in the soil around the roots of plants. This excess moisture fills the spaces in the soil, preventing air from getting to the roots, which is vital for their health. When roots don't get enough oxygen, plants struggle to grow and may die if the condition lasts. This is particularly problematic for crops, as it can lead to lower yields or complete failure of the crop.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to breathe while submerged in water – it's impossible to get the air you need. Similarly, when plants are 'submerged' in too much water, their roots can't 'breathe,' leading to unhealthy plants.
Control of Salinity and Alkalinity
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In arid and semi-arid regions, the upward movement of groundwater brings salts to the surface. Without proper drainage, these salts accumulate in the root zone, leading to salinization and alkalinization of soils, which severely hampers agricultural productivity.
Detailed Explanation
In dry areas, water from below the ground can bring salts up to the soil surface. If water doesn't drain away properly, these salts build up in the soil. High salt levels can interfere with plant processes, making it hard for them to absorb water and nutrients. This process, known as salinization, can make the soil unsuitable for farming and severely reduce crop yields.
Examples & Analogies
Think of salinization like adding too much salt to food. Just as an excess of salt can ruin a dish, excess salts in the soil can ruin the environment for plants, making it difficult for them to grow.
Maintenance of Soil Structure and Aeration
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Saturated soils lose their structure and porosity over time. Drainage helps maintain optimal soil moisture levels, which in turn supports good tilth, aeration, and microbial activity essential for healthy crops.
Detailed Explanation
When soil is constantly wet, it can lose its ability to hold its structure and allow air to move through it. This can lead to compacted, tight soil that doesn't drain well or provide a good environment for roots. Proper drainage keeps the soil at the right moisture level, which is important for maintaining its structure and allows air to circulate, which is needed for both plant roots and beneficial microorganisms that help crops thrive.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to walk through a muddy field. Your shoes get stuck because the soil is too wet. In contrast, firm, dry soil allows you to walk easily. Plants need healthy, well-structured soil, similar to how we need stable ground to walk on.
Protection of Civil Structures and Infrastructure
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
High groundwater tables can damage foundations, roads, and other infrastructure. Proper drainage ensures structural stability by keeping groundwater at a safe depth.
Detailed Explanation
When the water table is too high, the structural integrity of buildings, roads, and other infrastructure can be compromised. Excess water can erode foundations and lead to cracks or failures. By implementing proper drainage systems, we can keep the water tables lower and protect these structures from water damage.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a house built on a soggy area; eventually, if the ground is too wet, the foundation might sink or crack just like how a heavy object can sink into soft mud.
Increasing Crop Yield and Diversity
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Well-drained fields support the growth of a wider variety of crops and increase overall productivity. Drainage also allows timely land preparation and harvesting, reducing risks associated with delayed field operations.
Detailed Explanation
Fields that have efficient drainage can support more types of crops because different plants have varying water needs. Good drainage prevents crop loss during heavy rain and allows farmers to plant and harvest when they need to, which ultimately leads to higher yields for farmers.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a restaurant with a diverse menu. Just as a well-rounded menu attracts more customers, diverse crop options can enhance farmland productivity, providing food security and economic benefits.
Key Concepts
-
Prevention of Waterlogging: Essential to avoid root damage and crop failure.
-
Control of Salinity: Necessary for maintaining soil fertility.
-
Soil Structure Maintenance: Drainage prevents soil saturation and supports crop health.
Examples & Applications
In arid regions, failure to drain can lead to severe soil degradation due to salinity, affecting crops like wheat.
Proper drainage systems enabled farmers in California's Central Valley to increase crop diversity and yields.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Salts rise high, plants must sigh, without good drainage, crops may die.
Stories
Once there was a farmer who ignored drainage on his irrigated land. His crops began to drown, and soon enough, his fields turned to marsh. When he finally installed a drainage system, his crops flourished again!
Memory Tools
D-R-A-N-AGE - Drainage Reinforces Agricultural Needs, Aiding Growth and Efficiency.
Acronyms
W-A-R - Waterlogging Affects Roots.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Waterlogging
A condition when excess water saturates the soil, limiting oxygen to plant roots.
- Salinity
Concentration of salts in the soil which affects crop growth.
- Soil Structure
The arrangement of soil particles that influences water movement and root development.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
