What is a Linear Inequality?
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Linear Inequalities
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore what linear inequalities are. Can anyone tell me how linear inequalities differ from linear equations?

I think equations show a specific value, while inequalities show a range of values.

Exactly, well done! Linear inequalities use symbols such as < and > to compare values. Can anyone give me an example?

Like 2x - 3 < 5?

Great example, Student_2! Remember, inequalities are crucial in understanding constraints in real-life situations. Think about speed limits or budgets!

So, inequalities help us understand limits?

Yes, they help represent limits and ranges visually. Let's keep this in mind as we dive deeper into how to solve them.
Standard Forms of Linear Inequalities
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the basics, let's look at the standard forms of linear inequalities. In one variable, we use expressions like ax + b < 0. Can anyone identify a similar example?

Maybe something like 3x + 5 ≤ 10?

Perfect, Student_4! And what about in two variables?

It could be something like x + y > 3?

Exactly! Remember, these forms help us set up problems and visualize solutions later. Can someone summarize the difference between the one-variable and two-variable forms?

One variable focuses on a straight line, while two variables create a region on a graph!

Great recall, Student_2! This foundation is key to solving inequalities effectively.
Solving Linear Inequalities
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's move on to solving linear inequalities. What's the first step in solving 2x - 3 < 5?

I think we would add 3 on both sides to start.

Correct! And after simplifying to 2x < 8, what would we do next?

Dividing by 2 to get x < 4!

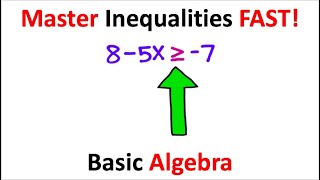
Absolutely! When we have to multiply or divide by a negative, remember to reverse the sign. Why is that important?

Because it changes the direction of the inequality!

Yes! This rule avoids confusion and is essential for correct solutions. Let’s visualize some inequalities on a number line.
Graphing Linear Inequalities
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

When graphing inequalities, how do we decide between an open or closed circle?

Open circles are for < and >, and closed circles are for ≤ and ≥!

Exactly! And shading indicates the range of solutions. If we have x < 3, which way do we shade?

To the left, because it includes all numbers less than 3.

Well put, Student_3! Remember, our goal is to visualize the inequality solutions effectively.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Youtube Videos
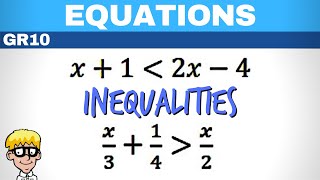

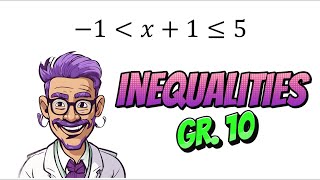

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Linear Inequalities
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A linear inequality is similar to a linear equation, but instead of an ‘=’ sign, it uses inequality signs:
• < (less than)
• ≤ (less than or equal to)
• > (greater than)
• ≥ (greater than or equal to)
Detailed Explanation
A linear inequality is an expression that represents a relationship between two values where one value is not necessarily equal to the other. Instead of using an equals sign, it employs symbols like <, >, ≤, or ≥. These symbols help us understand whether one side of the inequality is less than, greater than, or equal to the other side, providing a range of possible solutions instead of a single value.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a speed limit sign on a road. Instead of saying you must drive at exactly 50 km/h, it might say you must drive 'less than or equal to 50 km/h.' This gives drivers a variety of acceptable speeds, similar to how linear inequalities provide a range of values.
Key Concepts
-
Definition of Linear Inequality: A mathematical expression that uses inequality symbols <, ≤, >, or ≥.
-
Standard Forms: Inequalities can be expressed in standard forms for one or two variables.
-
Graphical Representation: Solutions are represented visually on number lines or coordinate planes.
Examples & Applications
Example of One Variable: Solve 2x - 3 < 5 leading to x < 4.
Example of Two Variables: Graph the inequality x + y ≤ 5 which represents the region below and including the line x + y = 5.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When the sign's a flip, just remember the tip, always check your moves before you take the trip.
Stories
Imagine a race with speed limits. Each interval shows where you can safely go, not just a single point but a range.
Memory Tools
Use BARS: Boundary, Analyze, Reverse, Shade for solving and graphing inequalities.
Acronyms
SLOPE
Solve
Locate
Outline
Plot
Evaluate for inequality graphing.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Linear Inequality
An inequality that involves a linear expression which can be one-dimensional or two-dimensional.
- Inequality Signs
Symbols (<, ≤, >, ≥) that indicate the relationship between two expressions.
- Boundary Line
The line that separates the regions on a graph for a linear inequality.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
