Standing Waves and Resonance
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Standing Waves
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start by discussing what standing waves are. They occur when two waves of the same frequency and amplitude travel in opposite directions and interfere with each other.

So, are standing waves the ones that don't appear to move?

Exactly! They create points called nodes where there’s no movement, and antinodes where the amplitude is maximum. Can anyone tell me how these are formed?

They form through constructive and destructive interference?

Yes! Great job! Nodes correspond to destructive interference, while antinodes correspond to constructive interference.

Can we see these in real life, like in a guitar string?

Yes! When you pluck a guitar string, standing waves are formed. Let’s remember that with the acronym N.A. for Nodes and Antinodes!

What about places where there is no movement?

Those are the nodes! Remember, they’re spots where we see no displacement in a standing wave. They’re crucial in applications such as musical instruments!

In summary, standing waves are the result of the interference of two traveling waves, leading to fixed points of no movement (nodes) and points of maximum displacement (antinodes).
Concept of Resonance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's move on to resonance. Can anyone explain what resonance is in simple terms?

Is it when something shakes a lot?

That's a good starting point! More specifically, resonance occurs when a system is driven at its natural frequency, leading to larger amplitude oscillations. Can anyone give me an example?

Like when you push a child on a swing at just the right time?

Exactly! If you push at the right timing, the swing goes higher. This is resonance in action! How about in structures?

A bridge could resonate and vibrate a lot during strong winds or heavy traffic.

Correct! If not controlled, this can cause structural failure, so engineers must consider this when designing bridges.

So resonance can be both beneficial and harmful?

