Vasco da Gama (1497–1499): Opening the Sea Route to India
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Background of Vasco da Gama's Voyage
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, class, we're exploring Vasco da Gama's important voyage to India. Who can remind me what drove Portugal to explore new trade routes?

Was it because they wanted spices and other goods from Asia?

Exactly! The demand for spices, especially, was high in Europe. Vasco da Gama was influenced by earlier explorations sponsored by Prince Henry the Navigator. Can anyone tell me what they remember about Prince Henry?

He was a Portuguese prince who supported sea voyages to discover new lands.

Right! So, fun fact: da Gama aimed to find a direct sea route to India to bypass the middlemen in trade. That's where our acronym 'GOLD' helps—G for Goods, O for Overland Routes, L for Longing for Spices, and D for Direct Sea Route!

Got it! He wanted to find a quicker way to get valuable goods.

Correct! Remember that the spice trade was lucrative, and they needed a more efficient way to access these resources.
The Voyage and its Challenges
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's dive into da Gama's journey. Who can summarize the key steps of his voyage?

He left Lisbon, sailed down the west coast of Africa, rounded the Cape of Good Hope, and reached India!

Great summary! Can anyone detail what significance rounding the Cape of Good Hope had?

It showed that they could travel around Africa to reach Asia, which was a major breakthrough.

Exactly! This was a significant navigation success. What challenges did he face once he arrived in India?

The local merchants didn't trust the Portuguese right away.

That’s true! Initial negotiations were quite difficult. But da Gama managed to secure spices nonetheless. Let’s remember 'COST' - C for Challenges, O for Opportunity, S for Spices, T for Trust.
The Impact of Da Gama's Voyage
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up our discussions, let’s talk about the wider impact of da Gama's voyage. How did it change trade for Portugal?

They established many new trade routes in Asia and started an empire!

Absolutely! Remember the term 'POWER'—P for Prestige, O for Overland Routes impacted, W for Wealth, E for Expansion, R for Resources. What was one of the immediate effects on existing trade networks?

It disrupted traditional overland routes and made the Portuguese dominant in trade.

Exactly! This was a total shift in trade dynamics, diminishing the role of previous players like the Venetians and Arabs.

So, da Gama really changed global trade!

