Contours and Relief Features
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Contours
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're discussing contours, which are essential lines on topographical maps. Who can tell me what contours represent?

Contours show elevation levels.

Correct! Contours connect points of equal elevation. Think of an *elevation line!* Now, why do you think this is important?

It helps us understand the landscape better.

Yes! Good job. Understanding this gives us insight into hills, valleys, and slopes. Remember 'Hills are circles, valleys are V's' to help you differentiate!
Identifying Relief Features
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know about contours, let’s discuss the different relief features we can identify. What does a closed loop contour signify?

It indicates a hill or a mountain.

Exactly! And what about a V-shaped contour?

That shows a valley!

Right again! It's crucial to recognize these patterns. Remember: 'Loops are up, V's are down!' How can we determine the steepness of a slope?

By seeing how close the contours are?

Yes! Closer contours mean a steeper slope. Let’s keep that in mind: 'Tight lines are steep, spread out lines are shallow.' Excellent work!
Contour Intervals and Their Importance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive into contour intervals. What do you think is the typical contour interval in ICSE maps?

It's usually 20 meters.

Exactly! Now, why might this be important for us?

It helps us know how much elevation changes over a distance.

Correct! The contour interval gives us a clear idea of the terrain’s steepness and helps with planning routes. Always remember: 'Intervals tell the rise, helping us advise!'
Practical Applications of Contours
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss practical applications. How might knowing about contours and relief features be useful in real life?

It can help in construction and urban planning.

Absolutely! And what about in nature, like hiking or wildlife studies?

They help us choose the best paths or locate animals.

Great points! As you consider contours, remember: 'Map the flow, know where to go!'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section explains the concept of contours on topographical maps, which connect points of equal elevation. It elaborates on the significance of contour intervals, the identification of various relief features like hills, valleys, and slopes, and different aspects related to their understanding.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
In topographical maps, contours are crucial as they depict lines that connect points of equal elevation, allowing users to visualize the terrain's relief features. The contour interval, typically set at 20 meters in ICSE topographical sheets, indicates the vertical distance between successive contour lines.
Key relief features that can be identified include:
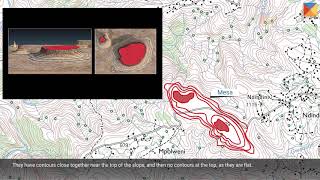
- Hills: Illustrated as closed loops where the elevation increases as you move inward.
- Valleys: Represented by V-shaped contours which indicate low-lying areas.
- Ridges: Depicted as elongated high ground, where contours typically run closely parallel.
- Steep and Gentle Slopes: Identified based on how closely the contours are spaced; closer contours indicate steeper slopes while wider spacing indicates gentle slopes.
Understanding these features is significant in geography, as they inform about the terrain's topology, impacting land use, navigation, and settlement patterns.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Contours
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Contours: Lines joining points of equal elevation.
Detailed Explanation
Contours are essential elements on topographical maps. They represent lines that connect points at the same elevation above sea level, allowing us to visualize the landscape's shape. When you look at a map, each contour line indicates that all points along that line are at the same height. This is crucial for understanding how high a hill is or how deep a valley might be.
Examples & Analogies
Think of contours like the rings on a tree stump. Just as the tree rings denote the years of growth at each level, contour lines indicate levels of elevation across the landscape. If you were to walk along a contour line, you would not go uphill or downhill; you'd stay at the same height.
Contour Interval
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Contour Interval: Usually 20 m in ICSE topo sheets.
Detailed Explanation
The contour interval is the vertical distance between successive contour lines on a map. On ICSE topographic maps, this interval is typically set at 20 meters. This means that if you move from one contour line to the next, you ascend or descend in elevation by 20 meters. Understanding this interval is important for estimating how steep a slope is based on how close or far apart the contour lines are.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine walking up a staircase where each step is 20 cm high. The space between each step gives you a sense of how steep the stairs are. If the steps are closer together, the incline is steep; if they are further apart, the incline is gradual. Similarly, on a map, closely spaced contour lines represent steep slopes, while wider spaced lines indicate gentler slopes.
Identifying Features
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Identify features like:
○ Hills (closed loops)
○ Valleys (V-shaped contours)
○ Ridges (elongated high ground)
○ Steep and Gentle Slopes.
Detailed Explanation
Topographical maps allow us to identify various physical features of the landscape through the arrangement and shape of contour lines. For instance, closed loops indicate hills, while V-shaped contours hint at valleys. An elongated set of contour lines typically represents ridges, while the spacing of these lines helps in identifying the steepness of slopes: close lines indicate steep slopes, and farther lines show gentle slopes.
Examples & Analogies
Picture a hilly park where you can see bumps and dips in the ground. When you look at the park's layout on a map, the bumps will appear as closed loops (hills), and V shapes pointing uphill will represent valleys. This is like tracing out a landscape with your finger to see where it rises and falls, helping you navigate the terrain more effectively.
Key Concepts
-
Contours: Lines that connect points of equal elevation.
-
Contour Interval: The vertical distance represented between two contour lines.
-
Relief Features: Specific landscape formations identifiable on maps, such as hills, valleys, and slopes.
Examples & Applications
A map showing contours where closed loops are present indicates hills in that area.
On a topographical map, V-shaped contours suggest the presence of a valley which can affect water flow.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Hills are rounds like peaks we climb, valleys V-shaped, in nature's rhyme.
Stories
Imagine hiking a steep mountain where closed loops show you’re going high. Suddenly, you find a valley shaped like a V, clear evidence of the low ground nearby.
Memory Tools
For hills and valleys, 'Loops are up, V's are down.'
Acronyms
RHS
Relief - Hills - Slopes.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Contours
Lines on a map connecting points of equal elevation.
- Contour Interval
The vertical distance between two successive contour lines, usually 20 meters in ICSE maps.
- Hills
Closed loops in contour lines indicating raised terrain.
- Valleys
V-shaped contours indicating low-lying areas.
- Ridges
Extended high ground depicted in contour lines.
- Slope
The steepness of the terrain determined by the spacing of contour lines.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
