Comparing European and Non-European Exploration
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Motivations of Exploration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss the primary motivations behind European and Chinese explorations. Can anyone tell me what motivated the European explorers like Columbus and da Gama?

They were looking for riches, especially spices and precious metals!

Exactly! The quest for economic gain was a significant driver. How did this differ from Zheng He’s expeditions?

Zheng He was more focused on diplomacy and collecting tribute, right?

That's correct! So, remember: European exploration = economic gain (think 'E for Economic'), and Zheng He = diplomatic prestige (think 'D for Diplomatic'). It’s a useful way to recall their motivations.
Scale and Duration of Voyages
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's look at the scale and duration of these voyages. Who can tell me about the fleets used by Columbus and da Gama?

They used smaller fleets, around 3 to 10 ships.

That's right! And how long did their voyages typically last?

Usually only 1 to 2 years.

Great! Now, how does this compare to Zheng He’s expeditions?

He had really huge fleets, sometimes with over 300 ships, and his voyages lasted for years.

Exactly! Keep in mind the acronym 'FLEET' for European voyages being smaller and shorter while Zheng He's were large and lengthy.
Political Control and Settlement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's discuss political control. What kind of political control did the European explorers establish?

They made direct colonial claims and established settlements.

That's right! And what about Zheng He?

He didn't intend to settle; he just established temporary diplomatic outposts.

Correct! To help remember, think of 'SETTLE' for Europeans: they settled, while Zheng He was more about 'CONNECT' with other cultures.
Technological Differences
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s turn to technology. What were some advancements that helped European sailors?

They used caravels and navigational instruments like the astrolabe!

Good job! Now, what about the technology used during Zheng He’s voyages?

He had massive treasure ships and strong navigational knowledge.

Perfect! You can remember 'NAV' for Navigational tools with Europeans and 'TREASURE' for Zheng He’s fleets.
Impact on Indigenous Peoples
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's discuss the impact on indigenous peoples. What was the impact of European exploring on these populations?

Many indigenous peoples faced colonization, disease, and forced labor.

Exactly! And how did Zheng He’s voyages impact indigenous groups?

They were more about trade and exchanges rather than colonization.

Right! To reinforce this, remember 'HARM' for Europeans and 'TRADE' for Zheng He: harmful impacts vs. trade-oriented impacts.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section explores the differing motivations and impacts of European and Chinese explorations. While European voyages focused on economic gain and territorial claims, Zheng He's explorations emphasized diplomatic prestige and trade. The impacts on indigenous peoples also differ, with European exploration leading to colonization, while Zheng He’s interactions were more transactional and diplomatic.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
This section compares European exploration, exemplified by figures such as Christopher Columbus and Vasco da Gama, and non-European exploration demonstrated by Admiral Zheng He of the Ming Dynasty. It highlights key aspects including:
- Primary Motivation: European explorers sought economic gain from precious metals and trade, alongside Christian conversion and empire building. In contrast, Zheng He's voyages aimed to establish diplomatic relationships and prestige rather than colonization.
- Scale and Duration: European expeditions often utilized smaller fleets (3–10 ships) for relatively short periods (1–2 years), while Zheng He's fleets were massive, sometimes exceeding 300 ships, and could last multiple years.
- Political Control: Europeans established direct colonial claims and permanent settlements, often leading to the domination of indigenous populations. Zheng He’s approach involved forming temporary diplomatic outposts without the intent of settlement.
- Technological Advancements: European navigation relied on advances such as caravels and new navigational instruments, while Zheng He benefited from massive treasure ships and established navigational knowledge from previous dynasties.
- Impact on Indigenous Peoples: European contact often resulted in colonization, disease introduction, and forced labor systems, contrasting with Zheng He’s mostly diplomatic engagements, which were more transactional in nature.
This analysis underscores the distinct motivations and outcomes of exploration, highlighting how these interactions shaped historical trajectories in diverse ways.
Youtube Videos



![European Exploration in the AMERICAS [APUSH Unit 1 Topic 3] 1.3](https://img.youtube.com/vi/TRrnYm_SwHc/mqdefault.jpg)





