Polar and Non-Polar Covalent Bonds
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Covalent Bonds
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome class! Today, we will be discussing polar and non-polar covalent bonds. Let’s start with the basics: what do you think a covalent bond is?

Isn't it when atoms share electrons?

Exactly! In covalent bonding, atoms share electron pairs. This is a key way that non-metal atoms bond together. Now, can anyone tell me the difference between polar and non-polar covalent bonds?

I think non-polar bonds share electrons equally?

Yes, right! Non-polar covalent bonds involve equal sharing of electrons. A good way to remember this is with the acronym 'EQUAL.' Everyone shares equally. Examples include diatomic molecules like H₂ and Cl₂. Now, what about polar bonds?

They have unequal sharing, right?

Correct! Unequal sharing happens because one atom is more electronegative than the other. This makes one end of the molecule slightly positive and the other slightly negative. Good job, everyone!
Examples of Polar and Non-Polar Bonds
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s look at some examples! Can someone give me a non-polar covalent bond example?

H₂ is a non-polar covalent bond!

That's right! H₂ molecules share the electrons equally. Now, how about an example of a polar covalent bond?

HCl, because chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen.

Perfect! In HCl, chlorine attracts the shared electrons more than hydrogen, creating a dipole. Why is it important to know about these bonds?

I guess it helps us understand how molecules behave in different situations?

Exactly! The behavior of molecules depends on their bond type, affecting properties like polarity and solubility.
Electronegativity and Bond Character
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive deeper into electronegativity. Why do you think electronegativity matters in bond formation?

Because it shows how strongly an atom attracts electrons?

Exactly! Atoms with high electronegativity, like chlorine, attract shared electrons more than those with low electronegativity. This is why HCl is polar. Can anyone share how we determine if a bond is polar or non-polar?

We compare the electronegativity values of the atoms involved!

Great point! If the difference is small, we have a non-polar bond. If it's significant, we have a polar bond. Remember the phrase 'Small equals shared, big means prepared!'
Significance of Polar and Non-Polar Bonds
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do we care about polar and non-polar bonds in the real world? How does this knowledge impact us?

It helps in understanding things like how oil and water don’t mix.

Exactly! Oil is non-polar, while water is polar, leading to their immiscibility. What else can this concept help us with?

It helps us know how substances might react in chemical solutions or biological systems.

Yes! Understanding polar and non-polar bonds is vital for chemistry, biology, and even environmental science. Great contributions today, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section outlines the characteristics of non-polar covalent bonds, where electrons are shared equally, and polar covalent bonds, where unequal sharing occurs due to differences in electronegativity. Examples such as H₂ and HCl illustrate these concepts.
Detailed
Polar and Non-Polar Covalent Bonds
In this section, we explore two main types of covalent bonds: non-polar and polar covalent bonds. A non-polar covalent bond is formed when two atoms share electrons equally, which typically occurs in diatomic molecules such as hydrogen (H₂) and chlorine (Cl₂). These molecules have similar electronegativities, meaning they attract electrons equally.
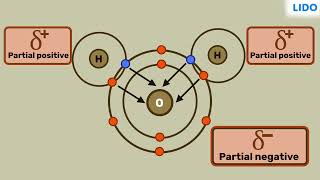
In contrast, a polar covalent bond arises when there is an unequal sharing of electrons between two atoms with dissimilar electronegativities, leading to a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other. A classic example is hydrogen chloride (HCl), where chlorine attracts the shared electron pair more strongly due to its higher electronegativity, resulting in a dipole moment. Understanding these types of covalent bonds is essential for predicting molecular behaviors and interactions in various chemical contexts.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Non-Polar Covalent Bond
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Non-polar covalent bond: Equal sharing of electrons (e.g., H2H_2, Cl2Cl_2).
Detailed Explanation
A non-polar covalent bond is a type of chemical bond where two atoms share a pair of electrons equally. This happens when the two atoms involved have similar electronegativities, meaning they have the same or similar ability to attract electrons. A common example is the bond in a hydrogen molecule (H2), where two hydrogen atoms share their electrons evenly. Since both atoms pull the shared electrons with the same strength, there is no charge difference across the molecule, making it non-polar.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine two friends sharing a pizza equally. If both of them love the pizza equally, they will each take the same number of slices. This equal sharing results in a fair situation, just like the equal sharing of electrons in a non-polar covalent bond.
Polar Covalent Bond
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Polar covalent bond: Unequal sharing of electrons due to difference in electronegativity (e.g., HCl).
Detailed Explanation
A polar covalent bond occurs when two atoms share electrons unequally. This typically happens when the atoms involved have significantly different electronegativities, which means one atom has a stronger pull on the electrons than the other. For instance, in hydrogen chloride (HCl), chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen, so the shared electrons spend more time near the chlorine atom. This creates a partial negative charge (δ-) on the chlorine and a partial positive charge (δ+) on the hydrogen, resulting in a polar molecule.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a game of tug-of-war. If one team is much stronger than the other, they will pull the rope closer to their side. In a polar covalent bond, one atom pulls the shared electrons closer to itself, similar to how the stronger team in tug-of-war dominates the game.
Key Concepts
-
Non-Polar Covalent Bond: Equal sharing of electrons between two atoms.
-
Polar Covalent Bond: Unequal sharing of electrons due to differing electronegativities.
-
Electronegativity: The ability of an atom to attract electrons.
Examples & Applications
In H₂, two hydrogen atoms share electrons equally, resulting in a non-polar covalent bond.
In HCl, the shared electrons are attracted more toward chlorine, establishing a polar covalent bond.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Polar and non-polar, they find their role, sharing electrons is their goal. Equal for one, but unequal they bind, the charges they carry, they try to unwind.
Stories
Imagine two friends, Hydrogen and Chlorine. They go to share a pizza. Hydrogen wants an equal slice, but Chlorine, being larger, dominates, making it an unequal share, showing a polar bond in action!
Memory Tools
For polar bonds, think 'Adapt', for they involve unequal attractions; for non-polar, think 'Equal', for they share with satisfaction!
Acronyms
Remember the acronym 'PANE' for Polar Atom Neglect Electrons, signifying the unequal nature of polar bonds!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Covalent Bond
A chemical bond formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms.
- NonPolar Covalent Bond
A covalent bond where electrons are shared equally between two atoms with similar electronegativities.
- Polar Covalent Bond
A covalent bond where electrons are shared unequally between two atoms with different electronegativities, resulting in a dipole moment.
- Electronegativity
A measure of an atom's ability to attract and hold onto electrons.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