Right! It's vital to harness it correctly, whether in music or engineering. To remember the concept of resonance, think R.E.S.O.N.A.N.C.E. - Really Engaging Systems Oscillating Naturally And Not Catastrophically. In summary, resonance leads to larger amplitudes, especially in systems driven at their natural frequency.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores standing waves formed by the interference of two waves with the same frequency and amplitude traveling in opposite directions, resulting in nodes and antinodes. It also discusses resonance, highlighting its importance in natural phenomena and applications like musical instruments and structural engineering.
Detailed
In this section on 'Standing Waves and Resonance,' we delve into the concept of standing waves, which are formed when two waves of the same frequency and amplitude travel in opposite directions and interfere with each other. This interference creates fixed points called nodes, where there is no motion, and points of maximum amplitude called antinodes. The significance of standing waves can be observed in various physical systems such as vibrating strings and air columns in musical instruments.\n\nThe section also covers the phenomenon of resonance, which occurs when a system is driven at its natural frequency, resulting in significantly amplified oscillations. This principle explains why musical instruments produce sound at specific pitches and highlights the potential risks of structural systems, like bridges, that may resonate due to external forces. In conclusion, understanding standing waves and resonance is crucial due to their wide applications in music, engineering, and physical sciences.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Standing Waves
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
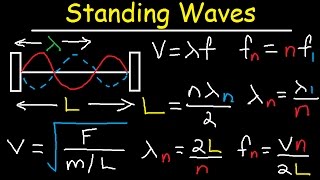
Standing waves are formed by the superposition of two waves traveling in opposite directions with the same frequency and amplitude.
- Nodes: Points of zero amplitude.
- Antinodes: Points of maximum amplitude.
Formation: Occurs in strings, air columns, and other mediums with fixed boundaries.
Detailed Explanation
Standing waves are a unique phenomenon in wave mechanics. They occur when two identical waves move in opposite directions along the same medium—think of two people on a trampoline bouncing up and down in phase with each other. Where these waves meet, they interfere constructively at certain points (antinodes), and at other points (nodes), they cancel each other out completely resulting in no motion at all. This creates a pattern that looks like it is standing still, hence the name 'standing waves'. This can happen in different mediums, like guitar strings or air columns in instruments.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a jump rope being shaken at both ends by two people; the waves created along the rope can form standing wave patterns where some points on the rope appear to be completely still (nodes) while others bounce up and down the highest (antinodes). This behavior can also be observed in musical instruments, such as in a guitar string when plucked.
Characteristics of Nodes and Antinodes
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Nodes: Points of zero amplitude.
- Antinodes: Points of maximum amplitude.
Detailed Explanation
In a standing wave, nodes and antinodes have critical roles. Nodes are the points on the wave where there is no movement; they remain stationary regardless of the wave motion. In contrast, antinodes are where the energy of the wave is maximized—they are the points of maximum displacement. When you visualize a standing wave, the nodes remain fixed while the antinodes oscillate to their fullest extent.
Examples & Analogies
If you think of a swing, the lowest point of the swing's motion can be compared to an antinode, where it swings the highest. The points where the swing doesn't move at all while someone pushes it would be like nodes.
Formation of Standing Waves
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Formation: Occurs in strings, air columns, and other mediums with fixed boundaries.
Detailed Explanation
Standing waves can only form in systems that have fixed endpoints, which create a situation where waves reflect back upon themselves. For example, when a string is fixed at both ends (like on a guitar), waves traveling down the string reflect back when they reach the ends. The interference between incoming and reflected waves leads to the characteristic pattern of standing waves. Air columns in wind instruments can also support standing waves as they create a series of nodes and antinodes based on how they are played.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a rope tied at both ends: when you shake it, coming waves reflect back to create specific patterns. Similarly, in a flute, when you blow air into it, standing waves form in the air column, producing the musical notes we hear.
Understanding Resonance
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Resonance occurs when a system is driven at its natural frequency, resulting in large amplitude oscillations.
Detailed Explanation
Resonance is an important phenomenon in which a system vibrates with increasing amplitude at certain frequencies—specifically, its natural (or resonant) frequency. This is the frequency at which the system naturally prefers to oscillate. If energy is added to the system at this frequency, it can lead to very large oscillations, at times causing the material to even break apart if the amplitude becomes too great.
Examples & Analogies
Think about pushing someone on a swing. If you time your pushes to match the natural rhythm of the swing, the person swings higher and higher. If you don't time your pushes, the person will not swing nearly as high. This perfectly illustrates the concept of resonance.
Real-Life Examples of Resonance
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Examples:
- Musical Instruments: Strings and air columns resonate to produce sound.
- Bridges: Can resonate due to wind or traffic, leading to structural failure if not damped.
Detailed Explanation
Musical instruments often rely on resonance. For example, a guitar string vibrates at frequencies that correspond to musical notes, producing sound due to resonance within the body of the guitar. Similarly, large structures like bridges can experience resonance from wind or traffic, which can lead to serious safety concerns if the structure begins to vibrate dangerously.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a swing bridge in the wind; if wind causes the bridge to sway at just the right frequency, the swaying can get bigger and bigger—a dangerous situation! Just like a singer can shatter a glass by matching the note that resonates with its frequency.
Key Concepts
-
Standing waves: Formed by the combination of two waves moving in opposite directions, creating nodes and antinodes.
-
Resonance: The significant amplification that occurs when a system is driven at its natural frequency, relevant to both sound and structural integrity.
Examples & Applications
The strings of a guitar resonate to produce different musical notes when played.
A swing oscillates higher and higher when pushed at regular intervals that match its natural frequency.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In waves that stand so grand, Nodes stay still, Antinodes command!
Stories
Imagine pushing a child on a swing. If you time your pushes right, the child swings higher - that's resonance at work, just like the guitar strings vibrating to create sound.
Memory Tools
Remember R.E.S.O.N.A.N.C.E. for resonance: Really Engaging Systems Oscillating Naturally And Not Catastrophically.
Acronyms
N.A. for Nodes and Antinodes in standing waves.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Standing Waves
Waves formed by the superposition of two waves traveling in opposite directions with the same frequency and amplitude.
- Nodes
Points in a standing wave where the amplitude is zero.
- Antinodes
Points in a standing wave where the amplitude is maximum.
- Resonance
The phenomenon that occurs when a system is driven at its natural frequency, leading to large amplitude oscillations.
- Natural Frequency
The frequency at which a system naturally oscillates when not subjected to external forces.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