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Differences in Motivation
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Primary Motivation
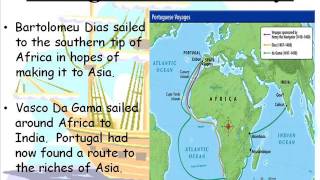
- European Voyages (e.g., Columbus & da Gama): Economic gain (spices, precious metals), religious conversion, empire building.
- Chinese Voyages (Zheng He): Diplomatic prestige, tribute collection, demonstration of power.
Detailed Explanation
European exploration was primarily driven by the desire for economic wealth through trade in spices and precious metals. Explorers like Columbus wanted to establish colonies and convert indigenous peoples to Christianity. In contrast, Chinese voyages led by Zheng He focused on diplomacy and collecting tribute, as well as showcasing China's might without the intention of establishing permanent settlements.
Examples & Analogies
Think of European exploration like a business expedition driven by profits, similar to how companies today venture into new markets to increase their revenue. On the other hand, Zheng He's voyages were more like diplomatic visits aimed at strengthening international relations without the goal of colonization.
Scale and Duration of Voyages
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Scale and Duration
- European Voyages: Smaller fleets (3–10 ships on early voyages), voyages lasting 1–2 years.
- Chinese Voyages: Very large fleets (hundreds of ships), voyages lasting months–years.
Detailed Explanation
European voyages were typically conducted with smaller fleets, allowing for shorter voyages of 1 to 2 years. This made it easier for European powers to manage their expeditions. In contrast, Zheng He commanded fleets of hundreds of ships, which embarked on longer voyages that could last several months or even years, reflecting a different scale and ambition in maritime exploration.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a small startup company launching a product with a small team going to nearby markets, versus a large corporation sending a massive team to explore international markets and establish a brand presence. The scale of their operations greatly influences their strategy and duration.
Political Control
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Political Control
- European Voyages: Direct colonial claims; establishment of permanent settlements.
- Chinese Voyages: Temporary diplomatic outposts; no intent to colonize or settle.
Detailed Explanation
European explorers sought to establish direct control over the lands they discovered through colonization, leading to permanent settlements. This assertive approach was aimed at expanding their empires and gaining resources. Conversely, Zheng He's voyages focused on establishing temporary diplomatic relationships without any intention of claiming land for China, showcasing a different approach to international interactions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a company that not only seeks to sell products in a new country but also sets up branches and takes over local businesses for maximum control. In comparison, think of a charity organization visiting another country to provide aid and form relationships without any plans of establishing local offices.
Technological Innovations
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Technology Used
- European Voyages: Caravels, carracks, early navigational instruments adapted from other cultures.
- Chinese Voyages: Advanced shipbuilding (massive treasure ships), well-established navigational knowledge.
Detailed Explanation
European expeditions utilized ships like the caravel and carrack, which were designed for speed and maneuverability, along with navigational tools adapted from other cultures to aid their travels. In contrast, Zheng He employed large treasure ships with advanced shipbuilding techniques and navigational knowledge, reflecting a lower reliance on adaptations, having developed their expertise over centuries.
Examples & Analogies
Think of how a modern sailing competition uses high-speed racing boats designed to outperform others. In comparison, Zheng He's fleet could be likened to a governor's luxurious yacht, built not just for speed but to showcase the power and wealth of the country.
Impacts on Indigenous Peoples
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Impact on Indigenous Peoples
- European Impact: Immediate colonization, disease introduction, forced labor systems (encomienda).
- Chinese Impact: Mostly diplomatic; limited settlement. Contact was more transactional than colonial.
Detailed Explanation
The arrival of European explorers typically led to the colonization of native lands, introduction of diseases that decimated populations, and systems imposing forced labor, such as the encomienda system. In contrast, Zheng He's encounters were largely diplomatic, marked by limited settlement and a focus on trade, highlighting a less invasive approach to indigenous societies.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a new franchise might move into a neighborhood, building storefronts and affecting local businesses and community structures. Conversely, think of cultural festivals where practitioners share traditions without claiming territory or resources altering the local way of life significantly.
Key Concepts
-
European Exploration: Driven largely by economic gain and imperialism.
-
Zheng He: Focused on diplomacy and trade rather than colonization.
-
Technological Advancements: Critical for successful navigation during the Age of Exploration.
Examples & Applications
Columbus' expedition led to the establishment of Spanish colonies in the Americas.
Zheng He's voyages resulted in enhanced trade relationships with Southeast Asian kingdoms.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To navigate the ocean blue, Columbus sought gold so true. Zheng He sailed, a different quest, diplomacy and trade, he thought was best.
Stories
Imagine two great explorers: Columbus, with maps and a treasure chest, crosses the Atlantic on his bold quest. Meanwhile, across the world, Zheng He sails with a fleet so vast, seeking friendship and trade, not a colonial cast.
Memory Tools
E.D.T.I. - Economic gain (Europe), Diplomatic (Zheng He), Technological (caravels vs. treasure ships), Impact on people (colonial vs. diplomatic).
Acronyms
C.E.D.I - Columbus/Europe - Economic, Zheng He - Diplomatic, Impact on Indigenous (colonial vs. trade), Duration & Fleet size differences.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Caravel
A small, highly maneuverable ship developed by the Portuguese in the 15th century, significant for exploration.
- Tribute
Wealth or goods given from one ruler to another as a sign of respect or acknowledgment.
- Diplomatic Prestige
The respect and influence that a state gains through its diplomatic relations and peaceful interactions.
- Colonial Claims
Formal declarations by a nation asserting sovereignty over a territory and its people.
- Encomienda System
A labor system where Spanish colonists were granted rights to the labor of indigenous people in exchange for their protection and Christian teaching.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
