Why is the MYP Design Cycle Important?
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
The Importance of Critical Thinking
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're exploring why the MYP Design Cycle is vital for developing skills like critical thinking. Can anyone tell me how they think critical thinking is involved in design?

I think you need to analyze the problems before coming up with a solution, right?

Exactly! Analyzing problems is a crucial first step. In fact, critical thinking helps us understand the context and anticipate challenges. We can remember this with the acronym A.C.T — 'Analyze, Context, Think'.

What kind of problems do we analyze?

Good question! We analyze both the existing solutions and the needs of users. Reflecting on these can lead to innovative solutions.

So without critical thinking, we might just jump into making something without knowing if it will work?

Precisely! That's why we always emphasize thinking before creating. Let's summarize: Critical thinking helps us analyze problems and think of solutions systematically.
Developing Creativity and Innovation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss how the design cycle nurtures creativity. What do you think happens in the brainstorming phase?

We come up with lots of ideas, right? Different designs and features!

That's right! The goal is to explore as many ideas as possible. Remember the term 'Divergent Thinking'? That's when we generate varied options without restrictions. What’s a tip to help keep ideas flowing?

Maybe we can use mind maps or sketches?

Excellent! Using tools like mind maps can enhance creativity. At the end of this stage, we narrow it down to the best ideas through evaluation. Who can summarize how this connects to innovation?

It shows that thinking creatively leads to new solutions and improvements!

Great summary! Creativity during the design cycle is encouraged, making innovation more attainable.
Reflection and Self-Assessment
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s wrap up by discussing self-assessment within the design cycle. Why do you think reflecting on our projects is important?

It helps us see what we did well and what could be better next time!

Exactly! Self-reflection allows us to recognize areas of improvement and build resilience. This is key in the Evaluating stage of the cycle. What’s a good method for self-assessment?

We could create a checklist of our goals and see if we met them!

Great idea! Using checklists can guide our reflection process effectively. To confirm our learning today, can someone summarize the role of self-assessment in design?

It allows us to improve and learn from each design cycle, making us better designers!

Perfect summary! Remember that reflection is a crucial part of growth, both personally and as a designer.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The MYP Design Cycle is a vital framework that guides students through the process of design and innovation. It builds essential skills such as critical thinking, creativity, and self-assessment, equipping students for future careers by fostering a mindset of problem-solving and reflection.
Detailed
Why is the MYP Design Cycle Important?
The MYP Design Cycle is not merely a process for creating products; it plays a significant role in cultivating a set of lifelong skills that are crucial in various fields. Here are the primary reasons underpinning its importance:
- Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving: The design cycle encourages students to analyze problems and think critically about potential solutions, essential skills in any profession.
- Research and Analysis: Engaging with research helps students identify challenges and gaps that their designs can address, teaching them to support their ideas with evidence.
- Time Management: The structured approach of the design cycle helps students learn to manage their time effectively, prioritizing tasks and setting milestones in the design process.
- Creativity and Innovation: By providing a framework for brainstorming and developing ideas, the design cycle fosters creativity, pushing students to explore various designs and solutions.
- Self-Assessment and Resilience: The iterative nature of the cycle promotes reflection on successes and failures, teaching students to continuously assess their work and develop resilience in overcoming challenges.
Overall, the MYP Design Cycle helps students grasp the impact of design and technology on society and the environment, resulting in a transferable mindset applicable across a multitude of careers.
Youtube Videos
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Building Lifelong Skills
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Critical thinking and problem-solving
- Research and analysis
- Time management
- Creativity and innovation
- Self-assessment and resilience
Detailed Explanation
The MYP Design Cycle promotes essential skills that last a lifetime. These include critical thinking, which allows students to analyze and make informed decisions. Problem-solving skills help students tackle challenges effectively. Research and analysis enable students to gather relevant information and interpret it correctly. Time management is crucial for completing projects efficiently, while creativity and innovation drive fresh ideas. Additionally, self-assessment teaches students to reflect on their work and improve continuously.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the MYP Design Cycle as a toolkit you carry throughout life. Just like a carpenter uses various tools to build a sturdy house, you can use critical thinking and problem-solving skills to build a successful career, whether in technology, healthcare, or any other field.
Impact on Society and Environment
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It helps you think deeply about the impact of technology and design on society and the environment.
Detailed Explanation
Through the MYP Design Cycle, students learn to evaluate how their designs and technological solutions affect people and the planet. This means considering not just how a product works, but also what happens after it's made—like its environmental impact, its social benefits, and how it serves the community. This awareness encourages responsible design practices that prioritize the well-being of both society and the ecology.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're creating a new smartphone. Beyond just its functions, you'd need to consider the materials used—are they sustainable? What about e-waste when the phone is outdated? Just like an architect weighs the aesthetics of a building with its environmental impact, designers need to be mindful of broader consequences of their work.
Transferable Mindset
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Whether you go into engineering, fashion, business, or education, the mindset you develop here is widely transferable.
Detailed Explanation
The skills and ways of thinking cultivated through the MYP Design Cycle extend beyond just design or technical fields. Students who learn to approach problems systematically, think critically, and innovate can apply these strategies in any discipline, be it the arts, sciences, or social work. This flexibility is important in today's fast-paced and ever-changing job markets, where adaptability is key.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a chef who learns to balance flavors and textures in cooking. Those skills are not limited to just making food; they translate well into other areas such as event planning or even interior design, where a similar sense of balance is required. Likewise, the MYP Design Cycle prepares you to adapt and succeed in various careers.
Key Concepts
-
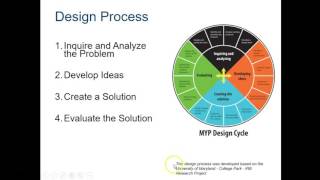
Design Cycle: A structured framework for problem-solving consisting of four stages: Inquiring and Analyzing, Developing Ideas, Creating the Solution, Evaluating.
-
Critical Thinking: Skills necessary for analyzing problems and devising effective solutions throughout the design process.
-
Creativity: The generation of novel and useful ideas that enhance design and innovation.
-
Self-Assessment: The practice of evaluating one’s own work to foster improvement and resilience.
Examples & Applications
When designing an eco-friendly product, students research existing solutions and identify gaps to address.
In the Developing Ideas phase, students may sketch different designs for a new product, considering functionality and aesthetics.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Think, Create, Reflect, and Innovate — follow the cycle, don’t hesitate!
Stories
Once in a creative kingdom, designers followed a cycle: they inquired about problems, crafted ideas, built solutions, and reflected on their work to improve the next creation.
Memory Tools
I.D.C.E: Inquire, Develop, Create, Evaluate.
Acronyms
C.I.R.C
Creativity
Innovation
Reflection
Challenges — four key elements of successful design.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Critical Thinking
The ability to analyze facts to form a judgment.
- Creativity
The use of imagination or original ideas to create something.
- SelfAssessment
The evaluation of one's own performance or understanding.
- Innovation
The process of translating an idea or invention into a good or service that helps improve life.
- Design Cycle
A structured process that guides the development of solutions through a series of stages.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