Yes, he did! The ripple effects of this voyage are still felt today!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Vasco da Gama, sponsored by Prince Henry the Navigator of Portugal, embarked on a significant voyage in 1497 that led him around the Cape of Good Hope to India. His arrival in Calicut in 1498 opened up direct sea trade, disrupting existing trade networks and establishing a Portuguese empire in the Indian Ocean.
Detailed
Vasco da Gama (1497–1499): Opening the Sea Route to India
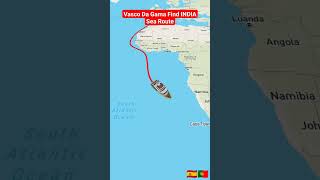
Vasco da Gama played a pivotal role in the Age of Exploration, particularly through his voyage from Portugal to India, which opened a direct maritime route to the lucrative spice markets. Sponsored by Prince Henry the Navigator, da Gama departed Lisbon in July 1497 with four ships. After successfully rounding the Cape of Good Hope, he arrived in Calicut on the Indian subcontinent in May 1498. Although initial attempts at trading were met with skepticism by local merchants, his journey demonstrated the feasibility of a sea route to India. Upon his return to Portugal in September 1499, da Gama brought back spices that he acquired at significantly low prices, which sold for large profits in Europe.
This voyage had far-reaching consequences, including the establishment of the Portuguese Empire in the Indian Ocean, with fortified trading posts set up in crucial locations such as Goa and Malacca. The competition for control of trade routes tailored by da Gama effectively bypassed traditional overland trading systems controlled by Venetian and Arab merchants, reshaping global trade dynamics and wealth distribution significantly.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Background of Vasco da Gama's Expedition
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Portugal’s Prince Henry the Navigator had sponsored earlier expeditions down the west coast of Africa. By the 1490s, Portuguese cartographers and sailors believed they could round the southern tip of Africa and sail eastward.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the context leading up to Vasco da Gama's voyage. Prince Henry the Navigator was instrumental in promoting exploration and maritime studies. His support for sailing expeditions along Africa's coast laid the groundwork for future explorations. By the late 1400s, Portuguese sailors had accumulated knowledge that led them to believe a sea route to India was not only possible but also practical.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a group of scientists in a lab who have been studying a particular disease for years. As they gather more data and insights, they become increasingly confident that they can develop a cure. This is similar to how the Portuguese explorers, through years of mapping and sailing, gained confidence in their ability to reach India by sea.
The Voyage Begins
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
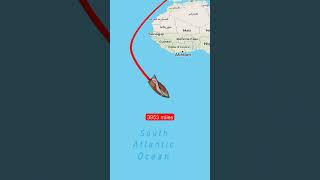
In July 1497, da Gama departed Lisbon with four ships. He sailed down Africa’s west coast, rounded the Cape of Good Hope in November, and entered the Indian Ocean.
Detailed Explanation
In this segment, we focus on the actual journey of Vasco da Gama. His fleet set out from Lisbon, which was a major maritime hub. Instead of heading straight to India, they navigated down the African coast, which was crucial for avoiding treacherous waters at that time. Rounding the Cape of Good Hope was a significant achievement, symbolizing a major milestone in the Age of Exploration. This route opened up new maritime pathways for trade and exploration.
Examples & Analogies
Think of rounding the Cape of Good Hope like a hiker successfully navigating a challenging mountain pass after weeks of preparation. Just as that hiker can now access new trails, da Gama’s crew accessed the vast opportunities of the Indian Ocean, expanding the known world.
Reaching Calicut
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In May 1498, he reached Calicut on India’s Malabar Coast. Although initial trading negotiations were difficult—local merchants distrusted unfamiliar Portuguese—the voyage proved a direct sea route to India was possible.
Detailed Explanation
When Vasco da Gama arrived in Calicut, it marked a crucial moment in history. Despite having traveled over 10,000 miles, the Portuguese faced skepticism from local traders, who had established their own networks. This setback emphasized the importance of trust and understanding between different cultures. However, the successful arrival in Calicut validated the potential of a direct sea route to India, opening new avenues for trade in spices and other valuable commodities.
Examples & Analogies
Consider this situation like an entrepreneur trying to sell a new product in a foreign market. They might face skepticism at first, but if they prove their product works, it could lead to significant success. Similarly, da Gama’s successful arrival was pivotal in establishing a new trading relationship between Europe and India.
Return to Portugal
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Da Gama returned in September 1499, laden with spices acquired cheaply in India, which sold for many times their cost in Europe.
Detailed Explanation
Upon returning to Portugal, Vasco da Gama's successful trip created a wave of excitement and optimism. The spices he brought back were prized in Europe and sold for a substantial profit, demonstrating the financial potential of direct trade with India. This success encouraged more expeditions, reinforcing the idea that maritime exploration could be extremely profitable and reinforcing Portugal's position as a leading sea power.
Examples & Analogies
This scenario can be likened to a tech startup that develops a revolutionary app. If the app proves popular and profitable upon its launch, it can inspire more investment in similar projects, reshaping the tech landscape. Likewise, da Gama’s success reshaped the dynamics of international trade.
Long-Term Consequences of the Voyage
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Within decades, Portugal established fortified trading posts at Goa (1510), Malacca (1511), and other ports along Africa and Asia’s coasts. By bypassing traditional overland routes (caravans, Silk Road) controlled by Venetian, Ottoman, and Arab traders, Portugal shifted the balance of trade and wealth in Europe.
Detailed Explanation
The long-term effects of da Gama's journey were profound. Portugal not only established a vast empire in the Indian Ocean but also disrupted existing trade networks that had dominated for centuries. By controlling these new sea routes and establishing fortified trading posts, Portugal significantly altered the economic landscape in Europe and Asia and gained immense wealth and power. This era of maritime dominance shifted the balance of trade away from the traditional overland routes.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a new road being built that bypasses an existing toll road where trucks have been delivering goods for years. Over time, more and more trucks choose the new route because it’s faster and cheaper, drastically changing the logistics industry. Similarly, da Gama’s route provided new, more efficient pathways for trade.
Key Concepts
-
Direct Trade Route: The establishment of a sea route to India allowed for direct access to spices without intermediaries.
-
Portuguese Empire: Da Gama’s voyage led to the formation of a Portuguese trading empire in the Asian markets.
-
Disruption of Trade Networks: His discovery disrupted existing trade routes controlled by other nations.
Examples & Applications
Vasco da Gama's arrival in Calicut demonstrated the importance of maritime trade, as it allowed Portugal to obtain spices like black pepper.
The establishment of fortified trading posts in Goa showcased Portugal's influence on global trade dynamics.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Round the Cape, sail through the tide, Vasco’s route to spices wide.
Stories
Once there was an explorer named Vasco, who took to the sea to trace a path to spice, discovering lands that changed everything in his price.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym 'COST' - Challenges faced, Opportunities found, Spices gathered, Trust gained.
Acronyms
The acronym 'POWER' represents Prestige, Overland impacted, Wealth gained, Expansion initiated, Resources acquired through da Gama's journey.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Vasco da Gama
A Portuguese explorer who was the first to sail directly from Europe to India, opening trade routes.
- Cape of Good Hope
A rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of South Africa, pivotal in maritime navigation.
- Calicut
A city on the southwestern coast of India, first reached by Vasco da Gama in 1498.
- Spices
Highly valued goods cost, particularly during the Age of Exploration, sought after for trade.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
