Coordinate (Dative Covalent) Bonding
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
What is Coordinate Bonding?
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore coordinate bonding, a fascinating type of bond where both electrons in the bond come from one atom. Can anyone guess what that means?

Does it mean that one atom donates both of its electrons?

Exactly! For instance, in the ammonium ion, NH4+, nitrogen donates both of its electrons to bond with a hydrogen ion. This showcases how versatile bonding can be.

So, is it different from regular covalent bonds?

Yes! In a regular covalent bond, each atom provides one electron. Coordinate bonds are a bit special as there's a donor atom providing both electrons. Let's keep this in mind!

Why is this important in chemistry?

Great question! It helps us understand complex ions and their behavior in reactions. Remember: *A donor is a shiner when it comes to bonding*! Let's move on to some examples.
Examples of Coordinate Bonds
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We've learned about the ammonium ion. Can anyone think of another example of coordinate bonding?

What about the formation of complexes with transition metals?

Exactly! Transition metals often form complex ions by accepting electron pairs from ligands. In such cases, the ligand acts as a donor. Remember, it’s all about pairing up!

So, are there any other notable examples?

Yes! Another example is the bonding in carbon monoxide (CO), where the carbon atom donates a pair of electrons to bond with oxygen. This dative bond is crucial in its stability.

It sounds like coordinate bonds play a key role in many reactions!

You got it! Let's keep those examples in mind as we proceed.
The Importance of Understanding Coordinate Bonding
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we have some examples, let’s talk about why understanding coordinate bonding is important. Why do you think this specific bond is crucial?

Because it helps explain how complex ions work?

Absolutely! It also helps us grasp biochemical processes and interactions, like the structure of certain proteins. Remember the phrase: *Dynamics in bonding lead to innovations in chemistry!*

How does this tie into real-world applications?

Great point! Coordinate bonds play significant roles in drug design, catalysis, and many biological systems, enriching our understanding of chemistry's practical implications.

It sounds more important than I thought!

Indeed! Let's keep exploring these exciting topics.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In coordinate (dative covalent) bonding, one atom donates both electrons in the shared pair, allowing for structures like ammonium ions (NH4+). This type of bonding contrasts with other forms of covalent bonding, where electrons are shared equally or unequally.
Detailed
Coordinate (Dative Covalent) Bonding
Coordinate (dative covalent) bonding is a unique type of chemical bond where a shared electron pair originates from the same atom. This differs from standard covalent bonds, where each atom contributes one electron. A prime example is the formation of the ammonium ion (NH4+), where nitrogen contributes both of its valence electrons to bond with a hydrogen ion (H+). This ability to donate both electrons can lead to the formation of complex molecular structures and is significant in various biochemical contexts. Understanding coordinate bonding helps elucidate the behavior of different compounds and the possibilities within molecular interactions.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Coordinate (Dative Covalent) Bonding
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● A bond in which both electrons in the shared pair come from the same atom.
Detailed Explanation
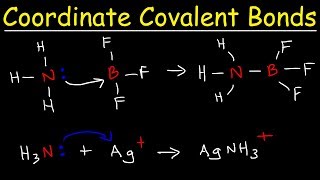
Coordinate (dative covalent) bonding occurs when a pair of shared electrons is supplied by only one of the two atoms involved in the bond. Unlike regular covalent bonds where each atom contributes one electron to the bond, in dative covalent bonds, one atom donates both electrons for the bond formation. This type of bond is essential in understanding how certain ions and complex molecules are formed.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a friendship where one friend consistently brings snacks to share during study sessions. In a usual friendship, both friends would contribute snacks (like in normal covalent bonds). In this scenario, one friend (the donor) brings all the snacks (both electrons), representing how one atom can solely provide the electrons in a coordinate bond.
Example of Coordinate Bonding
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Example: Formation of ammonium ion NH4+ where nitrogen donates both electrons to bond with H+.
Detailed Explanation
A concrete example of coordinate covalent bonding can be observed in the formation of the ammonium ion (NH₄⁺). In this case, the nitrogen atom has a lone pair of electrons. When it interacts with a hydrogen ion (H⁺), which has no electrons, nitrogen donates both electrons to form a bond with H⁺. This results in the ammonium ion, where four hydrogen atoms are bonded to a nitrogen atom through this coordinate bond, leading to a positively charged ion.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a librarian (nitrogen) who has a collection of books (electrons) and is approached by a student (H⁺) who wants to read a book but doesn’t have any to contribute. The librarian lends two books, allowing the student to borrow them (donating both electrons), thus allowing a new reading partnership (the ammonium ion) to form successfully.
Key Concepts
-
Coordinate Bond: A bond formed where both electrons in the pair come from one atom.
-
Ammonium Ion (NH4+): An example of a coordinate bond where nitrogen donates both electrons.
Examples & Applications
The ammonium ion (NH4+) is formed when nitrogen donates both electrons to bond with H+.
In carbon monoxide (CO), carbon donates a pair of electrons to oxygen, forming a coordinate bond.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When one gives away a pair, that's a bond with some flair!
Stories
Once upon a time, a nitrogen atom met a hydrogen ion. Without hesitation, nitrogen said, 'Take both my electrons, and let’s bond beautifully!' Thus, ammonium was born.
Memory Tools
D for Donor, D for Dative! Remember that in coordinate bonding, the donor is the star!
Acronyms
C.B. = Coordinate Bond, both electrons come from the same Buddy!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Coordinate Bond
A bond in which both electrons in the shared pair come from the same atom.
- Ammonium Ion
A positively charged ion (NH4+) formed when a nitrogen atom donates its electrons to bind with a hydrogen ion.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
